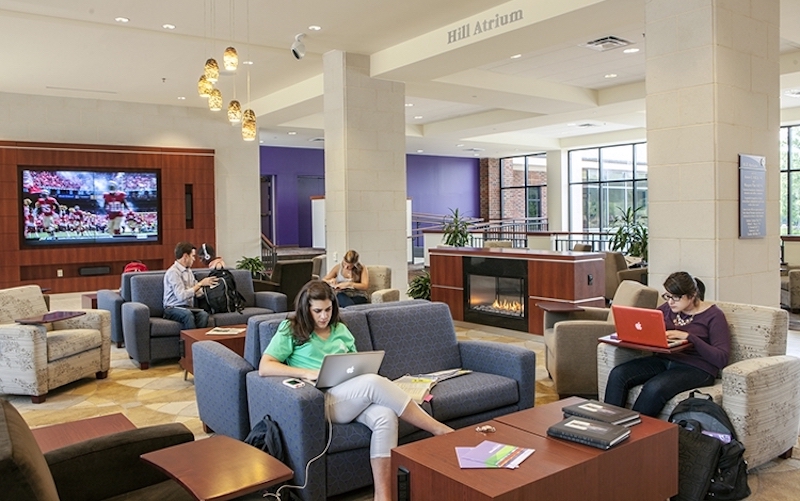
Welcome back for part three of the series, Designing for the Next Generation of Student Life. One of the major shifts in higher education today is the reality that Colleges and Universities are placing incredible emphasis on interdisciplinary studies. They are acknowledging that siloed academic disciplines don’t necessarily model today’s professional endeavors and are likely limited in solving some of the world’s greatest (or simplest) challenges. As this idea has taken hold, many Colleges and Universities are emphasizing interdisciplinary studies across campus. Along with this notion comes the realization that most campuses already have concentrations of students from different academic backgrounds in student housing, dining, sports and recreation, and student unions. This captive and blended audience seems to be the perfect opportunity to integrate academic and student life space into one holistic endeavor. Today, more than ever, Student Life is key to the academic enterprise!
This idea is not necessarily a new one. Several Universities have incorporated student interest groups, living / learning communities (LLCs), and residential colleges into Student Life in the past. But what’s different today is a defined curriculum around interdisciplinary study, teamwork, and academic experimentation, not just proximity or recreational interests. Many insitutitions have implemented degrees designed for academic cross-over (AKA portfolio programs), seminar courses that give students exposure to subjects outside their chosen major, and class projects designed to bring multiple academic majors together.
Since many academic departments have been concentrated in their own buildings or portions of campus, bringing these disciplines into a shared facility is fairly new territory. It also poses some basic challenges, such as shared space, equipment, furnishings, and faculty support. If we take this a step further and ask whether academic and student life spaces can be integrated, the same kinds of challenges present themselves, plus others: different funding sources, scheduling, security, maintenance, and hours of operation. How would a classroom in a residence hall be reserved, or maintained, or paid for over time? Who would be responsible? And importantly, how would this space be tuned to an interdisciplinary focus? These are the questions that set the stage for a new design opportunity.
LEARNING COMMONS
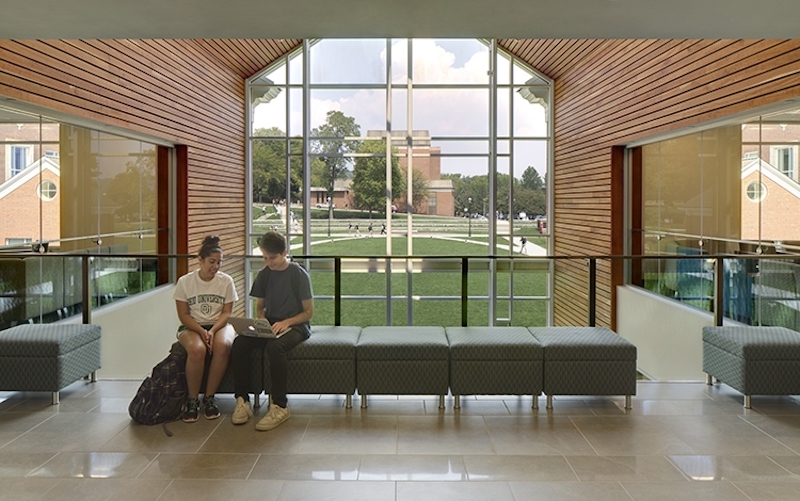 The Learning Commons at Ohio University.
