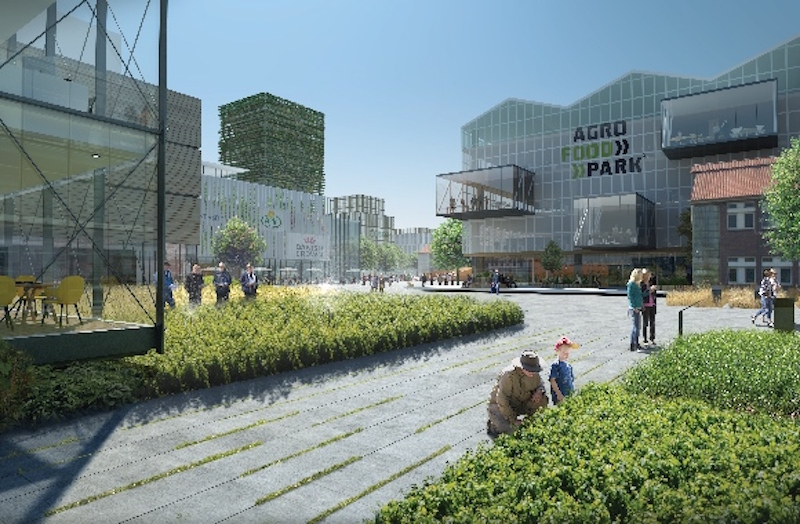
Argo Food Park is a center for food and agricultural innovation in Aarhus, Denmark that sits on about 250 acres of land. A new masterplan from William McDonough + Partners and 3XN/GXN has presented a proposal to develop the area into an urban environment that promotes innovation, knowledge sharing, and interaction between companies.
Farm fields surround the buildings located in the food park, and the proposal takes that into consideration, using the plant waste and manure from these farms as part of the new system design, fastcoexist.com reports. The proposal links the buildings for farm operations and office space in order to get enough heat or energy from the farm components to provide power for some of the buildings. The use of manure, biogas, and other farm waste will be used to power buildings and will be scaled up as new buildings are built.
The five main focus areas for the development are healthy materials, clean energy, increased biodiversity, healthy air, and clean water. “A carbon positive city demonstration at The Agro Food Park can be the embodiment of this new century—its clean water, air, soils and energy serving as a continuous source of economic and ecological innovation and regeneration, redefining how we act now for a positive future,” says William McDonough, FAIA, Int. FRIBAA, on the McDonough + Partners website.
The Argo Food Park proposal includes three primary spatial and landscape concepts called ‘The Strip,’ ‘The Plazas,’ and ‘The Lawn.’
The Strip acts as Argo Food Park’s main street. It is a street with open facades and shared amenities where the park’s companies can display their products and identities. It is built to be walkable and very pedestrian friendly.
The Plazas are a series of plazas meant to give local character to the surrunding buildings.
The Lawn is a central green space. It is meant to showcase the innovative and experimental happenings within the city’s agriculture and food production.
Currently, the masterplan calls for the work to be completed over four phases.
