During the Industrial Revolution, humans moved out of rural areas and into the cities, where it was easier to access factory jobs. This influx of people caused rapid and drastic changes in the way cities were designed. As ground space was eaten up, residential and commercial skyscrapers emerged as a way for builders to maximize their real estate.
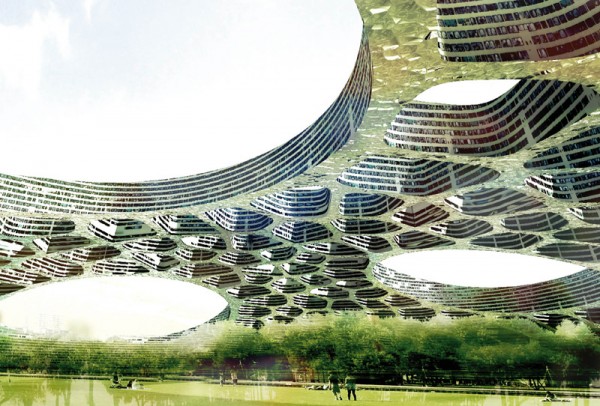
What would happen if, instead of building thousands of feet up into the sky, we developed a smarter design that allowed us to retain our connection to the natural world? That’s just the question a team of French designers hoped to answer with their “Flat Tower” design, a second place winner in the 2011 eVolo skyscraper competition.
Although the construction of skyscrapers has been an architectural solution for high-density urban areas for almost a century, it has also produced some rather negative side-effects: green spaces, trees, and in some cases, sunlight have become hard to find in big cities. Skyscrapers destroy the skyline, block out the sun, and disrupt the infrastructure of a specific location.
The Flat Tower design is based on a medium-height dome structure that covers a large area while preserving its beauty and previous function. The dome is perforated with cell-like skylights that provide direct sunlight to the agricultural fields and recreational spaces located inside.
“The dome’s large surface area is perfect to harvest solar energy and rainwater collection,” write the design team. “Community recreational facilities are located at ground level while the residential and office units are in the upper cells. An automated transportation system connects all the units, which are different shapes according to their program. It is also possible to combine clusters of cells to create larger areas for different activities.” BD+C
Related Stories
| Feb 1, 2012
New ways to work with wood
New products like cross-laminated timber are spurring interest in wood as a structural material.
| Feb 1, 2012
Blackney Hayes designs school for students with learning differences
The 63,500 sf building allows AIM to consolidate its previous two locations under one roof, with room to expand in the future.
| Feb 1, 2012
Two new research buildings dedicated at the University of South Carolina
The two buildings add 208,000 square feet of collaborative research space to the campus.
| Feb 1, 2012
List of Top 10 States for LEED Green Buildings released?
USGBC releases list of top U.S. states for LEED-certified projects in 2011.
| Feb 1, 2012
ULI and Greenprint Foundation create ULI Greenprint Center for Building Performance
Member-to-member information exchange measures energy use, carbon footprint of commercial portfolios.
| Feb 1, 2012
AEC mergers and acquisitions up in 2011, expected to surge in 2012
Morrissey Goodale tracked 171 domestic M&A deals, representing a 12.5% increase over 2010 and a return to levels not seen since 2007.
| Jan 31, 2012
AIA CONTINUING EDUCATION: Reroofing primer, in-depth advice from the experts
Earn 1.0 AIA/CES learning units by studying this article and successfully completing the online exam.
| Jan 31, 2012
28th Annual Reconstruction Awards: Modern day reconstruction plays out
A savvy Building Team reconstructs a Boston landmark into a multiuse masterpiece for Suffolk University.
| Jan 31, 2012
Chapman Construction/Design: ‘Sustainability is part of everything we do’
Chapman Construction/Design builds a working culture around sustainability—for its clients, and for its employees.
| Jan 31, 2012
Fusion Facilities: 8 reasons to consolidate multiple functions under one roof
‘Fusing’ multiple functions into a single building can make it greater than the sum of its parts. The first in a series on the design and construction of university facilities.