The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) recently unveiled new guidance on additional assistance funding for net zero buildings.
The funding is available for implementing net-zero energy projects with a tie to disaster recovery or mitigation. FEMA encourages applicants to incorporate net zero activities into eligible recovery and mitigation projects.
For projects to be identified as net-zero energy, buildings must meet or exceed the energy performance thresholds and renewable generation requirements specified in the zero energy appendices of the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC).
The increased costs of designing projects to be net-zero over traditional methods is allowable on certain eligible projects.
FEMA eligibility requirements for net zero energy buildings
For a FEMA project to be determined eligible as a net-zero energy project, each project must meet applicable program eligibility requirements. For new construction, major renovations, reconstruction, or code updates to be identified as net-zero energy, the following requirements will be taken into consideration to allow for additional costs, or other program or grant benefits.
New building construction and major renovations projects:
1. Are defined as new buildings or complete overhauls of existing buildings to salvage existing core structural elements, historical facades, etc. without any functional floor area being preserved in the process.
2. Must produce buildings that meet or exceed the energy performance thresholds and renewable generation requirements specified in the zero energy appendices of the 2021 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC), appendix CC and RC for commercial and residential, respectively. Code specifications or standards that are equivalent to or more stringent than the IECC require the project engineer, design professional, or other project professional to identify the energy requirements of such local code specifications or standard as equivalent to or more stringent to the IECC.
3. Must comply with these requirements using the methodology and requirements outlined in these IECC Appendices, or subsequent, more recent versions, or other versions of zero energy building codes as they may emerge and be specified by FEMA or Department of Energy (DOE) as eligible.
Existing buildings that are transitioning to net-zero energy projects:
1. Are defined as existing buildings which are eligible for FEMA funding that undergo an alteration, modification, or other retrofit.
2. Alterations, modifications, or other retrofits affecting part but not all of an existing building must meet or exceed the requirements outlined in Chapter 7 and Normative Appendix B (if applicable) in the 2021 or most recent version of the International Green Construction Code (IgCC). These construction and procurement requirements ensure that high performance equipment and materials are installed in the facility, even if the facility as a whole, will not meet the energy performance targets specified in the IECC Zero Energy Appendices. Code specifications or standards that are equivalent to or more stringent than the IgCC require the project engineer, design professional, or other project professional to identify the energy requirements of such local code specifications or standard as equivalent to or more stringent to the IgCC.
3. The project must procure renewable energy generation in an amount equivalent to or greater than the annual energy consumption of the alteration, modification, or other retrofit of the existing building. The amount of renewable energy generation required for the project can be calculated using the methodologies outlined in the IECC Zero Energy Appendices. Pairing this renewable generation with high performance equipment and materials will enable partial-building projects for existing buildings to achieve net-zero standards.
4. Compliance with these requirements will be performed using the methodology and requirements outlined in the IECC Zero Energy Appendices and the IgCC where specified above throughout the construction process.
Related Stories
Green | Apr 20, 2015
USGBC opens public comment period for LEED for existing multifamily buildings
The new LEED Operations and Maintenance: Multifamily program will offer solutions for existing multifamily projects with at least 20 units.
Cultural Facilities | Apr 16, 2015
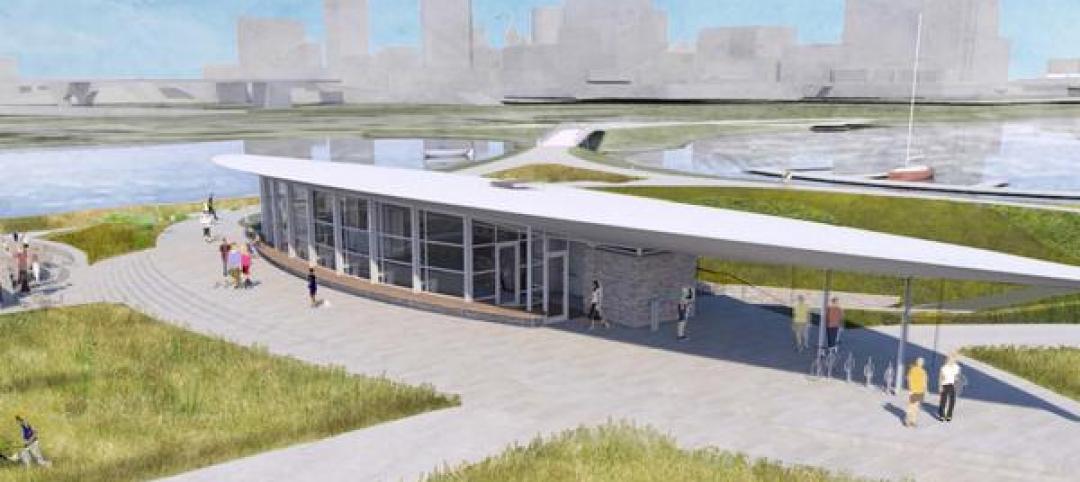
Milwaukee’s Lakeshore State Park visitor center will be ‘off the grid’
The plans also include a built-in wastewater treatment system and rainwater collection.
Green | Apr 16, 2015
Passive House Institute introduces new categories for building certification
The new evaluation procedure considers the building in an environment where only renewable energy is used. Sun and wind provide the primary electricity.
Green | Apr 16, 2015
New version of Building Energy Data Exchange Specification launched
BEDES is a dictionary that facilitates consistent exchange of building characteristics and energy use data between tools and databases in the building energy efficiency sector.
Green | Apr 14, 2015
USGBC will recognize energy and water standards for the Living Building Challenge
This move means that projects achieving the energy and water requirements in Living Building Challenge will be considered as technically equivalent to LEED.
Green | Apr 7, 2015
USGBC survey shows Fortune 200 companies prioritize green building
The world’s top-performing companies are prioritizing sustainability as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts, and a majority of them are using LEED to achieve their goals, according to the new survey.
Codes and Standards | Apr 6, 2015
DOE releases Better Buildings Workforce Guidelines
The guidelines are aimed at strengthening and streamlining commercial building workforce training and certification programs for workers in energy auditing, building commissioning, building operations, and energy management.
Green | Apr 3, 2015
Georgia may ban use of LEED on state buildings
Georgia's state legislature is considering a measure to require all state buildings to only use green building standards that permit the use of Georgia's lumber.
Green | Apr 3, 2015
Energy benchmarking law helps make D.C. top ranked Energy Star city
First-in-the-nation law requires public reporting of annual energy performance
Green | Apr 1, 2015
Global wind power installations expected to slow through 2019
After a 20% falloff in 2013, the global wind power industry made a strong comeback in 2014, with a record 51.2 gigawatts installed. But a new report from Navigant Research forecasts a curtailment in growth.