Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
“Energy is now a variable cost on the balance sheet, particularly with healthcare projects,” says Greg Turner, director of global offerings, Honeywell Building Solutions. “What we see happening for facilities managers is they’re talking to CFOs more regularly and the question is always. ‘What’s my energy cost going to be next quarter?’”
Building Teams and facility managers are using these energy analysis tools to keep clients’ bottom lines low and meet regulatory requirements for energy saving.
Green Building Studio: Innumerable design iterations
Green Building Studio is a Web-based tool that can help architects and designers perform whole building analysis, optimize energy efficiency, and work toward carbon neutrality earlier in the design process. Available via subscription service at www.greenbuildingstudio.com, Green Building Studio uses the DOE-2.2 simulation engine to calculate energy performance. It also creates geometrically accurate input files for EnergyPlus, the Department of Energy’s building simulation program. Crucial to the integrated interoperability of the program is the gbXML schema, an open XML schema of the International Alliance of Interoperability’s aecXML group. By using gbXML-enabled applications, Green Building Studio Web service users can eliminate redundant data entry and dramatically reduce the time and expense traditionally associated with whole-building energy simulation analyses.
“Our users will perform 50 to 100 iterations of a design,” says John Kennedy, senior manager, sustainable analysis products for Autodesk AEC Solutions and the CEO of GBS from its founding in 2004 through its acquisition by Autodesk in 2008. “They try out everything from type of glass to different levels of insulation, and each iteration requires a full simulation for proper energy use estimates. Running off of the Web, our users can run these calculations from the cloud and perform them a lot faster than if they were tied to their desktop resources.”
Engineering firm Glumac, based in Portland, Ore., uses GBS for energy analysis on many of its projects, such as the University of Hawaii at Manoa Recreation Center. Glumac’s scope of work included design review, whole building energy simulation, computational fluid dynamics analysis for natural ventilation, and sustainability consulting. The 67,000-sf project includes activity courts, locker rooms, aerobics facilities, and free weights. Glumac used GBS to quickly iterate energy consumption estimates for a variety of exterior shading devices, understanding energy use driven by landscape shading elements, and the effects of several different glazing configurations.
“Traditional analysis would have been too cumbersome to address these questions within our budget or within a fast enough timeframe to provide meaningful feedback to the design team,” says Skander Spies, an energy analyst in Glumac’s Portland office. Glumac created the initial geometry in Revit, then was able to import it into Green Building Studio and export a file compatible with other advanced analysis tools, such as EnergyPlus or eQuest. “This process results in more geometrically accurate models that take less time and budget to create, allowing our team to spend more time looking at the issues that matter,” says Spies.
In its most recent subscription update, Autodesk made the GBS service available to anyone with a Revit Architecture or Revit MEP subscription and integrated its features into Revit’s massing feature. Now, energy results are automatically updated in Revit, the company’s native building information modeling program.
“Building owners are asking more often for in-depth analysis,” says Autodesk’s Kennedy. “They want stronger performance guarantees for both new designs and renovations, and they’re asking about the drivers of building performance. We’re moving in the direction of making that data a normal, automated process.”
IESVE: Integrating documentation and design
Integrated Environmental Solutions was founded in 1994 in Scotland with the goal of developing primarily academic tools for building performance design and analysis and bringing them into mainstream use, according to founder and managing director Don McLean. In the interim, the company has launched commercially viable software that has grown to encompass design and analysis for all building design disciplines. Its products span a range of price and performance levels from the free and easy to the most detailed and rigorous.
IES’s main tool is its Virtual Environment (VE) Pro, a suite of software that integrates the entire process of designing buildings for environmental and energy considerations. Each module of the VE suite—for example, VE/Mechanical, VE/Electrical, or VE/Lighting—is tailored to analyze specific performance components of buildings. VE/Thermal includes energy performance measurement tools such as Apache SIM, Apache HVAC, and MacroFlo for total building and room-by-room energy calculation, simulation, and HVAC system design. VE Pro includes a full 3D modeling program for AEC professionals who want to create their designs natively. It can also import from Revit, SketchUp, or the gbXML file formats.
“You can perform the level of analysis you want all in one platform,” says Suzanne Robinson, an energy consultant at IES. “How detailed your building becomes is up to the user. We just want to engage them from the beginning in the design stage.”
