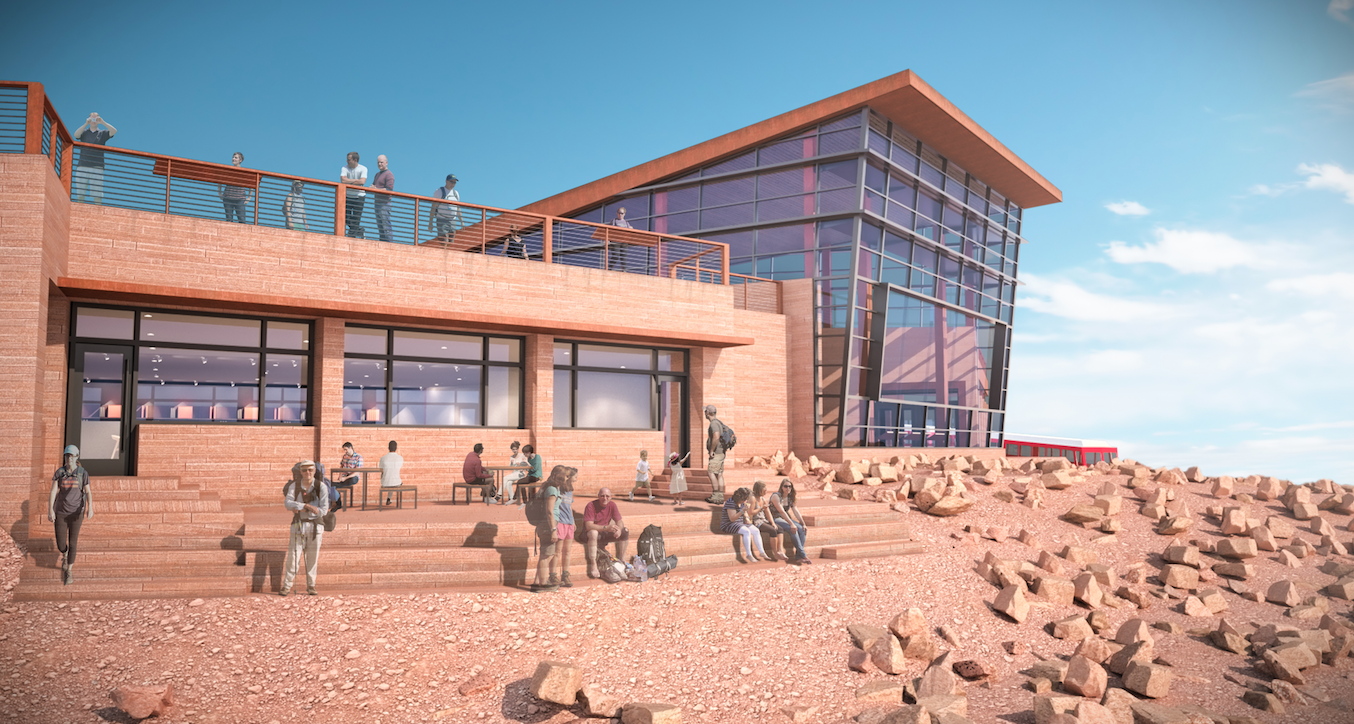
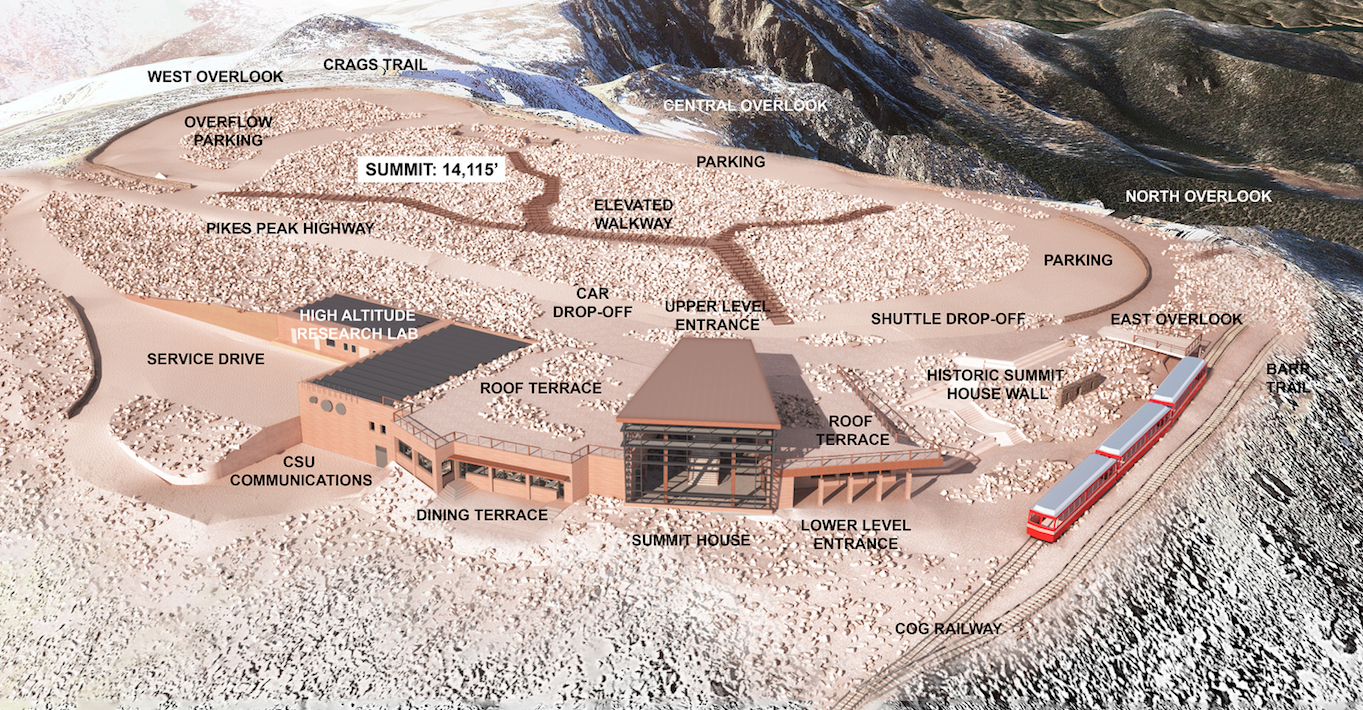
The design team for the new visitor center atop the 14,115-foot summit of Pikes Peak, led by design architect GWWO, Inc./Architects and architect of record RTA Architects, unveiled an unobtrusive, minimalist structure that will appear as if it’s carved into the mountainside.
The design, which incorporates input from the public collected during a months-long survey, will provide majestic views of the Rocky Mountains for the 600,000-plus people who visit the summit each year. Reminiscent of the crags and rock formations found above the tree line, the design uses shade, shadows, and fragmentation to coalesce into the peak.
Clad in material similar to Pikes Peak granite, the modern hue seamlessly blends into the mountainside. The orientation of the building to the south takes advantage of the enhanced solar gain at altitude, including daylight harvesting and photovoltaics. Other sustainable features include composting toilets and low-flow fixtures to conserve water.
“Captivating, but also functional, the building is sited to take advantage of the unique environmental conditions present on the top of Pikes Peak,” said Alan Reed, Principal with GWWO. “Nestled into the mountain, exposure to the harsh winds is minimized, while the mass of the building provides sheltered outdoor areas from which to enjoy the views.”

The deteriorating condition of the existing 50-year-old summit buildings has prompted the city of Colorado Springs, in partnership with the U.S. Forest Service, the U.S. Army, Colorado Springs Utilities, and the Broadmoor Pikes Peak Cog Railway, to embark on a process to design and build new facilities that incorporate the Summit House visitor center, the Plant Building, Communications Facility, and the High-Altitude Research Laboratory.