The Learning Commons at Ohio University.
At some institutions with remote centers of student activity, the University has employed a ‘learning commons’ concept to integrate academic and student life. This idea often dedicates the first floor or basement level of a few, dispersed residence halls to a casual suite of soft furniture, group tables, classrooms, and study rooms that are open to the entire neighborhood (or grouping of residential buildings). This concept requires a careful coordination of how neighborhood residents access the learning commons and how building residents access the upper floors in order to maintain security. But, the results have been groundbreaking. Not only has the learning commons resulted in valuable academic areas, but it has received rave reviews from teachers and students. Teachers are appreciating the increased exposure to students of varied academic disciplines, causing faculty-in-residence suites to be in higher demand. Students love the ability to walk downstairs to attend a class, study, or collaborate (in their pajamas if they wish) versus long travel distances to the campus core. And in many cases, the academic side of the house has agreed to share the maintenance and funding expenses for this unique learning space.
MULTI-MODAL CLASSROOM
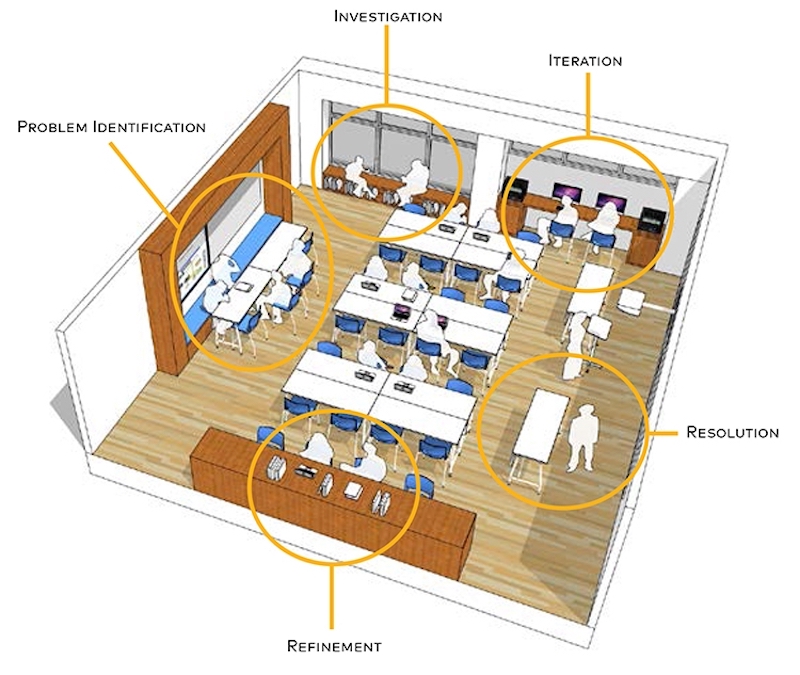 Multi-modal classroom prototype.
Multi-modal classroom prototype.
One of the keys to interdisciplinary learning is a new kind of venue, one that encourages multidisciplinary discovery. With a bit less emphasis on individual study and greater focus on collaborative problem solving, we often see project-based learning as an excellent backdrop for interdisciplinary studies. Project-based learning can take many forms but it follows a consistent process: real-world problem identification, investigation, iteration, refinement, and resolution. While each of these steps can represent their own space type, it might be more powerful to imagine one space that hosts all five activities at once. This is in direct counterpoint to the single mode classroom. In the past we have seen conference rooms, computer labs, woodshops, maker-spaces, and even active learning classrooms serving as project-based learning zones, but these rooms tend to fall into a single-use mode. Perhaps the future of interdisciplinary learning is one space that specifically and continuously fosters each step in the project-based learning process.
DISTANCE LEARNING…ON CAMPUS
Another major force in the combination of academic and student life space is the emerging priority of distance (or digital) learning. With the recent events related to the Coronavirus (COVID-19), we anticipate that this topic will receive dramatically increased attention.
