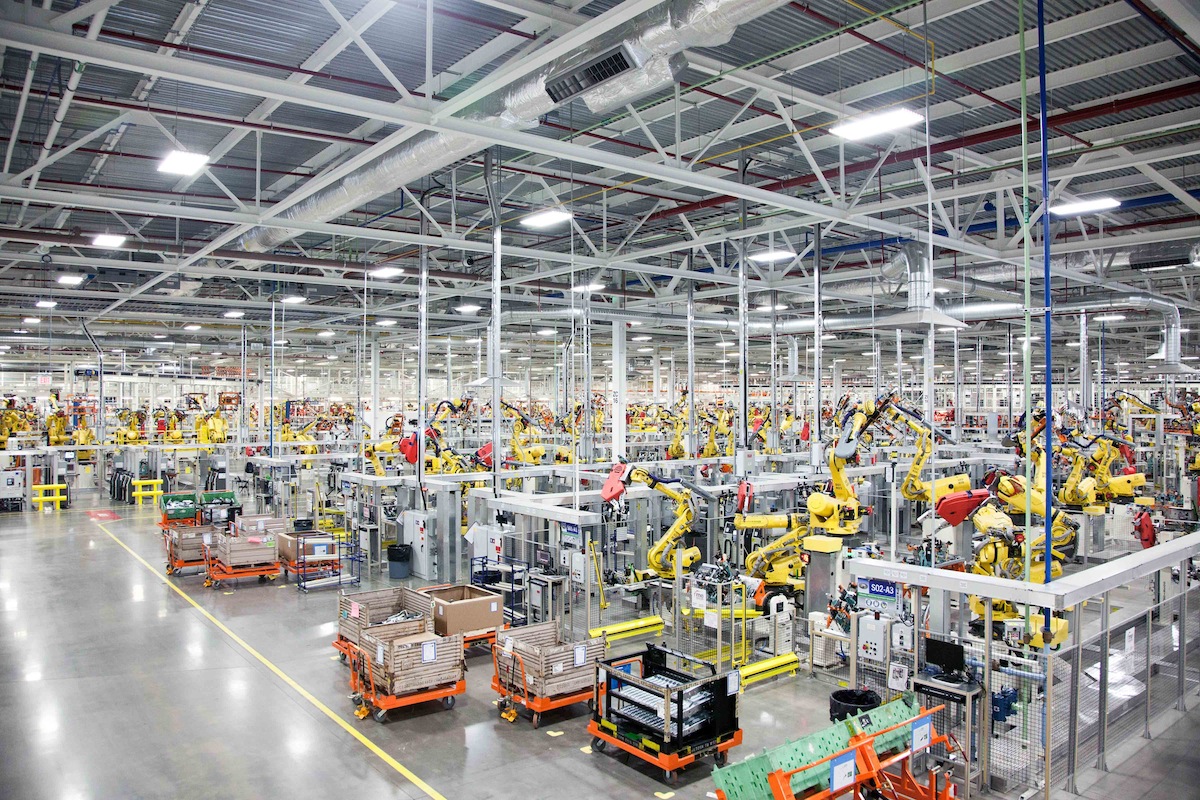
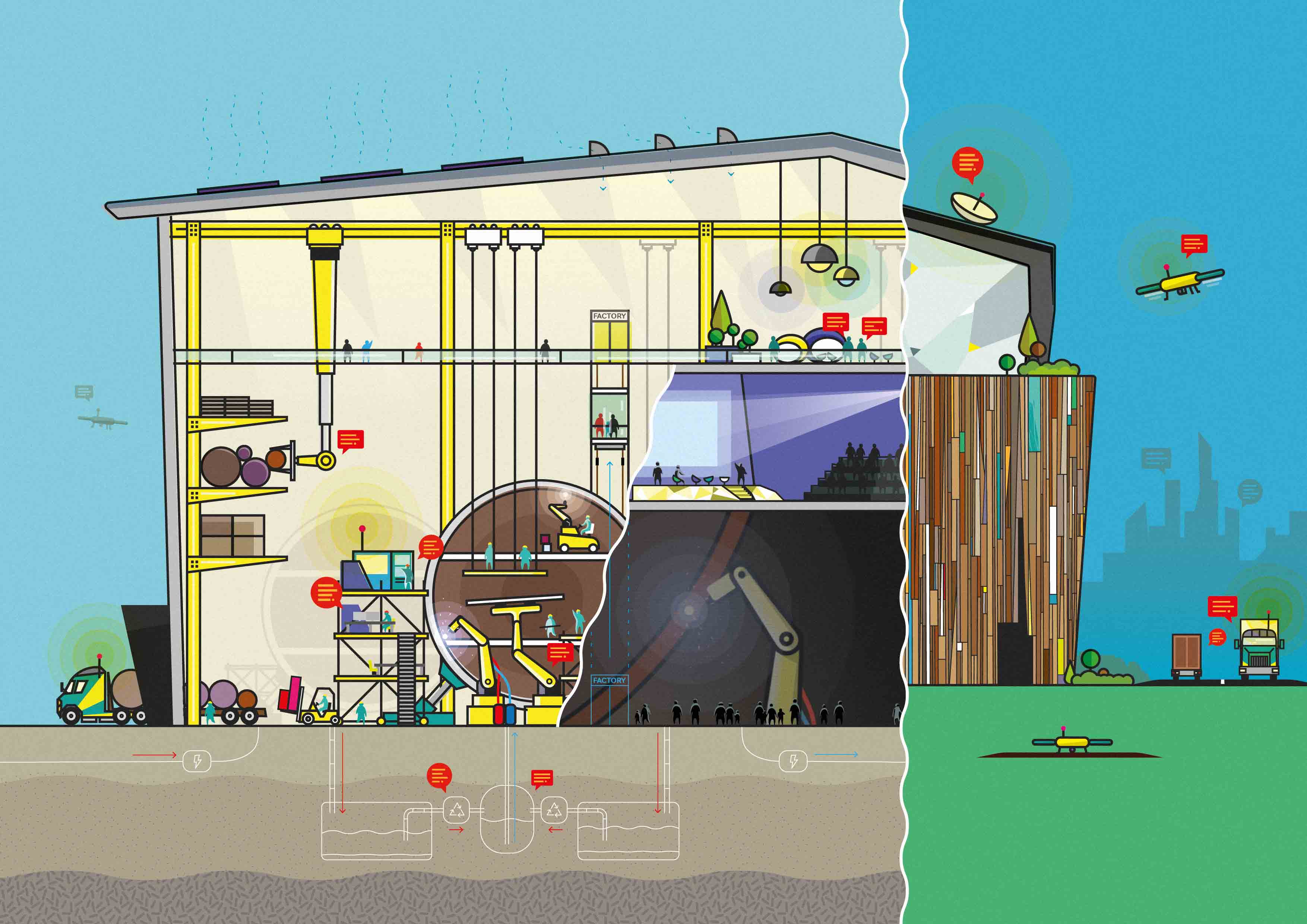
Global engineering and design consultantcy Arup launched "Rethinking the Factory," a report exploring the emerging trends, processes, and technologies that are transforming the manufacturing landscape. The report examines how the introduction of new technologies such as 3D printing, self-cleaning and self-healing materials, human/robot collaboration will lead to faster, more efficient and environmentally friendly production.
While many believe robots will replace humans in the factories of the future, the report, developed by Arup’s Foresight + Research + Innovation and Science and Industry teams, suggests collaboration between the two will be key. The integration of cameras and smart sensors already allow robots to adapt to their external environments.
Increasingly intuitive, their ability to infer a full task after being shown just a portion of it will enable workers to serve as robot supervisors, operating machinery and controlling smart production processes such as program and systems management and data analysis, rather than participating in manual labor. The increasing technicality of factories will mean that employees with STEM[1] skills will be particularly sought after, further exacerbating the international shortage of highly skilled workers, set to reach 40 million by 2020.
