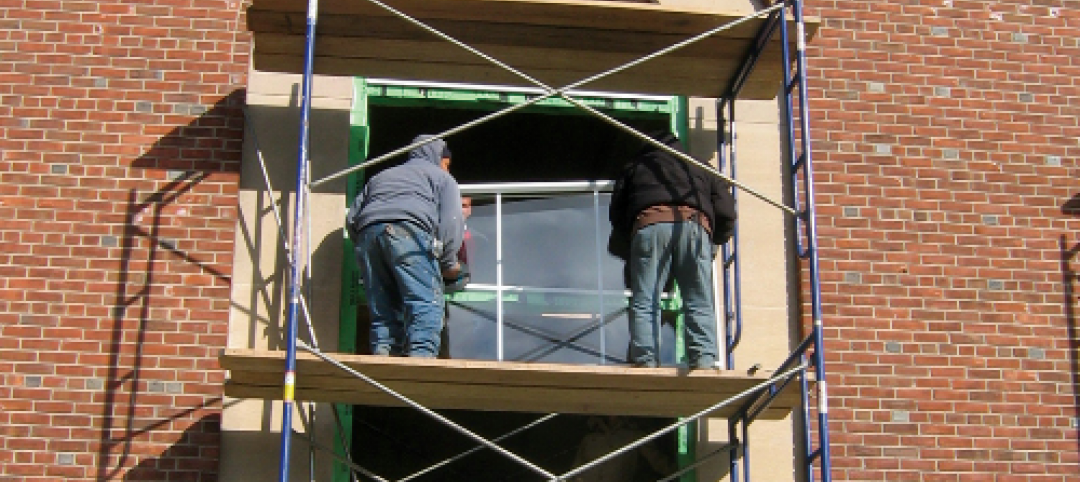
On Monday, Columbia University held a dedication ceremony for its 17-acre Manhattanville campus in the West Harlem section of New York City. This $6.3 billion campus, which when completed will comprise 6.8 million sf of new academic space, is the university’s most ambitious expansion since it relocated to its current campus at Morningside Heights in Harlem 119 years ago.
The new campus, which was master planned by Skidmore Owings & Merrill and Renzo Piano Building Workshop, has been in the works since 2003, roughly around the time Lee C. Bollinger became the university’s president. “We knew that Columbia had to have new space to fulfill its mission as a great university,” said Bollinger during the dedication’s luncheon, held inside the 450,000-sf Jerome L. Greene Science Center, Manhattanville’s first building to open.
The Center, which should be fully occupied by next spring, is home to the Mortimer B. Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute. (The publisher and philanthropist Mort Zuckerman; Christina McInerney, president and CEO of the Jerome L. Greene Foundation; three Nobel Prize laureates and two Pulitzer Prize winners were among the dignitaries in attendance.)
Over the next two years, the Manhattanville campus will open the 60,000-sf Lenfest Center for the Arts, which will feature the Miriam and Ira D. Wallach Art Gallery, a 150-seat screening room, and a 4,300-sf presentation space; and the 56,000-sf University Forum, with a 430-seat auditorium.
Eric Kandel, MD, co-director of the Zuckerman Mind Brain Institute (and a Nobel Laureate in 2002 for the category physiology or medicine), proclaimed this project “historically important” to the university’s stature as well as for accentuating the symbiosis on campus between “bioscience and the arts.”
By 2021, the Ronald O. Perlman Center for Business Innovation and the Henry Kravis Building—492,000 sf across two buildings designed by Diller Scofidio + Renfro in collaboration with FXFowle Architects—will be the new home for the Columbia Business School.
