Retail healthcare has been around for more than two decades, giving millions of people access to healthcare in nontraditional medical settings oftentimes referred to as “convenient care clinics.” Yet, it has been more recently that we’ve witnessed the popularity of these facilities take off in a remarkable fashion.
While 10 years ago there were only 350 retail health clinics in the U.S., today, the number exceeds 3,000, according to McKinsey. The number of visitors and scope of services provided have expanded significantly.
What is driving the consumerization of the healthcare experience? Physical access is certainly an important factor, because most healthcare consumers live in or around urban areas.
But there are other components at play, too. These include an easy process for making an appointment or, in many cases, the ability to simply walk in for service; convenient payment options either out of pocket or through health insurance; and lower costs compared to emergency room visits and private physicians.
Retail healthcare has succeeded, in large part, because it has adopted a unique personality that does not try to mimic a hospital experience. It plays up its differentiators and appeals to consumers’ desire for efficient and convenient care. This niche sector is far from mature. The future of retail health will encompass more options for preventative approaches and wellness with an emphasis on education.
In addition, payers are shifting to paying for convenience care to drive down hospitalization. As healthcare in the U.S. moves to value-based care, it will be more about prevention and education.
‘Patients expect care to be as convenient as ordering an Uber or requesting food delivery.
It makes sense that retail health has a big opportunity to continue to serve customers 24/7
through artificial intelligence and virtual healthcare.’
— Ray Costantini, CEO, Bright.MD
New players are reacting by redefining what retail health might look like by embracing technologies including mobile apps, telehealth, and artificial intelligence—and even creating new healthcare segments that directly address what we eat. As a result of the consumer’s engagement in proactively managing their health, we are confident that there will be more retail-driven solutions focused on fresh and healthy food and other related products and services.
Consumer demands change continuously, but this is nothing compared to the pace of innovation in the healthcare sector. Add to this an evolving view of what defines and influences individual and societal “health,” and it becomes clear why so many players are trying to stake a claim in a relatively young market.
Companies outside of healthcare—including tech powerhouses such as Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, as well as retail giants such as Disney, Walmart, Levi Strauss & Co., and 7-Eleven—all are exploring how they can be influencers in this space. Some providers may choose to go it alone; others will depend on strategic partnerships to advance their strategy. And in many cases, this may require thinking outside the clinics.
As healthcare systems experience a more competitive environment, they are becoming increasingly more patient-centric. They are responding by providing new retail-like services including food options as part of their patient experience strategy. One of these new retail services that thinks beyond the clinic includes the delivery of healthy food and other health-related items to enhance the consumer experience was developed by 7-Eleven.
“7-Eleven is always looking for new ways to provide convenience to customers, and we have been exploring nontraditional retail sites to offer the products and services most needed there,” said Charles Bantos, 7-Eleven’s Director of Corporate Development. “With our growing selection of better-for-you foods and beverages, hospitals seemed a natural fit. They, too, are open 24 hours, with medical staff, patients, and families needing a variety of items at all times of day. That is 7-Eleven’s specialty: Meeting our customers when and where they need it most.”
Dick Escue, Healthcare CIO and Innovation Leader at Fortium Partners, agrees with the notion of thinking outside the walls of a traditional retail clinic. “While retail health is a great alternative to primary care for many people, it is still limited because it is not typically 24/7 and is restricted to being inside a building.”
Escue explained the potential for growth that exists if and when retail health leaders incorporate virtual healthcare and mobile applications outside the walls of a clinic, reaching those individuals who can’t drive, don’t have the time, or simply think their medical needs can be handled more efficiently from their home or office.
For those serving organizations delivering healthcare services—be it medical services, healthy food and convenience, or technology that may lead to better patient outcomes—we need to stay ahead of how retail health is going to expand even further as technologies such as virtual health, blockchain, and artificial intelligence become more of our everyday reality. The healthcare consumer of tomorrow will come to expect an incredible experience, as efficiently as possible, for the lowest cost possible, all while positively impacting their health outcomes.