Many research studies have reported that in-person instruction and collaboration is still incredibly valuable, but the ability to hit ‘pause’ or ‘replay’ on a recorded piece of instruction is equally valuable. And surprisingly, students prefer this blended learning format regardless of whether they live on campus or off. As a result, we are seeing that blended learning isn’t just for remote or commuter students, it’s critical for on-campus residents as well. What this means for academic spaces in the student life realm is that they are likely to incorporate two specific aspects. Some spaces will be geared toward multidisciplinary collaboration, while other areas will be geared toward personalized, distance learning. We can predict that immersive video, individual study booths, and even virtual reality and augmented reality studios are part of this picture.
FUSION BUILDINGS
Here’s another possibility. What if a large residential complex were to host several academic classrooms and pair those classrooms with the University’s academic disciplines that need and want space in the Student Life realm? This idea is already upon us with the emergence of fusion or mixed-use buildings. I recently worked on a design competition where a number of classrooms were planned for a University residential complex. Each of these classrooms could have been reserved by academic departments wishing to promote their program or associated more specifically with the school’s individual "colleges". The objective was to showcase each of the school’s major fields of study outside of a singular building, making those investigations more visible and accessible to the entire student body and university community. As an added benefit, the colleges may choose to use this extra academic space to manage a temporary rise in enrollment, offer an additional class, or defer renovation or new construction needs in their academic department.
NEW ACADEMIC SUPPORT
Several research studies over the years have suggested that student success is positively influenced the longer a student lives on campus. Much of the reason for this increased performance is attributed to simply being surrounded by fellow students, faculty, and staff who care that the student is there and doing well. We can imagine that integrating academic space into the student life realm will only improve this student success potential. For example, tutoring spaces have historically been centralized (often located at the campus library), but we see faculty and peer tutoring becoming more distributed in the future, with open and enclosed spaces in the student union or residence halls. Speaking of student unions, we are seeing a huge increase in requests for small group study rooms and casual study areas, turning what was the social hub of campus into an academic center as well.
As our world continues to grow in complexity and employers look for graduates with greater interdisciplinary, collaborative problem solving skills, we are confident that this blend of social and intellectual learning will continue to grow on the higher education campus. Please feel free to share with us your experience with student life spaces becoming more academically aligned.
Related Stories
University Buildings | Nov 28, 2017
FXFOWLE and CO Architects collaborate on Columbia University School of Nursing building
The building has a ‘collaboration ribbon’ that runs throughout the building.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Nov 27, 2017
The University of Memphis unveils the new home of the men’s basketball program
The Laurie-Walton Family Basketball Center will provide a strong commitment to donor and VIP cultivation.
Adaptive Reuse | Nov 10, 2017
Austin’s first indoor shopping mall becomes Austin Community College’s new digital media center
Renovation of the defunct mall represents Phase 2 of ACC’s $100 million adaptive reuse project.
University Buildings | Nov 6, 2017
A reconstructed building sets the standard for future rehabs at Cornell
Early AE collaboration played a major role in moving this project forward efficiently.
University Buildings | Oct 13, 2017
The University of Oklahoma receives its first residential colleges
The residential communities were designed by KWK Architects and combine living and learning amenities.
University Buildings | Oct 12, 2017
USC to debut new bioscience center next month
The building is designed to maximize recruitment and interaction of scientists and researchers.
University Buildings | Oct 12, 2017
The Center for Wounded Veterans is a first for a university campus
The Chez Family Foundation Center for Wounded Veterans in Higher Education is the first building of its kind on a U.S. college campus.
University Buildings | Oct 10, 2017
A 1920s cheese factory is now a university science building
Almost 15,000 sf of space was added to the original, four-story building.
Sustainability | Oct 9, 2017
New Arizona State University building will reach triple net-zero performance
The science and research complex will include an atrium biome filled with plants and water.
Higher Education | Sep 18, 2017
Campus landscape planning of the future: A University of Wisconsin-Madison case study
Recognizing that the future health of the campus and lake are interdependent, this innovative approach will achieve significant improvements in stormwater management and water quality within the university’s restored, more connected network of historic and culturally rich landscapes.















