Finding true north is just as essential for project teams and capital projects as it is for personal journeys and accurate navigation. Ask any surveyor. They will tell you that true north by definition is not magnetic North. To find true north from a magnetic compass you have to know the local magnetic variation and how it has varied over time. If you want to get from a point at the bottom of a map to one at the top, you must head true north.
Metaphorically, true north refers to one’s direction in life, as we are often uncertain where we stand, where we are going, and what is the right path for us personally. Knowing our true north enables us to follow the right path.
The same holds true for the life of a healthcare project. Most healthcare projects can take four to five years or more to come to fruition when you account for the time vested in pre- and post-construction. Because healthcare projects take years to implement and given the size of the teams involved, developing a "true north charter" is essential for a healthcare capital project in order to keep the entire team on track and moving in the right direction.
Defining a true north for a capital project takes time and effort, but can yield great benefits and the impact can be transformational. By communicating a shared vision and mission between the client, the project team, and the project, a true north charter can help inspire.
The charter outlines the required conditions of satisfaction that should be strategic, operational, and project specific in nature. The charter should also assign measurable goals to help the team track and assess their achievements through the life of the project. The underlying benefit of defining a true north charter is developing team dynamics built on trust, accountability, transparency, respect, and collaboration.
FINDING BALANCE IN CHOPPY WATERS
Navigating the capital planning and implementation process was much easier when the economy was humming. There was adequate access to funding, and the key driver for planning was volume. However, the healthcare industry has been rapidly evolving under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and a soft economy. Healthcare reform has compelled health systems, hospitals, and physician groups to reduce costs and improve the quality of care-all with more regulatory requirements and less capital.
Changes to reimbursement methods, along with reductions in healthcare provider compensation, are forcing health systems to rethink their approach to balancing their assets and liabilities, including health care real estate. These factors, particularly when combined with a projected increase in demand for ~79 million aging baby boomers and ~30 million newly insured patients, has operators and owners of real estate repositioning portfolio requirements.
SETTING VISION AND MISSION
Finding true north in these choppy waters requires a keen sense of the market and a strong sense of the institution’s purpose. This starts with the mission and vision of the organization. While all health institutions exist to serve the community, the current market has forced many organizations to focus their efforts on meeting the greatest needs and offers specialization only when the market can support it financially.
A comprehensive strategic plan should highlight the organization’s vision, mission, and key areas of focus and be the baseline navigational tool for the institution and any capital spending. The true north for a capital project is then guided by the organization’s vision and mission statements, and further developed into a tangible project mission statement, guiding principles, target metrics, and target future state operations.
One Midwest health system’s vision and mission states:
“Our mission is to improve the health of the communities we serve through quality health care, education and research. Our vision is to be the best for those who need us. We value safety, compassion, respect and integrity.”
A sample of a project mission statement that could accompany such a corporate mission statement could be: “Through collaboration, team integration, and best practices, the project team endeavors to provide the expanded and improved facility within the owner’s schedule, efficiency, and budget goals while providing high levels of quality, safety, and team satisfaction. By delivering the XYZ Health System New Tower Project, the project team will meet the expectations set by the Health System board, administration, caregivers, support staff, and community through our innovation, collaboration, and professionalism."
STAYING ON TRACK
While the preceding project mission statement provides a framework for positive motivation and influence, it does not deliver the tangible metrics needed to offer feedback to the project team or client to know if the project is on the right path or that the desired outcomes have been achieved. In order to provide continuous feedback and help steer towards the projects "true north," goals must be tangible and measurable.
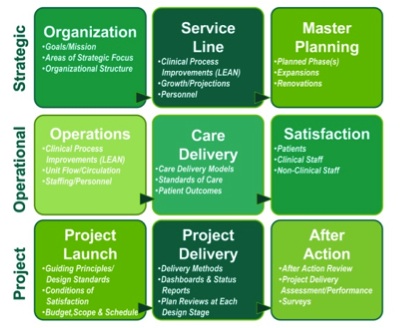
Guiding principles or goals should address the organization’s strategic and operational goals of the project, as well as the project-specific goals that address team performance. Each specific goal can then be supported by a tactic that can be mapped, tested, and monitored through specific key performance indicators, or KPIs. Prior to construction, KPIs for each tactic should be captured to establish baseline data in order for progress reports and post-occupancy data to be available for feedback and for comparison to future state.