Local construction company GE Johnson was selected by the city of Colorado Springs as the construction manager and general contractor to oversee construction of the City’s summit complex facilities. Off site fabrication is expected to start in early 2017, subject to the outcome of the Environment Assessment currently underway by the U.S. Forest Service.
Architects’ Statement on the Design
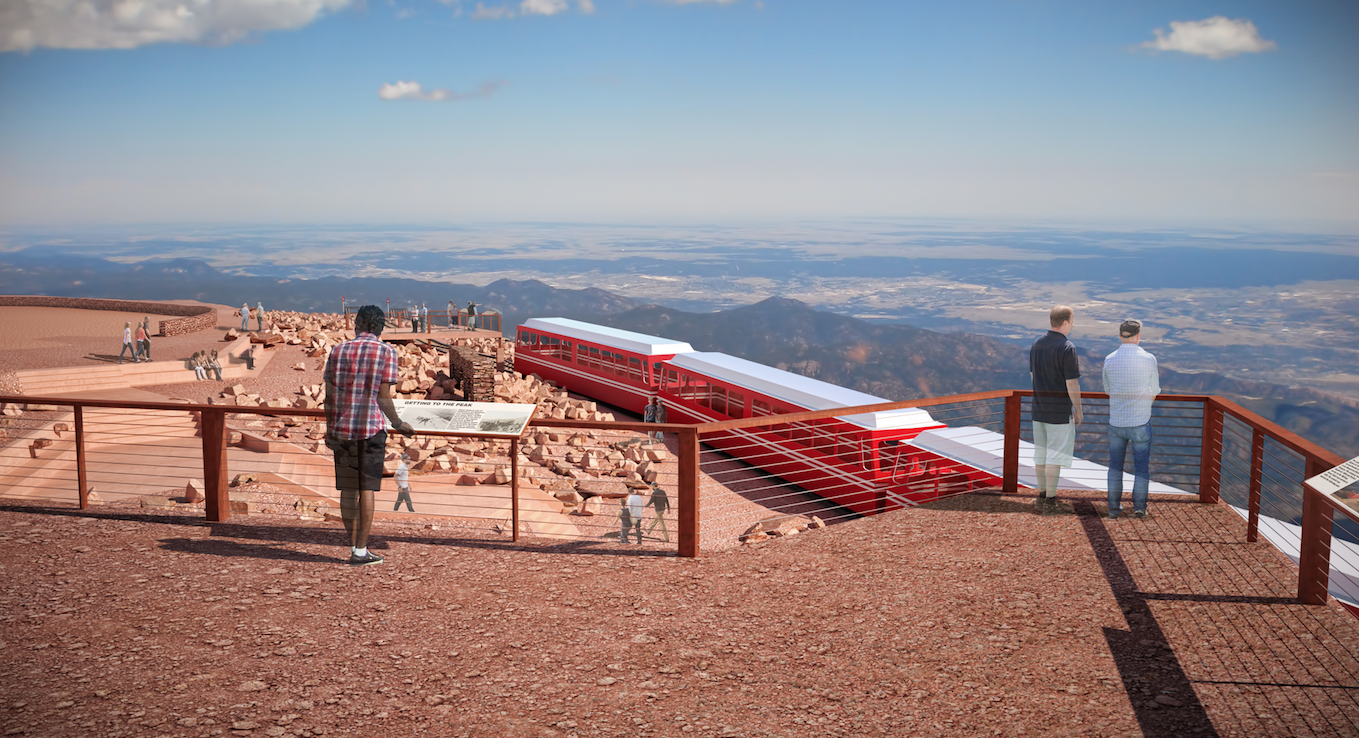
Predominately a one-story form seemingly carved from the southeast side of the Peak, the new Summit House offers unobstructed views to the east. Reminiscent of the crags and rock formations found above the tree line, the design uses shade, shadows and fragmentation to coalesce into the Peak. Clad in material similar to Pikes Peak granite, the modern hue seamlessly blends into the mountainside. Viewed from below, it is one with the mountain, yet as one arrives at the Peak, the modest entry pavilion is a clear destination.
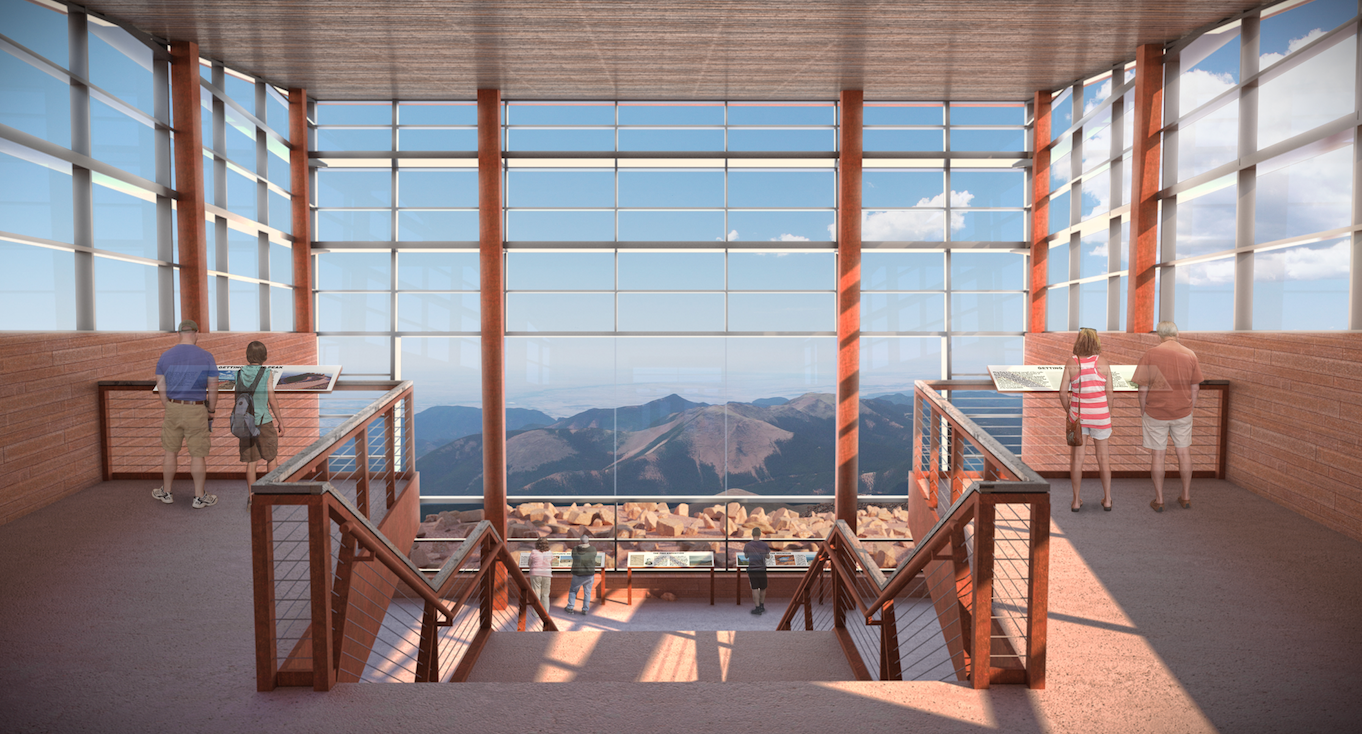
Upon approach to the summit, visitors take in the expansive and pristine views, just as Zebulon Pike saw and Edwin James, the first man to reach the summit, experienced over 200 years ago. The only indication that this peak has been touched by man is the glass enclosed pavilion capped with weathering steel emerging from grade. Sited to frame the view of Mt. Rosa, the location from where Pike viewed the Peak in 1806, the pavilion’s lobby provides a sheltered area to view the surrounding landscape, while affording access to the main level of the Summit House below.
