As recently as 2008, Duke University’s East Campus steam plant was an overgrown ruin. The former coal-burning plant had been shuttered for more than 30 years, it was covered in vines, and its roof had turned into a forest. Plant roots tore away at the 80-year-old brick façade, in some cases boring right through the 30-inch-thick walls, cracking them and shifting them out of plane and causing massive damage.
Despite these problems, the university saw value in repurposing the historic facility, and in June 2008, an $18.9 million sustainable renovation began that transformed the 6,341-sf building into a modern, efficient natural gas-burning steam facility. Duke engaged the Building Team of SmithGroup (architect), RMF Engineering (MEP), and Balfour Beatty (GC) to tackle the project, which is seeking LEED Gold.
The plant’s defunct coal-burning equipment was replaced by 15 energy-efficient Miura boilers, specifically chosen because their modular nature allowed them to be squeezed into the existing space better than traditional fire-tube and water-tube boilers. Even so, the Building Team had to construct a mezzanine to allow the new boilers to be stacked vertically. The Miura boilers produce steam much faster than traditional boilers, with a cold-to-steaming rate of less than five minutes, which reduces energy loss associated with startup, purge, and warm-up cycles. The boilers also have a factory-installed feedwater economizer that minimizes waste heat through the flue gas, increasing boiler efficiency by about 5%.
To further increase efficiency, the Building Team incorporated a blowdown heat recovery system that aids water savings by eliminating use of cooling water to temper the blowdown before it enters the sewer system. The coal-to-gas conversion helped Duke reduce its coal consumption by 70%. The facility itself operates 33% more efficiently than a baseline building.
As for the crumbling plant itself, the Building Team took on the restoration of the 1928 facility, which was designed by Horace Trumbauer, the architect behind numerous buildings on the Duke University campus.
Damage caused by years of neglect was remedied by rebuilding areas where masonry couldn’t be repaired, then cleaning and repointing brick that could be saved. A new cast-in-place roof deck was installed, along with a high-albedo, single-ply roof membrane. The building’s existing steel windows could not be salvaged, so they were replaced with new steel units that matched the profile of the originals. Low-e glazing was used on windows in the plant’s conditioned spaces; these same spaces were also insulated for greater efficiency. An old railroad trestle, which at one time brought coal cars up to the roof of the steam plant, was restored and the existing rooftop steel coal shed was rebuilt with corrugated fiberglass panels; now the coal shed glows at night.
In total, the Building Team was able to reuse 90% of the existing facility and diverted 85% of construction waste from landfills, a strong indication of the Building Team’s concerted effort to reuse or repurpose as much existing material as possible. For example, the original coal chutes were reused as part of the plant’s ventilation system; an old deaerator tank was put to use as a rainwater storage tank (rainwater is used within the plant to flush toilets); and old valves and wood floor decking were used to build benches for the terrace. Items that weren’t reused were donated to campus and community arts groups.
The project’s imaginative reuse of old elements and the careful addition of new ones caught the attention of our Reconstruction Awards judges. “It’s so carefully thought out,” said Walker Johnson, principal of Chicago-based Johnson Lasky Architects and honorary chair of the awards panel. “It’s absolutely one of the most unique projects,” said Darlene Ebel, Director of Facility Information Management at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
Summing up the judges’ reaction, George Tuhowski, Director of Sustainability for Leopardo Construction, Hoffman Estates, Ill., said: “They maintained a university icon. It’s functional, but it’s also a showpiece.” BD+C
PROJECT SUMMARY
Building Team
Submitting firm: SmithGroup (architect)
Owner: Duke University
CM: Balfour Beatty
MEP: RMF Engineering
General Information
Size: 6,341 gsf
Construction cost: $18.91 million
Construction time: June 2008 to July 2010
Delivery method: CM at risk
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 35 Veterans Affairs Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
LEO A DALY, Page Southerland Page, Guidon, and HDR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest Veterans Affairs facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 40 Military Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
Michael Baker International, HDR, Whitman, Requardt & Associates, and Stantec top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest military facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Office Buildings | Dec 12, 2023
Transforming workplaces for employee mental health
Lauren Elliott, Director of Interior Design, Design Collaborative, shares practical tips and strategies for workplace renovation that prioritizes employee mental health.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 150 Local Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HOK, Stantec, and Skidmore, Owings & Merrill top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest local government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 90 State Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Page Southerland Page, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Stantec, and NORR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest state government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Codes and Standards | Dec 11, 2023
Washington state tries new approach to phase out fossil fuels in new construction
After pausing a heat pump mandate earlier this year after a federal court overturned Berkeley, Calif.’s ban on gas appliances in new buildings, Washington state enacted a new code provision that seems poised to achieve the same goal.
Green | Dec 11, 2023
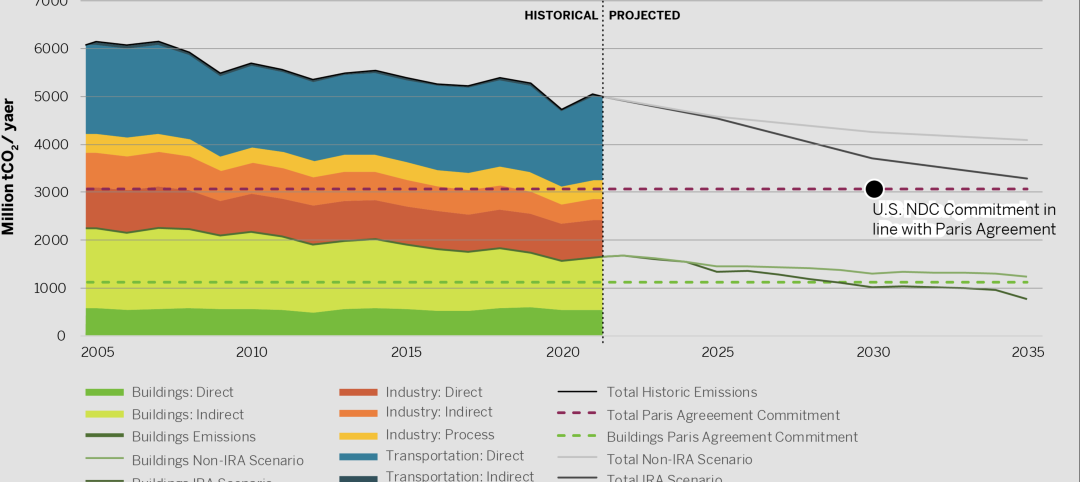
U.S. has tools to meet commercial building sector decarbonization goals early
The U.S. has the tools to reduce commercial building-related emissions to reach target goals in 2029, earlier than what it committed to when it signed the Paris Agreement, according to a report by the U.S. Green Building Council.
MFPRO+ News | Dec 11, 2023
U.S. poorly prepared to house growing number of older adults
The U.S. is ill-prepared to provide adequate housing for the growing ranks of older people, according to a report from Harvard University’s Joint Center for Housing Studies. Over the next decade, the U.S. population older than 75 will increase by 45%, growing from 17 million to nearly 25 million, with many expected to struggle financially.
Office Buildings | Dec 11, 2023
Believe it or not, there could be a shortage of office space in the years ahead
With work-from-home firmly established, many real estate analysts predict a dramatic reduction in office space leasing and plummeting property values. But the high-end of the office segment might actually be headed for a shortage, according to real estate intelligence company CoStar Group.
University Buildings | Dec 8, 2023
Yale University breaks ground on nation's largest Living Building student housing complex
A groundbreaking on Oct. 11 kicked off a project aiming to construct the largest Living Building Challenge-certified residence on a university campus. The Living Village, a 45,000 sf home for Yale University Divinity School graduate students, “will make an ecological statement about the need to build in harmony with the natural world while training students to become ‘apostles of the environment’,” according to Bruner/Cott, which is leading the design team that includes Höweler + Yoon Architecture and Andropogon Associates.