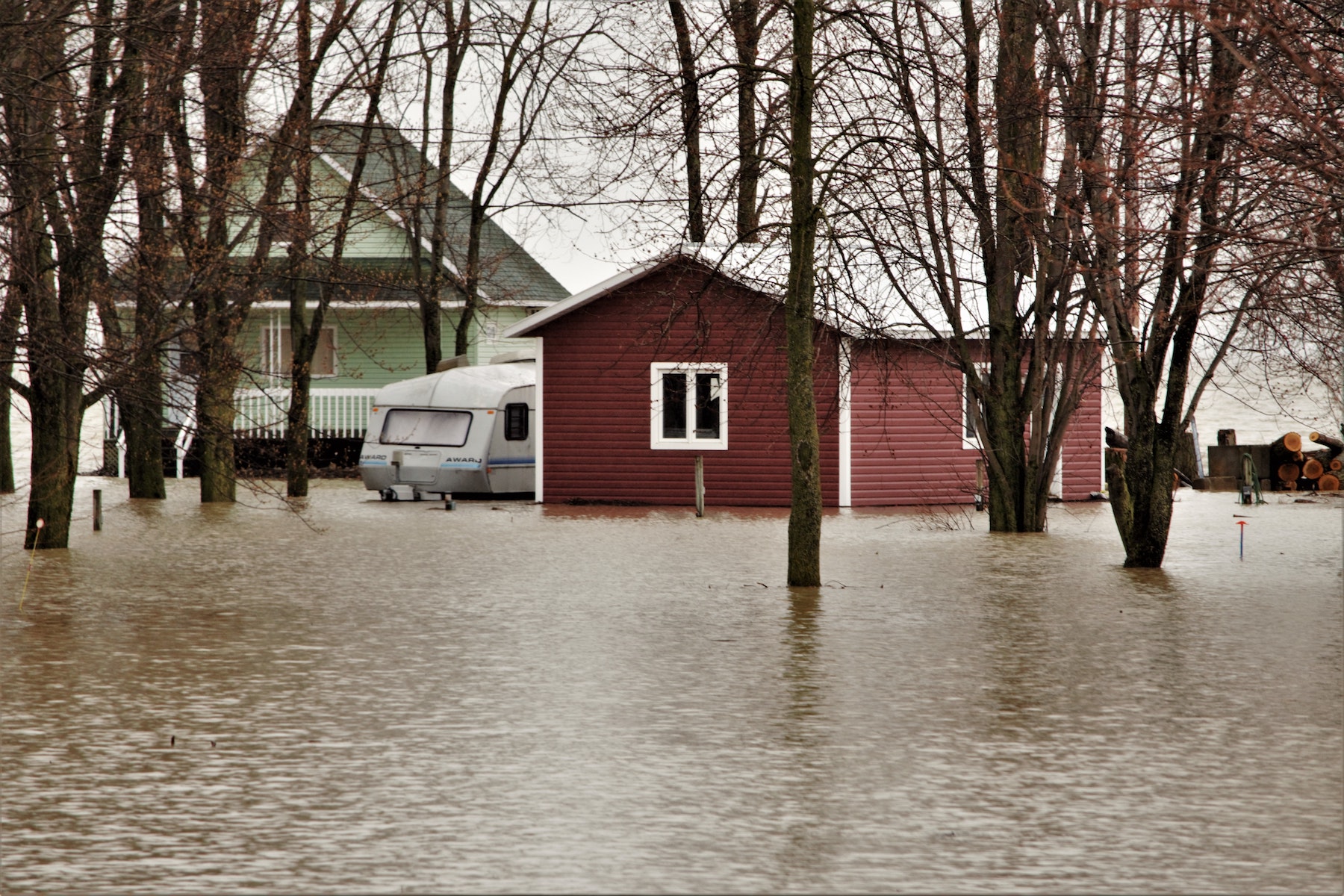
The Biden administration’s proposed major overhaul to the National Flood Insurance Program, or NFIP, would drastically alter how Americans protect homes and businesses against flooding.
The administration recently announced 17 legislative proposals that would represent the biggest reform to the NFIP since the program’s inception. One change would be a nationwide disclosure law that would ensure that prospective homeowners and renters have a property’s flood history before signing a contract. Today, 21 states have no such law.
Another proposal would prevent NFIP from issuing any new insurance policies for commercial buildings no matter where they’re located or when they were built because FEMA says it wants to promote growth in the private flood insurance market. Americans hoping to build new homes on eroding beaches and other flood-prone areas would also have to look elsewhere for insurance.
Homeowners would have to go to private insurance companies, which typically charge more expensive insurance premiums. People who hold mortgages on properties that flood multiple times and require insurance payouts of at least $10,000 each time, could lose access to government insurance on their properties after the fourth claim.
The proposals must pass Congress to become law, but there is support from both sides of the political aisle with a view that the status quo is becoming financially unsustainable.
Related Stories
| Nov 29, 2012
Government policies help accelerate adoption of green building
Green procurement policies or green building mandates can help accelerate the adoption of green building practices, according to research by Timothy Simcoe and Michael Toffel.
| Nov 26, 2012
Minnesota law to spur development, job creation produced few jobs
Legislation that allowed local governments to direct excess property tax dollars from tax-increment financing districts into other private developments was supposed to kick-start construction hiring in Minnesota.
| Nov 26, 2012
How to boost resilient systems that are sustainable
Cities of the future can be both more resilient and more sustainable by promoting strategies that include solar power and green roofs, programs that minimize demand for energy, rain gardens, and permeable pavement.
| Nov 26, 2012
Developer of nation’s first LEED platinum skyscraper focuses on carbon reduction
The Durst Organization, the developer of the first LEED platinum certified skyscraper in the country, says it will not seek LEED certification for its residential pyramid planned for New York’s West 57th Street.
| Nov 26, 2012
Questions linger over ability of Miami's newer high-rises to withstand hurricanes
Some towers in Miami, rebuilt after a hurricane in 2005, were allowed to be constructed under older building codes instead of newer ones created after Hurricane Wilma.
| Nov 26, 2012
Changes in development and building standards needed for health of Potomac River
The Potomac River’s health stands to suffer if the region does not change its development and building standards, according to the Potomac Conservancy.
| Nov 16, 2012
South Dakota prefers LEED over building code on state projects
“(LEED is) much better than a mandatory building code because you get a little wiggle room in these projects,” said Mike Mueller, a spokesman for the South Dakota Bureau of Administration.