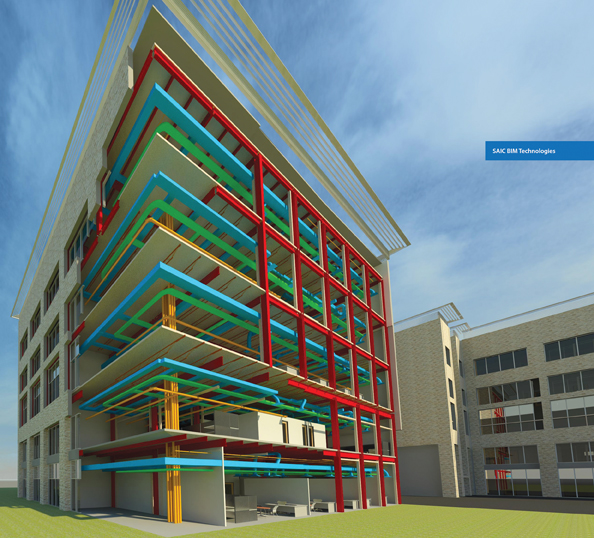
Building owners and developers are changing their tune regarding BIM services. A few years ago, when BIM was still in its infancy, a client or prospect might issue an RFP asking for some vague level of BIM scope on a proposed project. Today, clients and prospects are becoming much more sophisticated in demanding demonstrated BIM expertise and experience on real projects.
Today, clients take the technical implementation of BIM almost for granted. As a result, the number of clients willing to pay extra for BIM deliverables is practically nonexistent. The upshot is that if your firm isn’t telling the marketplace how your approach to BIM makes it stand out against others offering “standard” BIM services, it will soon be left behind.
As a veteran manager of BIM/CAD technologies, I believe there is a systematic way to make BIM a powerful marketing force for your firm—an eight-step approach to help your firm differentiate its BIM capabilities, become a trusted advisor, and win more work.
STEP 1. Recognize the business and marketing aspects of implementing BIM in your organization.
Under recent extreme competitive pressure, many AEC firms have had to embrace BIM without spending sufficient time on the complex processes involved in adopting such a transformative technology. As a result, firms have become so caught up in the implementation of the technology (admittedly not a trivial consideration) that they have largely ignored the business development aspects of BIM.
That is unfortunate, because BIM is changing how we do business and, consequently, how we go to market. Failure to strategize, analyze, and document how BIM integrates within your business structure will negatively impact your ability to compete in a highly competitive climate, with these consquences:
• Your organizational culture will look at BIM as a tool instead of as a business opportunity offering services beyond what AEC firms have traditionally offered.
• Your firm will suffer from a lack of BIM definition, capability, and expertise.
• Your client-facing staff will not understand your overall vision and goals for BIM.
• Your business development and marketing staff will rely on legacy capabilities instead of using new skills and capabilities that BIM makes available to your firm.
Moreover, client expectations vary greatly depending on how well they understand BIM and how much experience they’ve had with it. Often AEC firms are left with an unclear understanding of how much BIM is required on projects due to a lack of direction by the client, when in fact we should be the ones customizing a BIM approach for each project.
STEP 2. Establish a BIM vision that is linked tightly to your firm’s philosophy and goals and is fully enmeshed within the fabric of your organization.
Implementing BIM as a process and technology is one thing, but building your firm’s BIM credentials requires weaving BIM into the fabric of your organization.
A BIM vision should clearly reflect your organizational culture as it relates to BIM and how it will define future direction related to staff roles and responsibilities, skill sets, service offerings, and strategic positioning. In other words, how does BIM fit within your organization, both structurally and philosophically? How will it change your business?
STEP 3. Identify a BIM champion within your organization to lead the effort.
In order to bring BIM into your organization, a strong BIM leader must either come forward or be identified. This person may not necessarily come from the tech side of your organization. That’s because the job of making BIM an effective business component of your organization will require a multifaceted individual who understands the technology well enough to strategize, manage, and deploy from a “big picture” level, but who also has an understanding and appreciation of the business and operations side—someone who can champion the effort and has a feel for how BIM can strategically redefine the organization for the better.
This individual should hold the title of Director, Managing Director, or BIM Executive and should have the authority to engage with principals in the firm, establish the budget to prioritize spending, and set the tempo of BIM adoption within your organization.
As the face of BIM in your organization, your BIM champion will have to reach out to a wide group of stakeholders, both internal––marketing, finance, principals––and external––clients, prospects, and their representatives. The BIM champion must be the kind of person who can listen to and understand the needs of clients and prospects and implement business strategies to meet those demands most effectively. At the same time, this person must have the ability to push back on those who resist change.