VE Pro users can create baselines that integrate documentation in their design processes. The program’s LEED toolkit keeps track of compliance with LEED criteria and points across LEED-NC V2.2/V3, LEED for Schools V1/V3, and LEED Core and Shell V2/V3. The Sustainability VE toolkit tracks climate, natural resources, building metrics, construction materials, energy, carbon, daylight, solar shading, water, low- and zero-carbon technologies, and ASHRAE/CIBSE heating and cooling loads.
“It’s such a robust software engine we can more easily model complex designs,” says Mark Chu, a building physicist in AECOM’s advanced design group, based in Orange, Calif. “We can model things that we couldn’t before because the software isn’t constrained.”
Some of the projects AECOM has used VE Pro for energy modeling include the NASA Ames N232 Collaborative Support Building (registered for LEED Platinum) and NASA Johnson Space Center Building 26 (registered for LEED Gold).
Honeywell Energy Manager: Pinpoint performance issues
Energy Manager is a Web-based advanced energy management and information system designed to capture, analyze, and act on data to help solve energy problems in existing buildings. Energy Manager’s software uses an existing building’s in-place infrastructure to track energy dollars, impact of weather on consumption, and similar energy-related issues.
If a room or floor has leaky windows, Energy Manager can isolate higher heating costs in that area and report the problem back to the facility manager. It also uses diagnostics to show metrics and behaviors of pieces of equipment to be analyzed for peak performance. Energy Manager’s data can be accessed anywhere from the Web and can be used to set up daily or weekly weather-neutralized energy consumption reports e-mailed directly to supervisors.
“It’s designed to mine data,” Turner says. “You can create as many virtual metering solutions as your building needs. It’s designed to let customers add the functionality they need without adding new systems.” BD+C
—Jeff Yoders, Contributing Editor
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Apr 12, 2023
Watch: Trends in urban design for 2023, with James Corner Field Operations
Isabel Castilla, a Principal Designer with the landscape architecture firm James Corner Field Operations, discusses recent changes in clients' priorities about urban design, with a focus on her firm's recent projects.
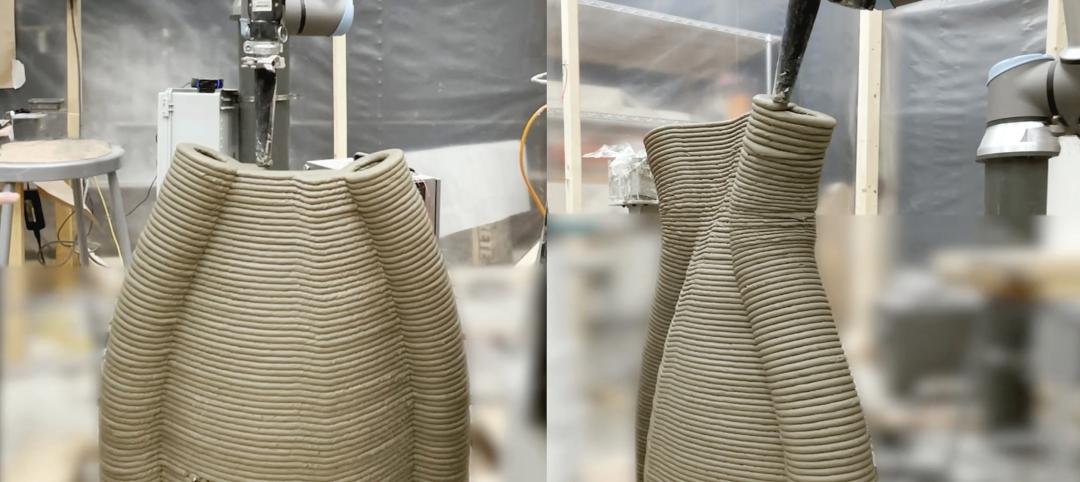
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
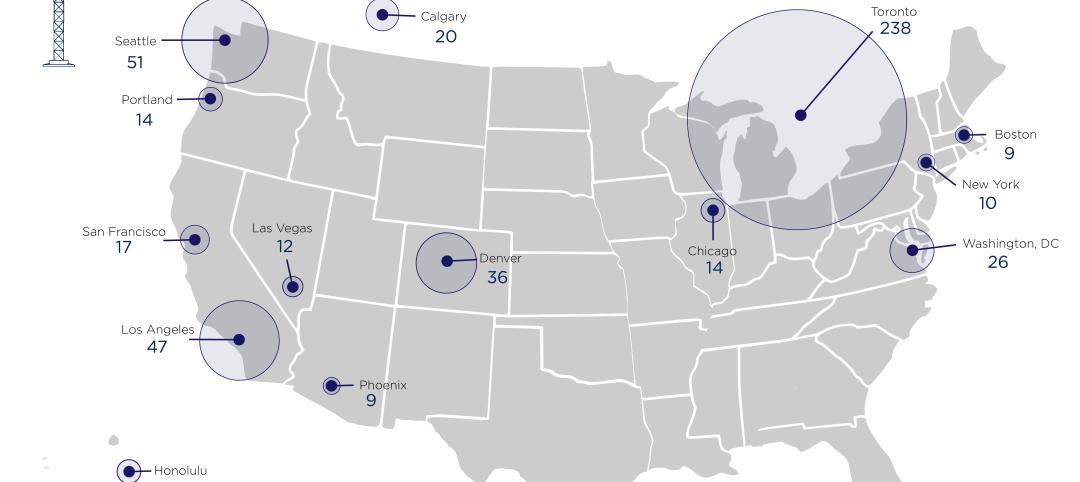
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.