Beyond machines, new materials have the potential to improve the production process and increase product performance. A variety of self-healing and self-cleaning materials are being developed—such as bio-inspired plastic, which replicate the strength, durability, and versatility of a natural insect cuticles—which are capable of repairing damage without human intervention. These technologies will extend the lifetime of manufactured goods and reduce demand for raw materials.
Big data, technology, and 3D printing
The utilization of 3D printing—or more accurately, additive manufacturing—will allow manufacturing to be more mobile and dispersed. Factory locations are therefore likely to become both more varied and closer to the consumer, including the emergence of nontraditional spaces such as small offices in a city center. This will allow production to take place closer to the point of use, lowering transport costs and emissions.
Intelligence based on Big Data, advanced analytics, and the Internet of Things will create new opportunities for competitive advantage. Analysis of data will reveal detailed customer insights, identify new product opportunities sooner, and get new products and designs to market faster. Additive manufacturing and digital technologies will also make this mass customisation, faster, easier and more affordable.

Resilient and Adaptive Spaces
Flexibility will be critical to tackling changing consumer demands and shifting market trends. Factories will be adaptable, with modular building techniques to enable efficient re-scaling and diversification of production across various locations. This will also allow energy, water, and material consumption to be managed more effectively in an increasingly constrained resource market, while producing an environment best suited to meet the multiple needs of its highly skilled workforce.
Using tools such as BIM in factory design, planning and management will play a critical role in allowing manufacturers to foresee and mitigate issues based on access to resources, location choices, weather risks and transportation needs.
The design of the factory will also be more focused on consumer experience, utilising the factory as a showroom. The concept of the "transparent factory" will gain increased importance as more people get involved in making products or as they expect closer insight into how products are manufactured, especially at a customised level. The opportunity for factory owners and operators lies in adapting their existing spaces to enable these types of experiences to take place.
“The convergence of the physical and digital worlds means that manufacturers have to continue to adapt and adopt new processes quicker than ever before," Duncan White, Science and Industry Leader at Arup said in a press release. "While developing sustainable and resilient practices will be essential, having access to a skilled pool of workers will prove to be equally important and challenging as these changes are made. As such, it is critical that companies and policy-makers have a comprehensive understanding of the changing manufacturing landscape."
Rethinking the Factory is part of Arup’s Future of… series that envisages the possible futures by highlighting innovations from around the world. Previous reports include the Future of Highways, Future of Rail, Cities Alive, and It’s Alive.
For further information on Rethinking the Factory please download the report.
Related Stories
| Jul 21, 2011
Bringing BIM to the field
A new tablet device for construction professionals puts 3D data at the fingertips of project managers and construction supervisors.
| May 18, 2011
New Tool Takes PDFs Beyond 2D
Our IT expert puts a new PDF creation package through its paces and sees value for AEC firms that want to move more aggressively into 3D documents.
| May 16, 2011
Dassault Systèmes to distribute Gehry Technologies’ digital project
Dassault Systèmes and Gehry Technologies announced that Gehry Technologies’ Digital Project products will be integrated into the Dassault Systèmes’ portfolio and distributed through Dassault Systèmes. Digital Project is a suite of 3D BIM applications created by Gehry Technologies using Dassault Systèmes’ CATIA as a core modeling engine.
| May 3, 2011
Scott Simpson of KlingStubbins on how to get more value from BIM
Too few AEC professionals have developed a strategic idea of how BIM can and should re-shape professional practices and drive dramatic improvements in both creativity and production, according to Scott Simpson, FAIA, senior director of KlingStubbins. While BIM enables the exploration of design ideas quickly and in new and different ways, it can lead people to think they’re making more progress than they actually are. A simple adjustment in perspective is all it takes to put things right.