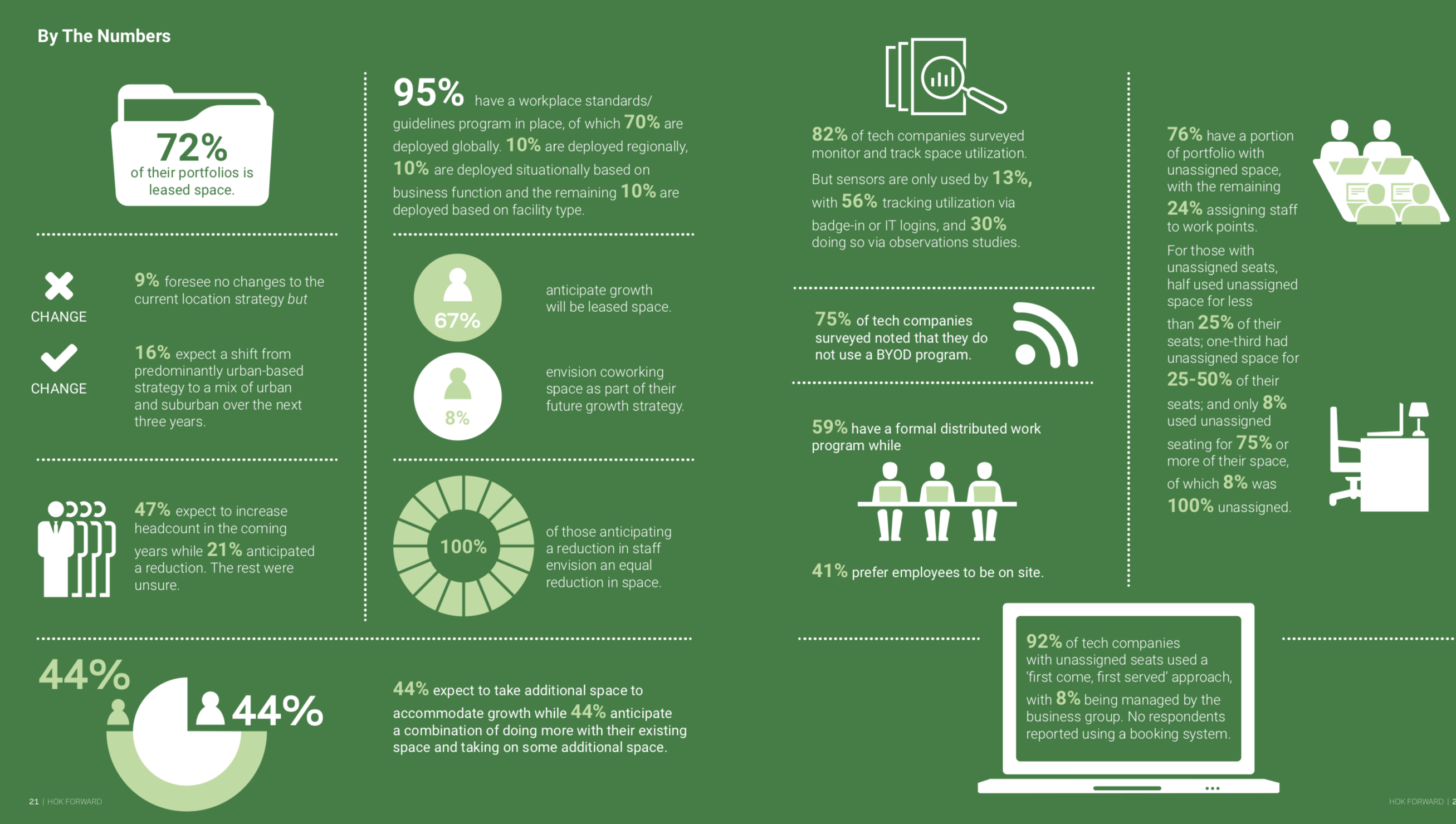
How are leading tech firm responding to their workplace challenges? That’s a question that HOK, the global design firm, examines in “HOK Forward: Tech Workplace Takes Center Stage,” an 83-page report based on input from the firm’s Workplace leadership and global delivery network partners.