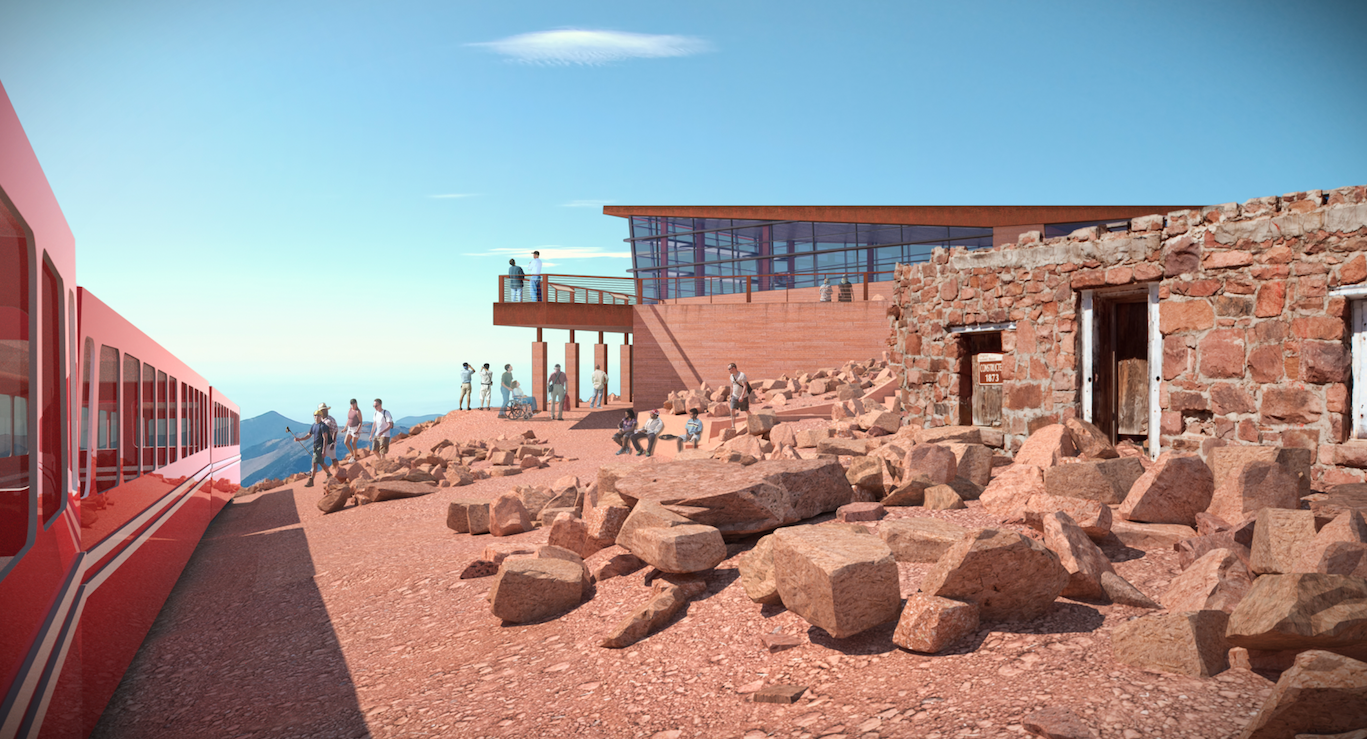
Accentuating the relationship between the two landforms, the 4 degree angle from Pikes Peak to Mt. Rosa is reflected in the downward tip of the lobby walls. That same angle is mirrored in the upward slope of the roof acknowledging the expansive views to the east. To the left and right, rooftop terraces become an extension of the summit, blending with the tundra and bringing visitors closer to the edge to experience 180 degrees of the same unobstructed and undisturbed views that James saw and Katharine Lee Bates beheld as she penned the lyrics to America the Beautiful. An extended platform to the north provides optimal views of the ruins of the original 1873 Summit House and embraces the relationship with the cog.