Tech meets retail health
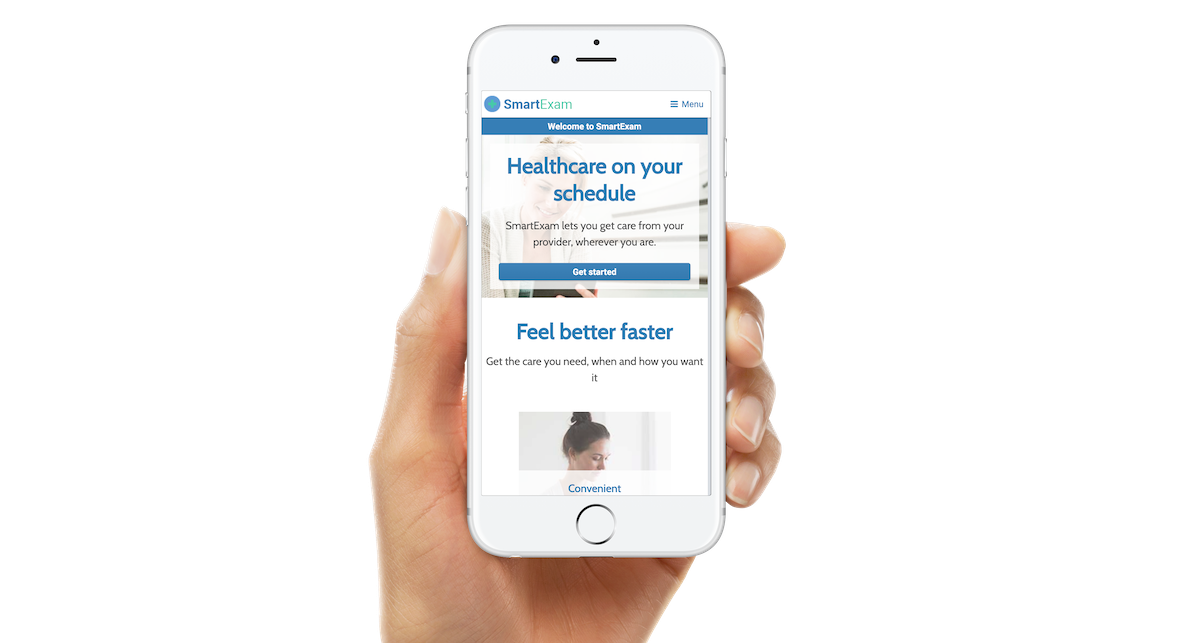
It’s no easy task staying on top of how new technology is transforming healthcare delivery. For example, the budding field of artificial intelligence is only just beginning to shape solutions for more efficient treatments and better patient care. SmartExam, a virtual care platform by Portland, Oregon-based Bright.MD, attracts a significant number of patients under the age of 40 who do not have a primary care doctor and want a convenient experience. SmartExam delivers direct-to-patient care remotely for more than 450 low-acuity conditions without video. It is being used at several locations, including Providence Healthcare’s retail care facilities in the Northwest. The competitive healthcare environment has made branding, price, and patient-centricity core components of the retail marketing strategy.
“Patients expect care to be as convenient as ordering an Uber or requesting food delivery,” said Ray Costantini, CEO of Bright.MD. “It makes sense that retail health has a big opportunity to continue to serve customers 24/7 through artificial intelligence and virtual healthcare.”
The ubiquitous use of technology by millennials and the generations that follow will continue to drive innovation. For example, Uber is addressing the issue of missed doctors’ appointments due to lack of reliable transportation through Uber Health, which allows healthcare associates to book rides for those in need via an online dashboard. Autonomous vehicles with lockboxes may soon be equipped to deliver pharmaceuticals to retail outlets. Drones could deliver uncommon medical equipment to retail outlets.
The futurist Ray Kurzwell teaches that “our intuition about the future is linear, but information technology is exponential.” What does this mean for retail healthcare? A future that we can barely imagine is just around the corner.
About the Authors
Lisa Feeley is VP, Project & Construction Management with Transwestern. Sarah Carter is VP, Healthcare Advisory Services with Transwestern
Related Stories
| Oct 30, 2014
CannonDesign releases guide for specifying flooring in healthcare settings
The new report, "Flooring Applications in Healthcare Settings," compares and contrasts different flooring types in the context of parameters such as health and safety impact, design and operational issues, environmental considerations, economics, and product options.
| Oct 30, 2014
Perkins Eastman and Lee, Burkhart, Liu to merge practices
The merger will significantly build upon the established practices—particularly healthcare—of both firms and diversify their combined expertise, particularly on the West Coast.
| Oct 21, 2014
Passive House concept gains momentum in apartment design
Passive House, an ultra-efficient building standard that originated in Germany, has been used for single-family homes since its inception in 1990. Only recently has the concept made its way into the U.S. commercial buildings market.
| Oct 21, 2014
Hartford Hospital plans $150 million expansion for Bone and Joint Institute
The bright-white structures will feature a curvilinear form, mimicking bones and ligament.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 13, 2014
Debunking the 5 myths of health data and sustainable design
The path to more extensive use of health data in green building is blocked by certain myths that have to be debunked before such data can be successfully incorporated into the project delivery process.
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Oct 8, 2014
Massive ‘healthcare village’ in Nevada touted as world’s largest healthcare project
The $1.2 billion Union Village project is expected to create 12,000 permanent jobs when completed by 2024.
| Oct 3, 2014
Designing for women's health: Helping patients survive and thrive
In their quest for total wellness, women today are more savvy healthcare consumers than ever before. They expect personalized, top-notch clinical care with seamless coordination at a reasonable cost, and in a convenient location. Is that too much to ask?