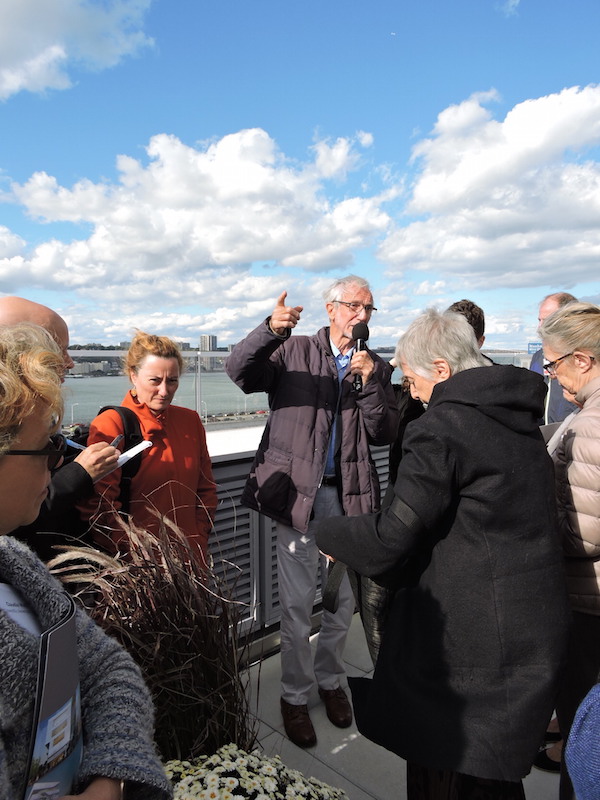
Architect Renzo Piano describes the Jerome L. Greene Science Center in relation to its surrounding environment, which includes New York City's West Side Highway and the Hudson River. Image: BD+C
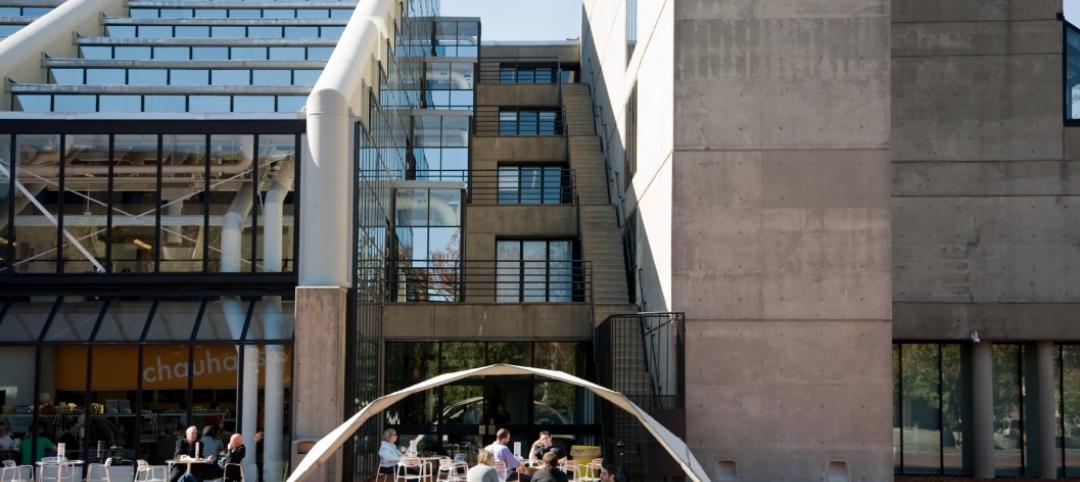
Architect Renzo Piano spoke at the dedication, at which he referred to the Jerome L. Greene Science Center as both a “palace” and a “factory that explores the secrets of the mind.” Piano also talked about the “urban layer” that will connect the campus to the community via reversed ground-floor setbacks, widened sidewalks, the absence of walls or gates (which is in marked contrast to the fortress-like Morningside Heights campus), height limitations (the Center is nine stories above ground), and a custom-glazed curtainwall.
His firm designed the Center to be as transparent as possible. The facility’s first floor, in fact, is open to the public. And its offices, labs, and other workspaces are organized on an open floor plan, divided into quadrants along North-South/East-West axes that expose workers and visitors to ample daylight.
Jerome L. Greene Science Center is across the street from an elevated subway line whose noise level measures 88 decibels. To mitigate that noise, the building was designed with a double-pane glass wall system whose 16-inch-wide air cavity in between exhausts air from the HVAC system and lets occupants open windows and glass doors from the inside. Open-air staircases connect the floors and encourage interaction between departments.
A 75,000-sf central energy plant, beneath the Greene and Lenfest buildings, will deliver electricity, chilled water, and high-pressure steam to nearly all of the buildings on campus.