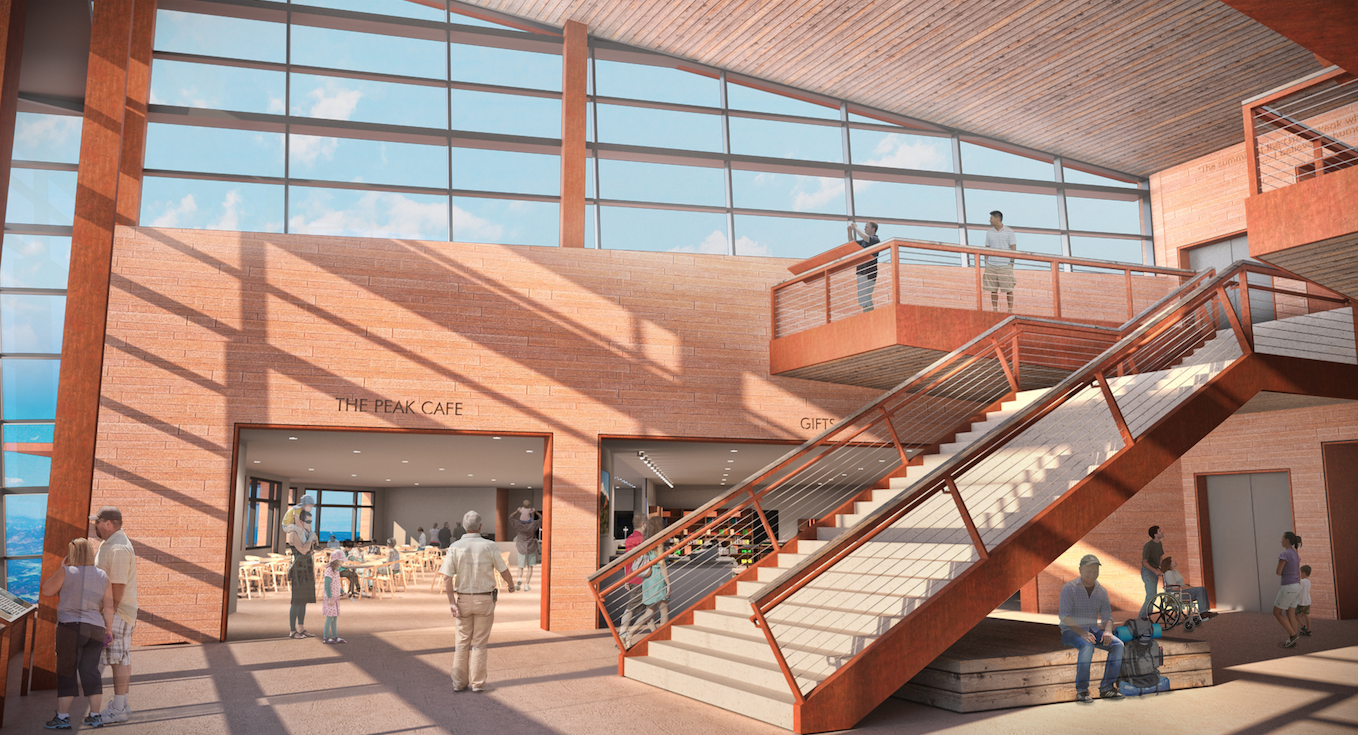

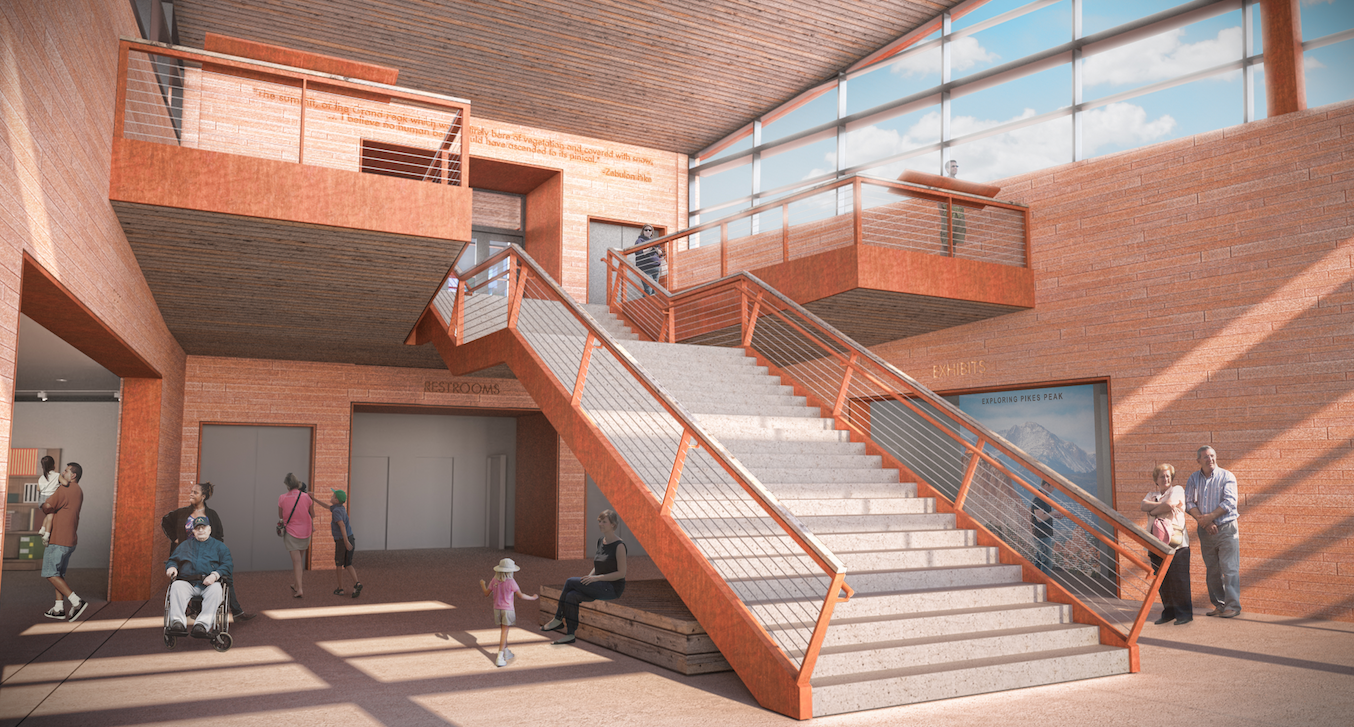
Inside, visitors are taken aback by the boundless sky and perfectly framed views of Mt. Rosa. Stairs to the main level appear to fold down out of the mountain as visitors descend to the main floor to access exhibits, dining, a gift shop and restrooms. Warm, rustic colors fortified by the ceiling’s beetle kill pine uniquely tie the interior to the region.
Those arriving via cog are given the choice to explore the Peak, interpret the ruins, or enter the Summit House via the main level. Providing access to these multiple destinations naturally disperses the crowds, resulting in a more enjoyable individual experience.
Captivating, but also functional, the building is sited to take advantage of the unique environmental conditions present on the top of Pikes Peak. Nestled into the mountain, exposure to the harsh winds is minimized, while the mass of the building provides sheltered outdoor areas from which to enjoy the views. The orientation of the building to the south takes full advantage of the enhanced solar gain at altitude, including daylight harvesting and the incorporation of photovoltaics to generate electricity. In addition, the thermal mass of the building’s stone cladding helps capture and radiate heat generated by the sun to the interior of the building. Other sustainable features include composting toilets and low flow fixtures to conserve water.