STEP 4. Clearly delineate your BIM capabilities to clients.
Your firm must decide how far you’re going to go in terms of BIM capability. Then make your clients and prospects aware, through your BIM marketing program, of precisely what you can offer them:
• 3D BIM: Modeling and Documentation - Allows for using BIM as a tool to develop and deliver smarter designs for all disciplines in a 3D-intelligent format as well as studying and analyzing the design intent.
• 4D BIM: Integration for Construction - The ability to leverage the benefits of BIM tools during the construction phase results in numerous benefits for a client, including the ability to solve construction headaches through the virtual environment and improved coordination, study timeline and schedule attributes to ensure on-time delivery, and smooth constructability and delivery of projects.
• 5D BIM: Cost Estimation - A totally new way of looking at construction cost in a more virtual and automated methodology, offering up-to-date information to compare actual costs to estimates throughout a project’s life cycle.
• 6D BIM: Building Life Cycle Integration - Enhances facility management by utilizing 3D, 4D, and 5D BIM information in the operation, maintenance, and future renovation of the building.
STEP 5. Embed BIM into your firm’s marketing content. Start by creating a BIM portfolio.
Your firm’s BIM capability is almost worthless if it is not fully assimilated into your marketing content. Because business development material is dynamic and therefore must be updated frequently, you must think of ways to incorporate BIM into these materials.
The BIM portfolio is your firm’s BIM résumé. You will need to combine your recent BIM project success stories with your core services to build a new presentation of your more robust capabilities. BIM can be presented as a set of processes, workflows, and technologies leveraged within your firm to aid in your core-service delivery. BIM portfolios should include a mix of media—images, animations, and roadmaps––that showcase your BIM capabilities. There is also an important collaboration management and execution piece to BIM that most AEC organizations don’t even mention. You should.
You should leverage your existing media capabilities as well as new ones to market your portfolio. It is critical to add BIM material to your company’s website, either as a project subset or as a full capability with proper leadership contacts and services. Additional outreach could include BIM-related social networking activities and Web interviews with your BIM Leader and software leaders. Finally, build a BIM presentation slide deck that talks about how your firm is transforming with BIM.
The point is not to overwhelm your customers with more BIM, but rather to broadcast your established BIM vision internally and externally through your marketing material.
STEP 6. Educate your client-facing staff on BIM trends, language, and culture.
Even the best marketing materials cannot win business without personal intervention. Client-facing staff, especially senior management and business development staff who interact with prospective and existing clients, need to know how to speak the language of BIM. They should not be expected to become technical experts, but they do need to stay on top of the trends in BIM within the industry and how your firm’s BIM vision addresses those trends.
This kind of individual involvement will put your firm in a position to offer expert guidance to clients based on their specific BIM needs. As a result, your firm will become the expert consultant, not the generic BIM provider.
STEP 7. Customize responses to RFPs and tailor them to the BIM-related needs of the client.
RFPs encompassing BIM requirements can typically be broken down into three categories:
Generic RFP – BIM not included in the scope, except perhaps for a small subsection.
Technology RFP – Focus is mainly on the use of technology software. Leaves a large gap in defining other issues, such as process, integration, standards, and workflow.
Advanced RFP – Elaborates on BIM scope at length. May include complete exhibits with detailed requirements that cover:
• Standards and processes
• Strategy plan – template to develop a project BIM execution plan
• Software requirements for each discipline
• Workflow processes and methodologies: meetings, clash detection, takeoffs, and reporting
• BIM model management procedures, content management, and archiving
Proposals should always be customized and tailored to the needs of the client. If the client doesn’t know what to ask for from a BIM perspective, take it as an opportunity to offer guidance as a BIM consultant and expert.
STEP 8. To prepare a customized approach, start by studying the BIM scope.
Here is where you show your understanding of the client’s needs and expectations relating to BIM. Ask questions and offer suggestions (if invited to do so). Appreciate the client’s motive for using BIM. Brief the client on potential processes or obstacles they may not be aware of. Finally, write the response around the client’s scope and showcase the BIM portfolio and capabilities.
Over time, you will be able to develop RFP and marketing templates that address different types of BIM approaches. While these templates need to cover the basics, they must always be customized for each project depending on the dynamics of the client relationship.