The exterior bracing is visible to call attention to Greene’s “industrial” affinity with surrounding buildings in the neighborhood. That connection is reinforced by Columbia’s adaptive reuse of existing buildings on Manhattanville’s campus—specifically a one-time Studebaker auto-manufacturing plant and milk processing plant—that now serve, respectively, as university administration offices and Columbia’s center for the study of jazz and computer-generated music.
Manhattanville was the original name of this neighborhood, and Columbia and its AEC partners are at great pains to position this campus expansion as integral to a community that in the past has been wary about the university’s growth intentions. Bollinger, in his comments, went so far as to state that the new campus “is the best thing that could happen to upper Manhattan.”
Outdoor plazas within the campus will be accessible to the general public. The Jerome L. Greene Science Center will include a 1,920-sf Wellness Center that conducts free programs to raise awareness about stroke and related risk factors, and trains local residents to become community health workers. The Wellness Center will also be home to Mental Health First Aid, a program dedicated to improving the quality of mental health services in Upper Manhattan.
A 1,500-sf Education Lab within the Center will provide programs about brain science for the community and K-12 schools. Columbia has contracted with BioBus, an independent nonprofit, to run this program, and to bring learning into the community.
“This campus puts Columbia into the world,” observed Marilyn Jordan Taylor, a consulting partner with SOM (where she spent 33 years) and the former dean of the University of Pennsylvania’s School of Design.
Columbia|Manhattanville’s buildings are targeting LEED Platinum ND certification. Lendlease and McKissack Construction are the construction managers on the Greene and Lenfest buildings, Skanska and Velez Organization are the CMs on the University Forum building. And Turner will be the CM on the business school.
Related Stories
| Nov 3, 2014
An ancient former post office in Portland, Ore., provides an even older art college with a new home
About seven years ago, The Pacific Northwest College of Art, the oldest art college in Portland, was evaluating its master plan with an eye towards expanding and upgrading its campus facilities. A board member brought to the attention of the college a nearby 134,000-sf building that had once served as the city’s original post office.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 14, 2014
Proven 6-step approach to treating historic windows
This course provides step-by-step prescriptive advice to architects, engineers, and contractors on when it makes sense to repair or rehabilitate existing windows, and when they should advise their building owner clients to consider replacement.
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
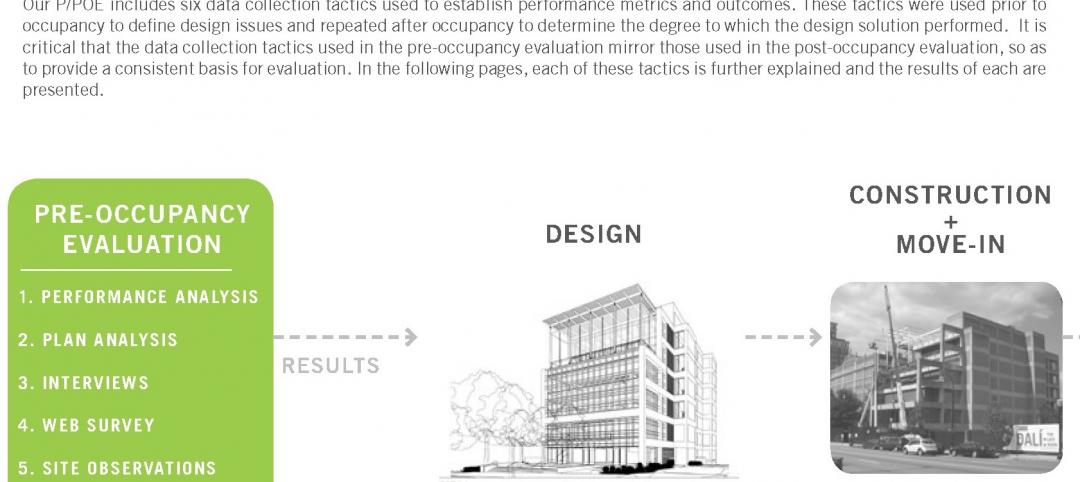
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 17, 2014
New hub on campus: Where learning is headed and what it means for the college campus
It seems that the most recent buildings to pop up on college campuses are trying to do more than just support academics. They are acting as hubs for all sorts of on-campus activities, writes Gensler's David Broz.