One of the many things that make Pikes Peak so special is that it is America’s Mountain—the only fourteener that everyone, no matter age or fitness level, can experience. As such, the design offers visitors the same pristine and untouched experience as those ascending other fourteeners while providing modern amenities and expanded interpretive opportunities, ultimately leaving visitors in awe and overwhelmingly satisfied with their experience.





Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Gold Award: Eisenhower Theater, Washington, D.C.
The Eisenhower Theater in the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts in Washington, D.C., opened in 1971. By the turn of the century, after three-plus decades of heavy use, the 1,142-seat box-within-a-box playhouse on the Potomac was starting to show its age. Poor lighting and tired, worn finishes created a gloomy atmosphere.
| Aug 11, 2010
Giants 300 University Report
University construction spending is 13% higher than a year ago—mostly for residence halls and infrastructure on public campuses—and is expected to slip less than 5% over the next two years. However, the value of starts dropped about 10% in recent months and will not return to the 2007–08 peak for about two years.
| Aug 11, 2010
Reaching For the Stars
The famed Griffith Observatory, located in the heart of the Hollywood hills, receives close to two million visitors every year and has appeared in such films as the classic “Rebel Without a Cause” and the not-so-classic “Charlie's Angels: Full Throttle.” Complete with a solar telescope and a 12-inch refracting telescope, multiple scientific exhibits, and one of the world...
| Aug 11, 2010
The Art of Reconstruction
The Old Patent Office Building in Washington, D.C., completed in 1867, houses two Smithsonian Institution museums—the National Portrait Gallery and the American Art Museum. Collections include portraits of all U.S. presidents, along with paintings, sculptures, prints, and drawings of numerous historic figures from American history, and the works of more than 7,000 American artists.
| Aug 11, 2010
Silver Award: Pere Marquette Depot Bay City, Mich.
For 38 years, the Pere Marquette Depot sat boarded up, broken down, and fire damaged. The Prairie-style building, with its distinctive orange iron-brick walls, was once the elegant Bay City, Mich., train station. The facility, which opened in 1904, served the Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad Company when the area was the epicenter of lumber processing for the shipbuilding and kit homebuilding ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Bowing to Tradition
As the home to Harvard's Hasty Pudding Theatricals—the oldest theatrical company in the nation—12 Holyoke Street had its share of opening nights. In April 2002, however, the Faculty of Arts and Sciences decided the 1888 Georgian Revival building no longer met the needs of the company and hired Boston-based architect Leers Weinzapfel Associates to design a more contemporary facility.
| Aug 11, 2010
Silver Award: Please Touch Museum at Memorial Hall Philadelphia, Pa.
Built in 1875 to serve as the art gallery for the Centennial International Exhibition in Fairmount Park, Memorial Hall stands as one of the great civic structures in Philadelphia. The neoclassical building, designed by Fairmount Park Commission engineer Hermann J. Schwarzmann, was one of the first buildings in America to be designed according to the principles of the Beaux Arts movement.
| Aug 11, 2010
Financial Wizardry Builds a Community
At 69 square miles, Vineland is New Jersey's largest city, at least in geographic area, and it has a rich history. It was established in 1861 as a planned community (well before there were such things) by the utopian Charles Landis. It was in Vineland that Dr. Thomas Welch found a way to preserve grape juice without fermenting it, creating a wine substitute for church use (the town was dry).
| Aug 11, 2010
Team Tames Impossible Site
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, the nation's oldest technology university, has long prided itself on its state-of-the-art design and engineering curriculum. Several years ago, to call attention to its equally estimable media and performing arts programs, RPI commissioned British architect Sir Nicholas Grimshaw to design the Curtis R.
| Aug 11, 2010
Silver Award: Hanna Theatre, Cleveland, Ohio
Between February 1921 and November 1922 five theaters opened along a short stretch of Euclid Avenue in downtown Cleveland, all of them presenting silent movies, legitimate theater, and vaudeville. During the Great Depression, several of the theaters in the unofficial “Playhouse Square” converted to movie theaters, but they all fell into a death spiral after World War II.