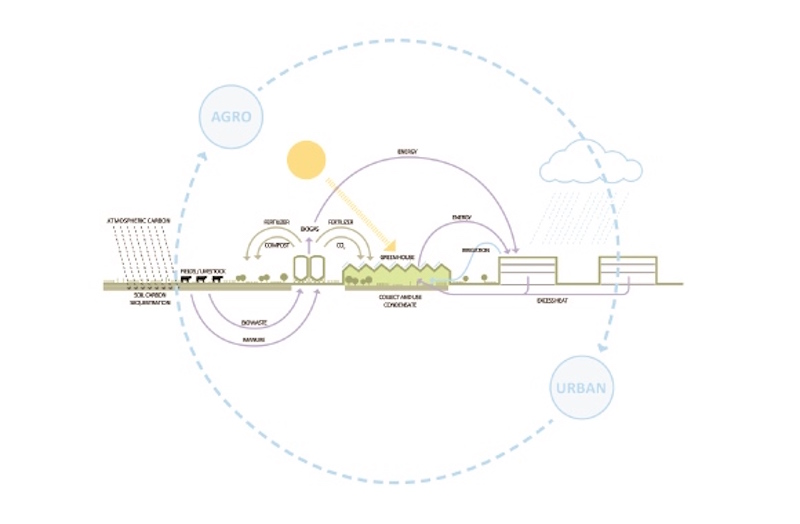 Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
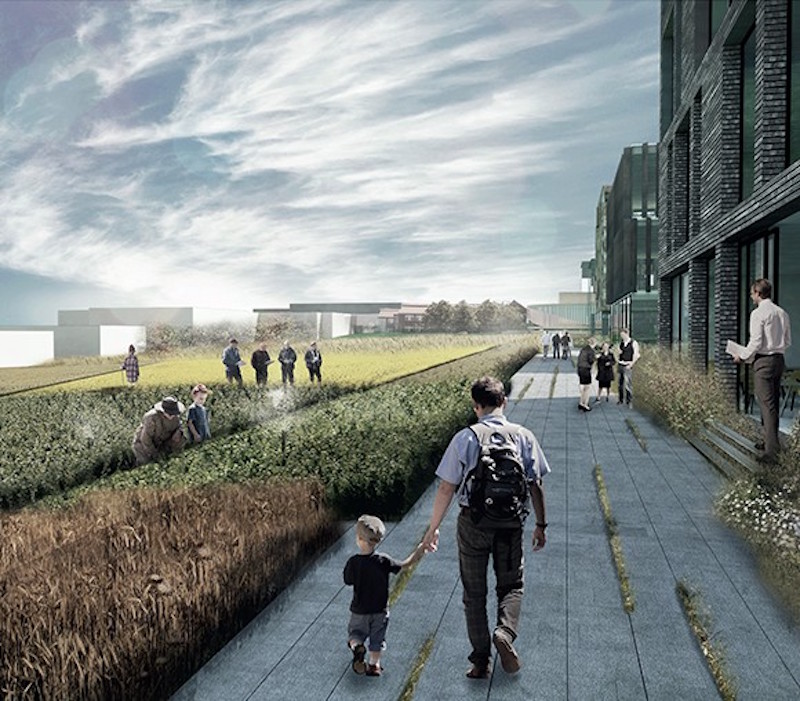 Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
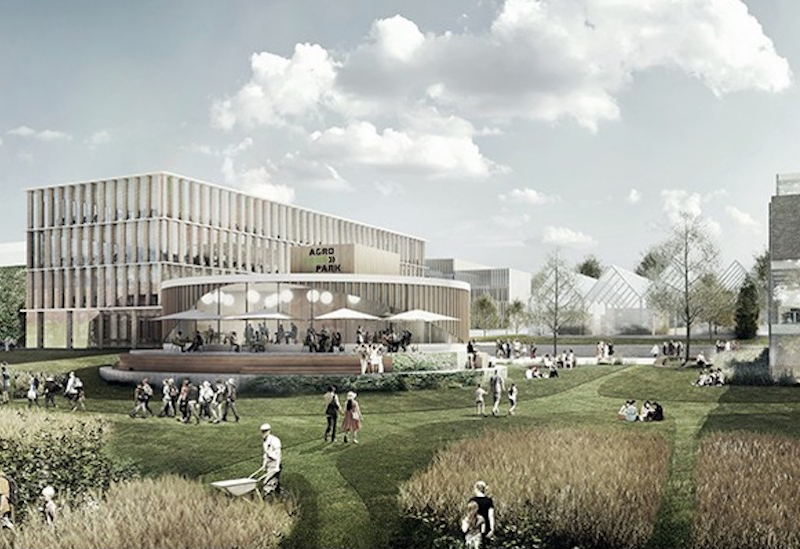 Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
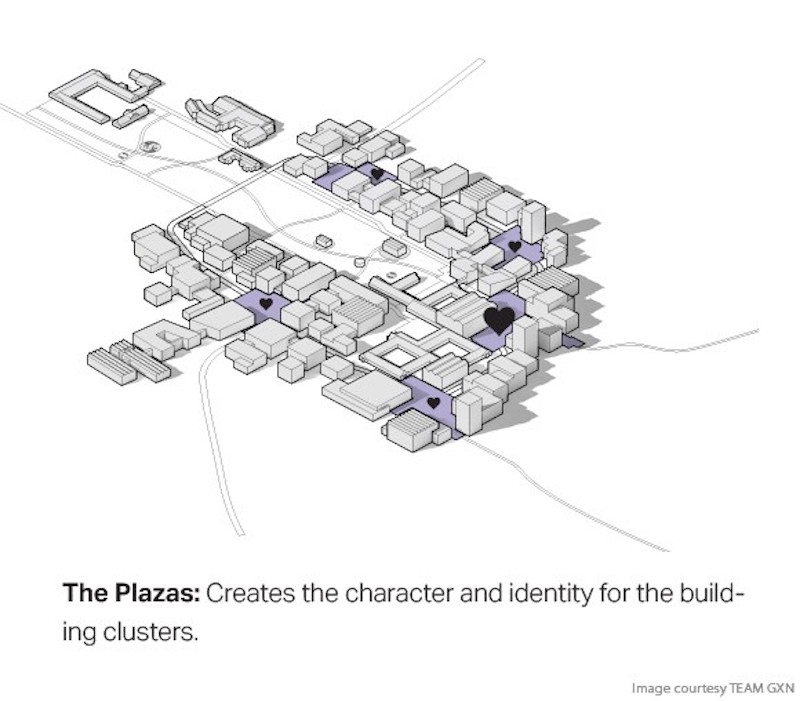 Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
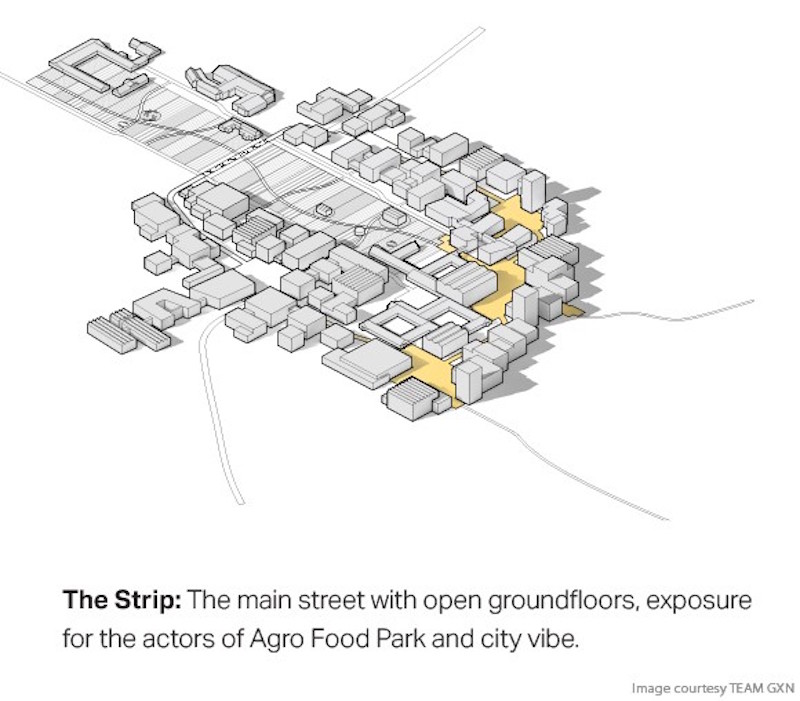 Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
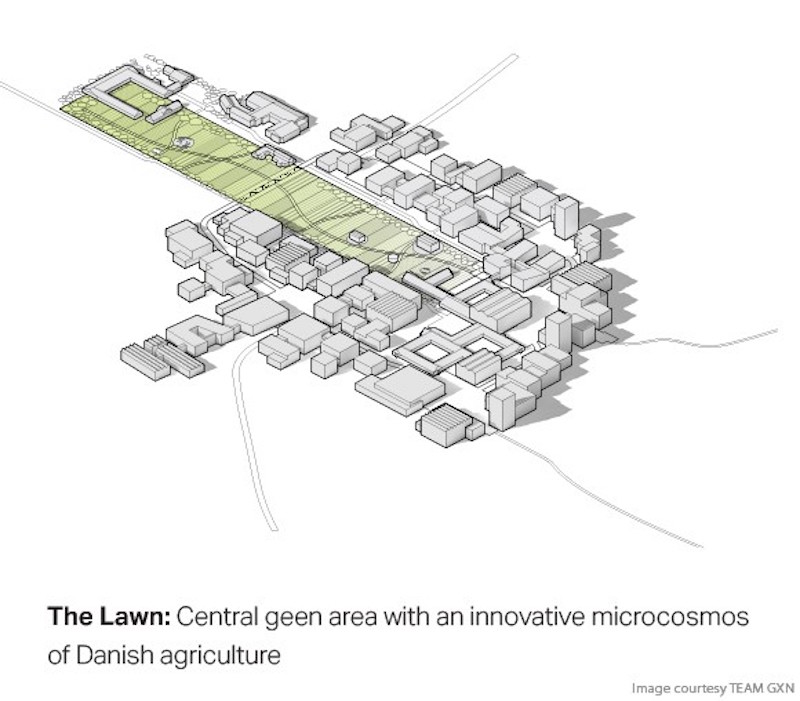 Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Image courtesy of 3XN/GXN
Related Stories
Wood | Feb 5, 2018
The largest timber office building in the U.S. will anchor Newark, N.J. mixed-use development
Michael Green Architecture is designing the building.
Green | Jan 31, 2018
U.S. Green Building Council releases annual top 10 states for LEED green building per capita