Example strategic goal areas
- Increase Market Share
- Accommodate Private Bed Model
- Invest in New Model of Care
- Invest in Infrastructure to Decrease Operational Costs
Example Operational Goal Areas
- Maximize Staff Efficiency
- Improve Occupancy Efficiency by 15% (throughput)
- Reduce Cycle Times by 10%
- Reduce Medical Errors
- Increase Patient Satisfaction Scores
- Increase Flexibility of the Space
Example Project Goal Areas
- Safety During Construction
- Schedule Adherence
- Quality Product
- Cost Control
- Community Relationships
- Communication and Commitments
- Team Behavior and Relationships
ACHIEVING TRUE NORTH
Perhaps the greatest benefit to setting a capital project’s true north is the ability to provide feedback. It helps build trust for the project team, creates accountability, provides transparency, affords respect, and encourages collaboration for the entire team. Two reporting tools used to inform leadership and project teams on the success in navigating toward true north are the project status report (PSR) and the after action review (AAR).
The PSR, as its name suggests, provides an overview of your project’s trajectory. More than a reporting mechanism, the PSR should be a management tool that aides the team in achieving the established KPIs.
While many KPIs are tangible and measurable, others related to team dynamics and communication which may only be measured through a survey.
Still, other outcomes can only be measured post-occupancy. The AAR is a structured debrief process and knowledge management tool that provides accountability and insight. Perhaps the greatest benefit of the AAR is the lessons learned that can be applied to future work, teams, and processes. The AAR is developed by the entire project team after project completion. It captures true-north desired outcomes, measurable goals, tactics, and pre-construction metrics in order to summarize the capital project’s process, work products and post construction results.
CONCLUSION
Regardless of the terminology used, be sure to invest time in identifying the direction and process that will deliver the desired results for your project. By following the old adage of “plan your work and work your plan,” your project team will set the foundation to follow true north and ultimately achieve success. And in the process, you will find the underlying benefit of continual improvement.
About the Authors
Steve Higgs is Managing Director and Lora Schwartz is Principal Consultant with CBRE Healthcare.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
SAFTI FIRST hires Tim Nass as National Sales Manager
SAFTI FIRST, a leading USA manufacturer of fire rated glazing and framing systems, is pleased to announce the addition of Tim Nass as National Sales Manager. In his new role, Tim will be working closely with architects and contract glaziers in selecting the appropriate and most economical fire rated glazing solution for their project. He will also be coordinating SAFTI FIRST’s extensive network of architectural representatives throughout the United States.
| Aug 11, 2010
NCARB welcomes new board of directors
The National Council of Architectural Registration Boards (NCARB) introduces its Board of Directors for FY10, who were installed during the culmination of the Council’s 90th Annual Meeting and Conference in Chicago.
| Aug 11, 2010
Berkebile wins $100K award for commitment to environment
Robert Berkebile, the founding principal of BNIM Architects and a founding member of the U.S. Green Building Council, has been selected to receive a $100,000 Heinz Award. The award honors his role in promoting green building design and for his commitment and action toward restoring social, economic, and environmental vitality to America’s communities through sustainable architecture and planning.
| Aug 11, 2010
Polshek Partnership unveils design for University of North Texas business building
New York-based architect Polshek Partnership today unveiled its design scheme for the $70 million Business Leadership Building at the University of North Texas in Denton. Designed to provide UNT’s 5,400-plus business majors the highest level of academic instruction and professional training, the 180,000-sf facility will include an open atrium, an internet café, and numerous study and tutoring rooms—all designed to help develop a spirit of collaboration and team-oriented focus.
| Aug 11, 2010
University of Florida aiming for nation’s first LEED Platinum parking garage
If all goes as planned, the University of Florida’s new $20 million Southwest Parking Garage Complex in Gainesville will soon become the first parking facility in the country to earn LEED Platinum status. Designed by the Boca Raton office of PGAL to meet criteria for the highest LEED certification category, the garage complex includes a six-level, 313,000-sf parking garage (927 spaces) and an attached, 10,000-sf, two-story transportation and parking services office building.
| Aug 11, 2010
Draft NIST report on Cowboys practice facility collapse released for public comment
A fabric-covered, steel frame practice facility owned by the National Football League’s Dallas Cowboys collapsed under wind loads significantly less than those required under applicable design standards, according to a report released today for public comment by the Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
| Aug 11, 2010
Callison, MulvannyG2 among nation's largest retail design firms, according to BD+C's Giants 300 report
A ranking of the Top 75 Retail Design Firms based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants