|
Healthcare construction spending grew at a compound rate of more than 10% for seven years through mid-2008, but has stalled since then. The stall, however, still represents better growth than almost any other construction market during the recession, which deepened as a result of the fall 2008 credit freeze.
During the stall, hospital construction spending increased 9% from the period before the credit freeze, while spending for nursing homes and other residential care facilities dropped 20% and spending for specialized medical office buildings fell 17%. Hospital construction spending is projected to remain steady through 2010, rising only as a result of higher project costs.
Hospital managers are enjoying a steadily rising revenue stream from patient care, but offsetting that are concerns about possible cuts in fees from states for “free care” and cuts in Medicaid and Medicare. As a precaution, some projects have been trimmed back or deferred.
The recent slowing trend for medical offices and residential care buildings parallels trends in other developed financed sectors, although the slowdown began later and so far has been less severe. Some developers lost credit access because of weakened income and balance sheets. Others lost credit access because lenders are concerned about cash flow coming from new capacity in a depressed economy. Bank examiners have also been steering regional and local lenders away from nonresidential mortgages. As a result, those two small commercial healthcare sectors will continue to decline, along with other commercial properties, through the winter. Following that, they will decline further because spending for other commercial properties will have begun to expand and projects in the pipeline will have fallen substantially.
Look for healthcare construction spending to return to a 10% annual growth pace in 2011, reflective of the usual cyclical surge after a recession. The rebound for hospital construction spending results from delayed stimulus plan funding and the resumption of work that was put on hold while healthcare was debated in Washington. —Jim Haughey, BD+C economist
Related Stories
Products and Materials | Jul 31, 2023
Top building products for July 2023
BD+C Editors break down 15 of the top building products this month, from cleanroom doors to window storm protection systems.
Mass Timber | Jul 11, 2023
5 solutions to acoustic issues in mass timber buildings
For all its advantages, mass timber also has a less-heralded quality: its acoustic challenges. Exposed wood ceilings and floors have led to issues with excessive noise. Mass timber experts offer practical solutions to the top five acoustic issues in mass timber buildings.
Building Materials | Jun 14, 2023