Now is the time for your firm to take a position as a BIM leader and expert. The software implementation alone is not enough; building a BIM capability and portfolio that is part of a company’s brand, services, and DNA is a prerequisite. Only then can your firm successfully use BIM to help it compete in today’s extremely grueling design and construction market. +
--
Joseph Joseph is SAIC’s Managing Director overseeing all BIM/CAD Technologies strategies and initiatives, including strategizing, standards, and implementation of BIM in a design-build environment.
Related Stories
| Feb 15, 2011
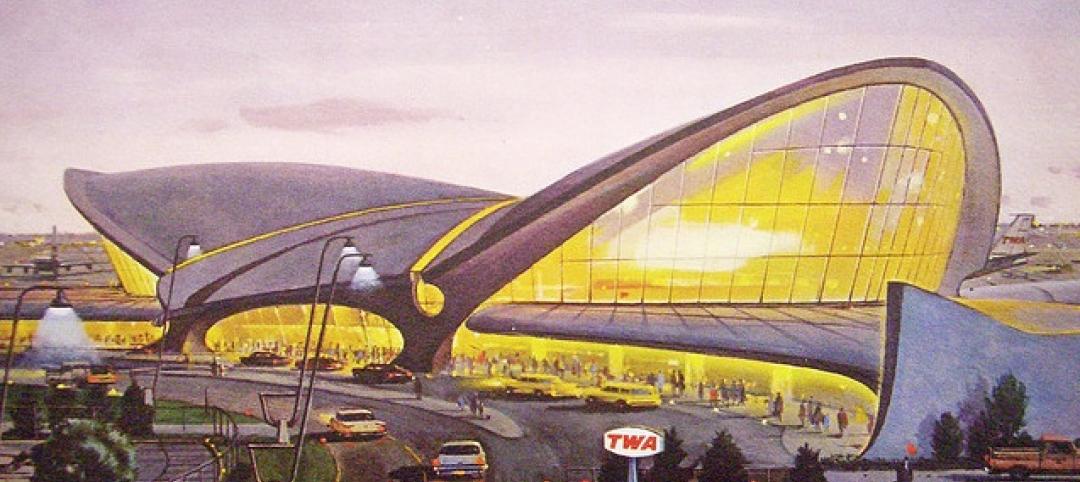
Iconic TWA terminal may reopen as a boutique hotel
The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey hopes to squeeze a hotel with about 150 rooms in the space between the old TWA terminal and the new JetBlue building. The old TWA terminal would serve as an entry to the hotel and hotel lobby, which would also contain restaurants and shops.
| Feb 15, 2011
New Orleans' rebuilt public housing architecture gets mixed reviews
The architecture of New Orleans’ new public housing is awash with optimism about how urban-design will improve residents' lives—but the changes are based on the idealism of an earlier era that’s being erased and revised.
| Feb 15, 2011
LAUSD commissions innovative prefab prototypes for future building
The LA Unified School District, under the leadership of a new facilities director, reversed course regarding prototypes for its new schools and engaged architects to create compelling kit-of-parts schemes that are largely prefabricated.
| Feb 15, 2011
New 2030 Challenge to include carbon footprint of building materials and products
Architecture 2030 has just broadened the scope of its 2030 Challenge, issuing an additional challenge regarding the climate impact of building products. The 2030 Challenge for Products aims to reduce the embodied carbon (meaning the carbon emissions equivalent) of building products 50% by 2030.
| Feb 15, 2011
New Urbanist Andrés Duany: We need a LEED Brown rating
Andrés Duany advocates a "LEED Brown" rating that would give contractors credit for using traditional but low cost measures that are not easy to quantify or certify. He described these steps as "the original green," and "what we did when we didn't have money." Ostensibly, LEED Brown would be in addition to the current Silver, Gold and Platinum ratings.
| Feb 15, 2011
AIA on President Obama's proposed $1 billion investment in energy conservation
The President’s budget increases the value of investment in energy conservation in commercial buildings by roughly $1 billion, reports AIA 2011 President Clark Manus, FAIA. The significant increase from the current tax deduction of $1.80 per sq. ft. now on the books is an increase for which the AIA has been advocating in order to encourage energy conservation.
| Feb 14, 2011
Sustainable Roofing: A Whole-Building Approach
According to sustainability experts, the first step toward designing an energy-efficient roofing system is to see roof materials and systems as an integral component of the enclosure and the building as a whole. Earn 1.0 AIA/CES learning units by studying this article and successfully completing the online exam.
| Feb 11, 2011
Four Products That Stand Up to Hurricanes
What do a panelized wall system, a newly developed roof hatch, spray polyurethane foam, and a custom-made curtain wall have in common? They’ve been extensively researched and tested for their ability to take abuse from the likes of Hurricane Katrina.