University Buildings | Apr 11, 2023
Supersizing higher education: Tracking the rise of mega buildings on university campuses
Mega buildings on higher education campuses aren’t unusual. But what has been different lately is the sheer number of supersized projects that have been in the works over the last 12–15 months.
Architects | Apr 10, 2023
Bill Hellmuth, FAIA, Chairman and CEO of HOK, dies at 69
William (Bill) Hellmuth, FAIA, the Chairman and CEO of HOK, passed away on April 6, 2023, after a long illness. Hellmuth designed dozens of award-winning buildings across the globe, including the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company Headquarters and the U.S. Embassy in Nairobi.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Mixed-Use | Apr 7, 2023
New Nashville mixed-use high-rise features curved, stepped massing and wellness focus
Construction recently started on 5 City Blvd, a new 15-story office and mixed-use building in Nashville, Tenn. Located on a uniquely shaped site, the 730,000-sf structure features curved, stepped massing and amenities with a focus on wellness.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
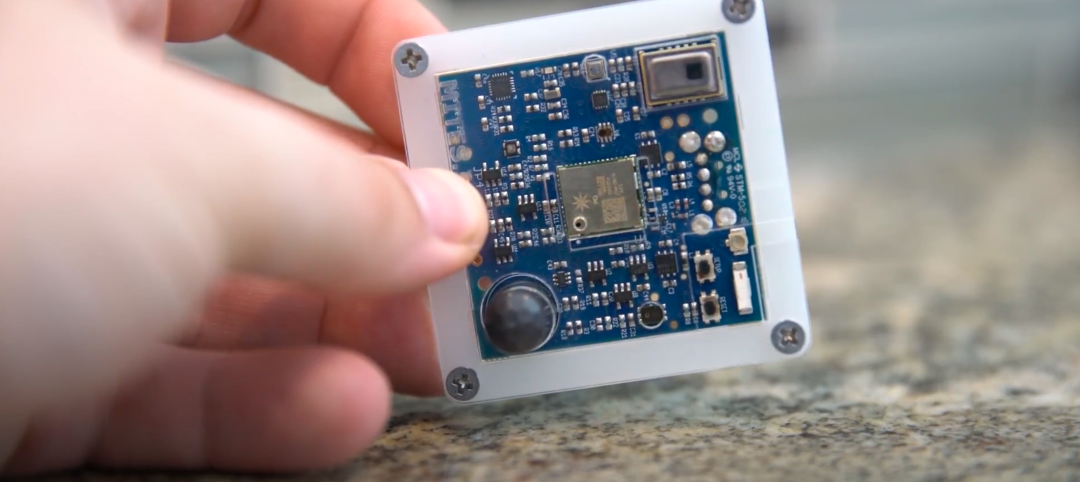
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Affordable Housing | Apr 7, 2023
Florida’s affordable housing law expected to fuel multifamily residential projects
Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis recently signed into law affordable housing legislation that includes $711 million for housing programs and tax breaks for developers. The new law will supersede local governments’ zoning, density, and height requirements.
Energy Efficiency | Apr 7, 2023
Department of Energy makes $1 billion available for states, local governments to upgrade building codes
The U.S. Department of Energy is offering funding to help state and local governments upgrade their building codes to boost energy efficiency. The funding will support improved building codes that reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency, according to DOE.