Construction input prices fall 0.6% in May 2023
Construction input prices fell 0.6% in May compared to the previous month, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Producer Price Index data released today. Nonresidential construction input prices declined 0.5% for the month.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Jun 5, 2023
27 important questions about façade leakage
Walter P Moore’s Darek Brandt discusses the key questions building owners and property managers should be asking to determine the health of their building's façade.
Multifamily Housing | Apr 27, 2023
Watch: Specifying materials in multifamily housing projects
A trio of multifamily housing experts discusses trends in materials in their latest developments. Topics include the need to balance aesthetics and durability, the advantages of textured materials, and the benefits of biophilia.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
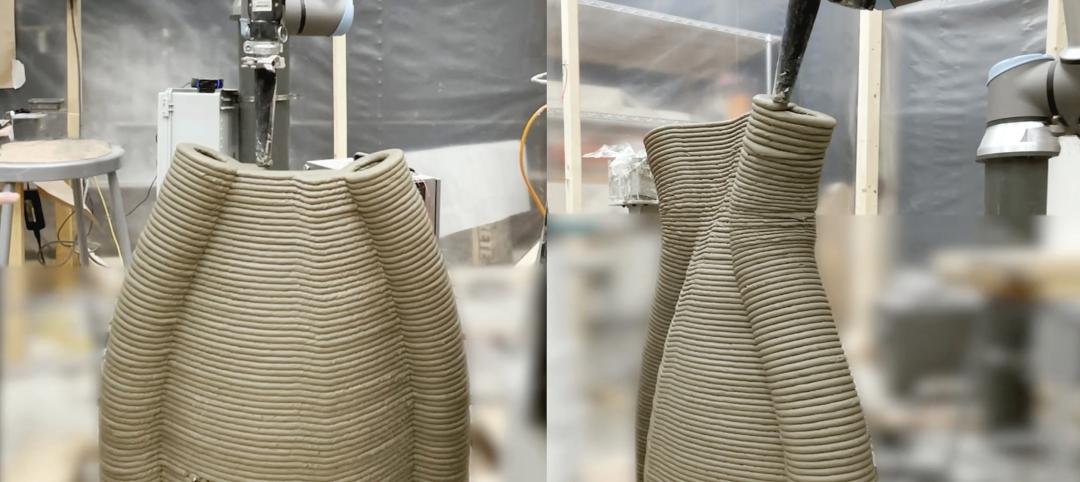
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Apr 5, 2023
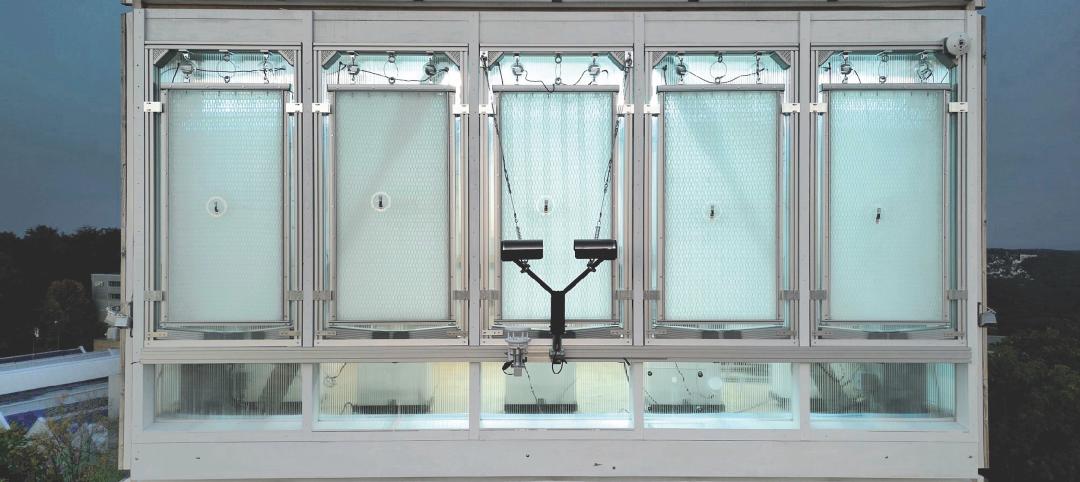
Façade innovation: University of Stuttgart tests a ‘saturated building skin’ for lessening heat islands
HydroSKIN is a façade made with textiles that stores rainwater and uses it later to cool hot building exteriors. The façade innovation consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator.
Windows and Doors | Apr 4, 2023
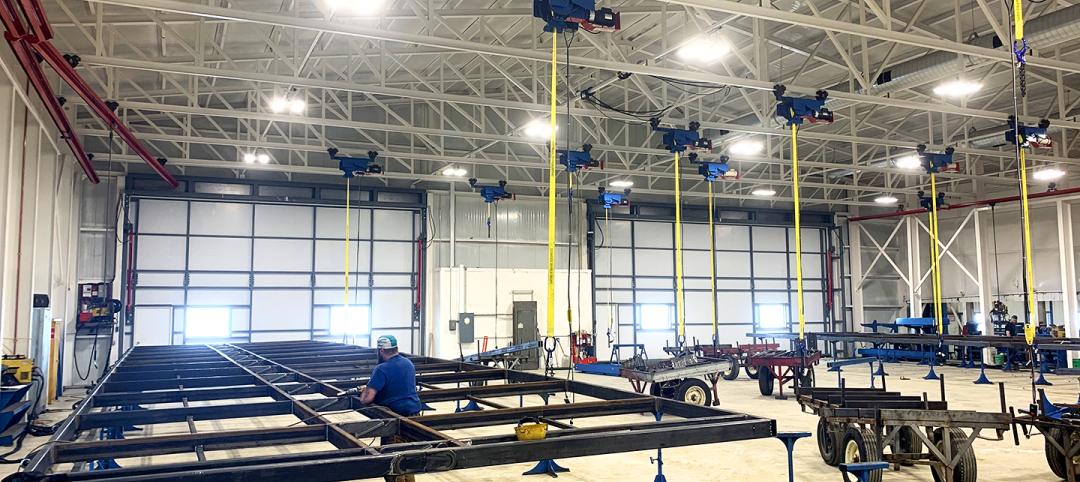
Schweiss Doors erects manufacturing building to showcase new doors
Schweiss Doors, the premier manufacturer of hydraulic and bifold liftstrap doors, erected a new manufacturing facility which will also serve as a showcase for the company’s new “free-standing” header frames.
Windows and Doors | Mar 5, 2023
2022 North American Fenestration Standard released
The 2022 edition of AAMA/WDMA/CSA 101/I.S.2/A440, “North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for windows, doors, and skylights” (NAFS) has been published. The updated 2022 standard replaces the 2017 edition, part of a continued evolution of the standard to improve harmonization across North America, according to a news release.
AEC Innovators | Mar 3, 2023
Meet BD+C's 2023 AEC Innovators
More than ever, AEC firms and their suppliers are wedding innovation with corporate responsibility. How they are addressing climate change usually gets the headlines. But as the following articles in our AEC Innovators package chronicle, companies are attempting to make an impact as well on the integrity of their supply chains, the reduction of construction waste, and answering calls for more affordable housing and homeless shelters. As often as not, these companies are partnering with municipalities and nonprofit interest groups to help guide their production.