Massachusetts tops the list for the second year; New York, Hawaii and Illinois showcase leadership in geographically diverse locations.
Green | Jan 30, 2018
Welcome to the Jungle: Amazon’s Spheres have opened to employees and the public
The Spheres provide the most unique aspect of Amazon’s downtown Seattle headquarters.
Resiliency | Jan 17, 2018
Climate adaptation project addresses current and future climate changes in Randers, Denmark
The C.F. Møller-designed project is slated for completion in 2021.
Sustainability | Jan 16, 2018
The nation's capital of sustainable design
Major cities, like Washington, D.C., make up less than 2% of the world’s landmass, but they contribute 77% of the world’s CO2 emissions.
Museums | Jan 11, 2018
Suzhou Science & Technology Museum will highlight new cultural district in Shishan Park
The 600,000-sf museum will be about 62 miles northwest of Shanghai.
Urban Planning | Jan 10, 2018
Keys to the city: Urban planning and our climate future
Corporate interests large and small are already focused on what the impact of climate change means to their business.
Sustainability | Dec 7, 2017
Busting the myths: What the “S-word” can mean for construction and development
Sustainability, it’s a trendy term. The problem, however, is that it’s being used in so many different ways that people don’t even know what it means anymore.
Sponsored | Sustainability | Nov 2, 2017
Galileo’s Pavilion is a true showcase of sustainability
Galileo’s Pavilion is a 3,000-square-foot academic building.
Greenbuild Report | Oct 18, 2017
Rebuild, retreat, or resist
Hurricanes Harvey and Irma expose the necessity—and limitations—of resilient design and construction measures.
