As part of its research to identify best practices, HOK’s team interviewed a who’s who of end-user tech companies, including Cisco Systems, Google, IBM, Microsoft, Nokia, Spotify USA, and T-Mobile.
One of the report’s observations is that tech is now all-pervasive in the workplace. “We are quickly evolving toward an era in which tech is not just a discrete sector but a foundational element of all businesses,” the report states. ”More and more companies are considering themselves ‘tech’ companies regardless of the sector they are in.”
The report notes that as tech companies expand into traditional industries, they often have a competitive advantage because they fall outside the purview of state and federal regulations. However, that regulatory climate is changing, as options for nascent technologies are defined and sometimes restricted, and bigness is no longer seen as an unassailable virtue.
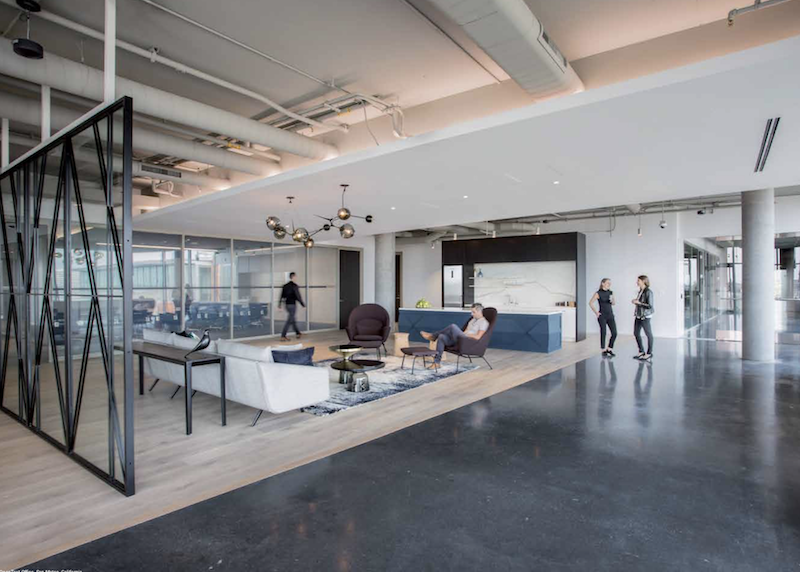
The HOK report, based on input from the firm's Workplace leadership and global delivery partners, portrays a tech industry that is weighing all kinds of factors that might enhance the user experience. (Click for larger image) Image: HOK Forward report
There is also the question of whether technology is, inadvertently, accelerating the expected obsolescence of businesses. Globally, the average life expectancy of a company is less than 20 years. Up to 80% of today’s businesses may not exist in 10 years, states the report.
On top of—or, perhaps, because of—that churn, nearly half of all global employers are struggling to fill positions. Consequently, Tech employers are enticing professionals to join their organizations from other sectors. “To ensure that their people remain valuable, productive and engaged, tech employers must adopt retraining and redeployment strategies,” the report states.
In this high growth sector, HOK’s survey portrays an industry whose companies tend to lease in urban environments. These companies continue to increase their headcounts, but envision accommodating more people within their existing footprint before deciding to expand. More than two-fifths (43%) of companies polled prefer to have employees on-site, and are designing their environments to encourage synergy, ideation, and speed to market.

The right mix of amenities is critical to creating a workplace that foments innovation and productivity. Image: HOK Forward report
The cost of real estate—the cost per sf for tech office space ranges from $80 to $300, and averages around $190—and time spent at the office continue to be the most important factors influencing workspace allocation. These companies’ top priorities include enhancing the employee experience and creating flexible spaces.
While tech companies insist that they value sustainable design, 87% said they wouldn’t seek formal LEED certification for their workplaces, and—here’s a stunner—92% did not intend to seek formal WELL certification for workplace wellness.
That being said, amenities are evolving: Companies looking to attract and retain top talent now offer everything from nap pods and wellness rooms to medical clinics and maker spaces.
“Smart“ workspaces, tracked by networks of sensors, are increasing, too, as designers and clients continue to learn how to leverage data in order to optimize and right-size space that reflects the company’s culture, work style, mobility profiles, and business goals.
The report provides a wealth of case studies that illustrate many of its findings. It also offers readers a list of “priority actions” that revolve around flexibility, employment empowerment, training, and “leveraging the contingent workforce.”
The report predicts that the next generation of high-performance tech workplaces will function as engagement centers and dynamic hubs where people gather, connect and innovate.
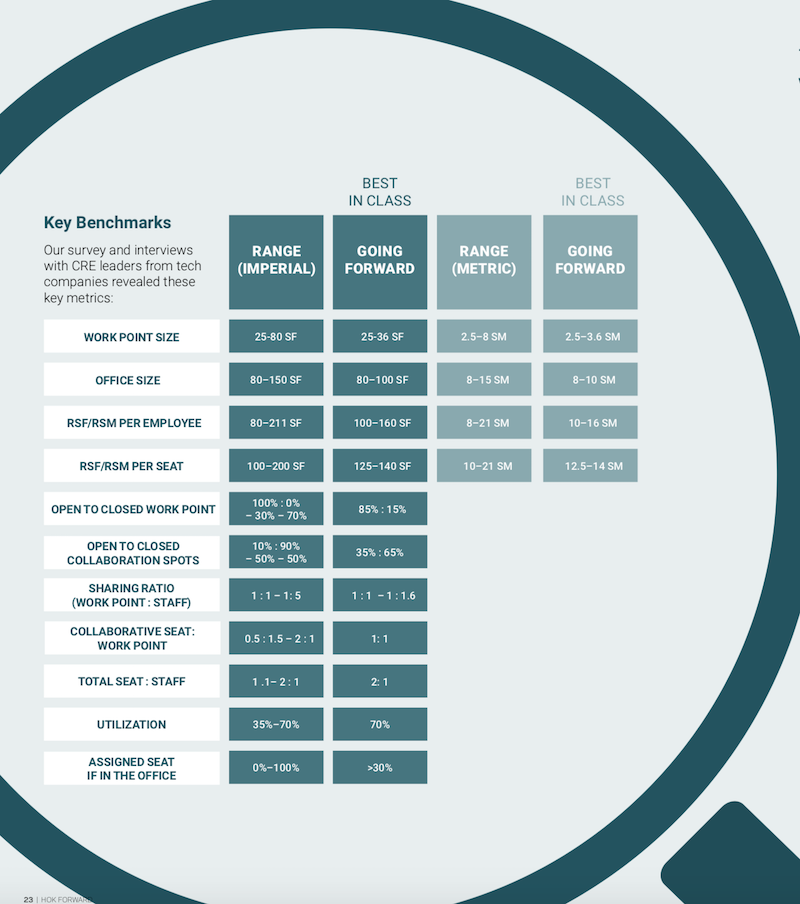
Some of the key office metrics, gleaned from interviews with leading tech companies. Image: HOK Forward report
“By focusing on human-centric metrics and thinking outside the box, we can create resilient tech workplaces that adapt to whatever the future may bring. We need to design this next- generation workspace with courage if we want to keep pace and truly transform the work experience.”
The report recommends 10 “focus areas” for growth-minded tech companies. They must create a “curated” workplace that emphasize innovation, amenities, and occupant wellbeing, which includes giving workers greater control over their work environments.
Companies should also be looking beyond sustainability—and toward net-zero energy and water, biophilia, and human health. They should also be using sensors more to gather data in order to track employee patterns and preferences.
HOK’s report advocates that companies rethink the suburban campus of the past and move toward a “new urban model” that emphasizes “blended, mixed-use environments that are revitalizing urban zones and catering to neo-urbanites.
The conundrum of this recommendation, however, is that building offices in urban centers is challenging and expensive. In addition, while the population migration to cities is “unprecedented,” a big portion of the middle class—“the bedrock of a city’s workforce,” acknowledges the report—continues to relocate to the suburbs, “posing additional challenges for urban locations that aspire to serve as thriving work centers.”
Related Stories
| Feb 12, 2013
OMA's 'perimeter core' design wins competition for Essence Financial Building in Shenzhen
OMA partners David Gianotten and Rem Koolhaas rethink traditional office tower design with a plan that shifts the building's core to the edge for large, unobstructed plans.
| Feb 8, 2013
5 factors to consider when designing a shade system
Designing a shade system is more complex than picking out basic white venetian blinds. Here are five elements to consider when designing an interior shade system.
| Feb 6, 2013
RSMeans cost comparisons: office buildings and medical offices
RSMeans' February 2013 Cost Comparison Report breaks down the average construction costs per square foot for four types of office buildings across 25 metro markets.
| Feb 1, 2013
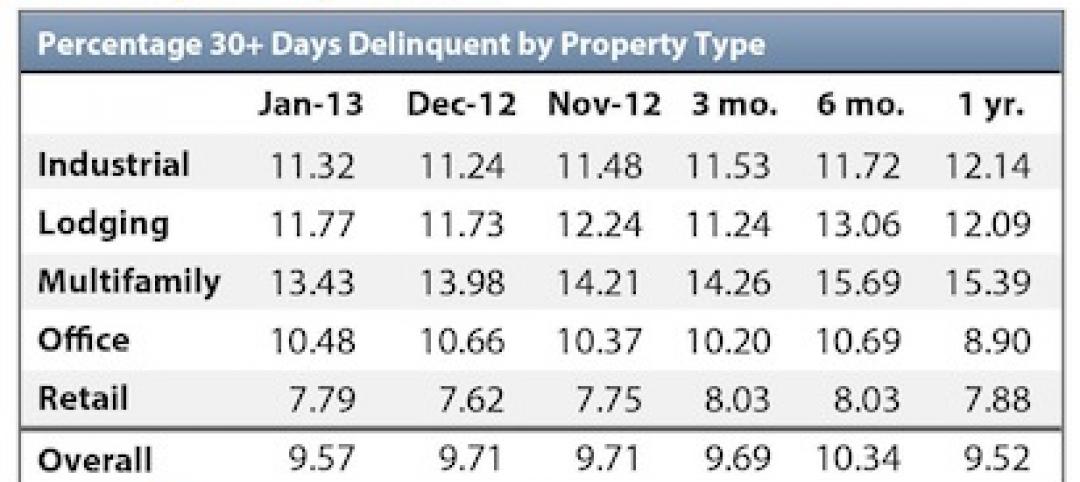
Delinquency rate for U.S. commercial real estate loans hits 11-month low
The delinquency rate for U.S. commercial real estate loans in CMBS fell 14 basis points in January to 9.57%. This is the lowest level in 11 months, according to Trepp, LLC's latest U.S. CMBS Delinquency Report.
| Jan 31, 2013
The Opus Group completes construction of corporate HQ for Church & Dwight Co.
The Opus Group announced today the completion of construction on a new 250,000-square-foot corporate headquarter campus for Church & Dwight Co., Inc., in Ewing Township, near Princeton, N.J.
| Jan 31, 2013
More cities requiring large buildings to use EPA’s energy management and reporting
In 2012, Philadelphia joined several other U.S. cities in passing a requirement that large buildings use Portfolio Manager, the Environmental Protection Agency’s energy management tool, to measure and report energy performance.
| Jan 29, 2013
Astellas' New Headquarters for the Americas Earns LEED Gold Certification
The new headquarters for Astellas in the Americas in Northbrook, Ill., has been awarded LEED Gold certification by the USGBC.
| Jan 16, 2013
SOM’s innovative Zhengzhou Greenland Plaza opens
The 2.59-million-square-feet building houses a mixed-use program of offices on its lower floors and a 416-room hotel.
| Dec 9, 2012
The owner’s perspective: high-rise buildings
Douglas Durst on the practicalities of development: “You must think about a building from the inside out.”