For all the hoopla about the ecommerce boom and “last mile” order fulfillment driving demand for more warehouse and manufacturing space, construction of industrial buildings actually declined over the past five years, albeit marginally by 2.1% to $27.3 billion in 2022, according to estimates by IBIS World. Still, construction in this sector remains buzzy: Last May, JLL reported that developers had delivered 90 million sf of new building inventory in the first quarter of this year, with another 531 million sf under construction. Logistics, distribution, and ecommerce accounted for one-fifth of the total leased square footage.
The AEC Industrial Sector Giants that BD+C contacted for this article reported increases in their sector business last year. RC Andersen, a division of STO Building Group, had its highest-producing year to date in 2021, boasts Neil Ascione, its President. Ryan Companies’ industrial sector business was up 40%, says Todd Schell, the firm’s Executive Vice President–Industrial. And Alston Construction’s work in place in this sector has risen by more than 25% year-over-year for the past five years, says Paul D. Little, Alston’s CEO.
Parenthetically, design and construction aren’t the only revenue generators in this sector. Dallas-based Austin Industries reported more than $931 million in industrial sector revenue last year, 55% of that firm’s total. The firm’s spokesman, Bill Maselunas, elaborates that most of its industrial revenue derived from maintenance contracts with Gulf Coast-based petrochemical companies.
Some AEC firms wonder if demand for industrial buildings might be ebbing. Ryan Companies—which, over the years has completed 430 industrial projects in almost every state—expects its business to be flat this year. And in the first half of 2022, RC Andersen’s industrial revenue was down from a comparable period a year ago. Ascione attributes this slide to his firm currently working on smaller buildings, with a higher percentage of them being built speculatively by developers.
That industrial developers are going smaller is borne out by one of Ware Malcomb’s recently completed projects, for which it provided architecture, design, and civil engineering services to Panattoni Development on a 23-acre site in Oshawa, Ontario, that includes two buildings totaling 58,600 sf, according to the firm’s Principal Frank Di Roma. This trend, though, is hardly conclusive, as that same developer retained Ware Malcomb for a 308,500-sf facility on 14 acres in Mississauga, Ontario.
Purpose defines industrial building design
Among the design considerations for industrial buildings, Di Roma singles out larger truck courts (up to 135 feet), more parking, and amenities that attract workers. Everyone is fielding requests for higher ceiling clearances, some up to 64 feet, says Danial Peddicord, Senior Vice President for Pepper Construction. Schell of Ryan Companies says some industrial buildings are designed to accommodate automated material handling cranes that reach up 150 feet, as well as automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) that go as high as 100 feet.

Schell asserts that a “critical factor” in industrial design “is understanding the business operating inside the building: what product is being built, moved, or stored? How quickly? This can guide how big and tall the building needs to be, as well as the equipment used to operate it.” What separates one project from another, says RC Andersen’s Ascione, is how the site is used: “Where can you maximize trailer parking, what size building can fit between setbacks and buffers, etc.? And the most important thing is to consider the needs of every tenant.”
Site conditions can’t be minimized. “A site may appear to be nearly perfect, but combined with the size of the building foundation, truck access, parking, trailer storage, etc., extraordinary means may be necessary to facilitate proper stormwater control,” explains Dave Knudson, Executive Vice President–Operations with Choate Construction. “It is not uncommon for client teams to create alternative plans, schedules, and cost models that evaluate surface retention/water quality treatment versus subterranean water drainage/filtration systems,” he adds.
ALSO SEE: 2022 INDUSTRIAL SECTOR GIANTS:
• Top 95 Industrial Facility Architecture and AE Firms
• Top 90 Industrial Facility Engineering and EA Firms
• Top 110 Industrial Facility Contractors and CM Firms
Right now, a major roadblock to any industrial project is supply chain delays. Peddicord notes that in most cases, his firm has between eight and 10 months to secure materials and meet an established delivery date. That’s challenging when materials such as precast, steel, and roofing are enduring critical long lead times, and cement and aggregate are scarce. “This has led to the need to secure trade partners much earlier in the process,” he says.
Delays and shortages are causing some clients to postpone design, so “scheduling has become more important than ever,” says Gregory Brogley, PE, PMP, the architecture and engineering firm SSOE Group’s Senior Vice President and Strategic Business Unit Manager–Automotive and Manufacturing Facilities Northern Operations. SSOE has explored what Brogley calls “alternate and innovative” engineering solutions that are “based on what is available within the supply chain.”
Building automation maximizes operations in warehouses, industrial buildings
Industrial sector experts agree that there’s been a steady uptick in automation within industrial buildings. “A lot of our work is for clients who use fully automated sort and robotics systems, and material handling equipment,” says Eric Nay, Executive Vice President with Layton Construction, another STO Building Group company. Pepper Construction’s Peddicord thinks that robotics is only a year or two away from being seen as a standard trend for the industrial sector.

Alston Construction’s Little says clients like Amazon, Target, Proctor & Gamble, and other large retailers with significant distribution capacities are finding ways to automate and make their processes more efficient, and to fill gaps created by labor shortages. He cautions, however, that while automation works well when things are operating with precision, “you still need human labor where there’s nuances, such as when a pallet wasn’t wrapped correctly.”
Brogley notes that his firm’s Mexico operations have been involved with distribution centers that are designed to include an ASRS option, and manufacturing plants with building management systems that facility managers can operate using a smartphone or tablet. One of SSOE’s recent projects—a 24,250-sm automotive electronic components manufacturing plant and office building in Aguascalientes, Mexico, for Continental AG—has a complex BMS that Brogley says “auto balances” and operates the facility’s HVAC system within a small temperature and humidity range.
Ventilation is more important to industrial projects, as developers pay closer attention to meeting employee comfort expectations. “Prioritization for ventilation in industrial facilities has progressed in substantial ways,” says Choate Construction’s Knudson. “In addition to delivering cleaner, safer air, emphasis is growing on ventilation systems that protect assets and investments from environmental factors. And when you stop to consider the increasing warehouse ceiling height, ventilation systems are getting more dynamic—going beyond simply cooling and heating functions.”
Choate has seen a shift toward circulation instead of exhaust using high-volume, low-speed (HVLS) and ZOO fans that circulate and mix air, and regulate temperatures within the building. Knudson adds that fresh-air ventilation helps dissipate buildup and avoid “sweating slab syndrome” during the spring and fall months.
Multistory warehouses are still the exception
RC Andersen’s Ascione notes that as industrial buildings have gotten taller, code minimums for ventilation have adjusted. He explains that where one-eighth of an air exchange per hour is the code minimum for a 40-foot-high building, future provisions are being prepared to accommodate one or two air exchange per hour.
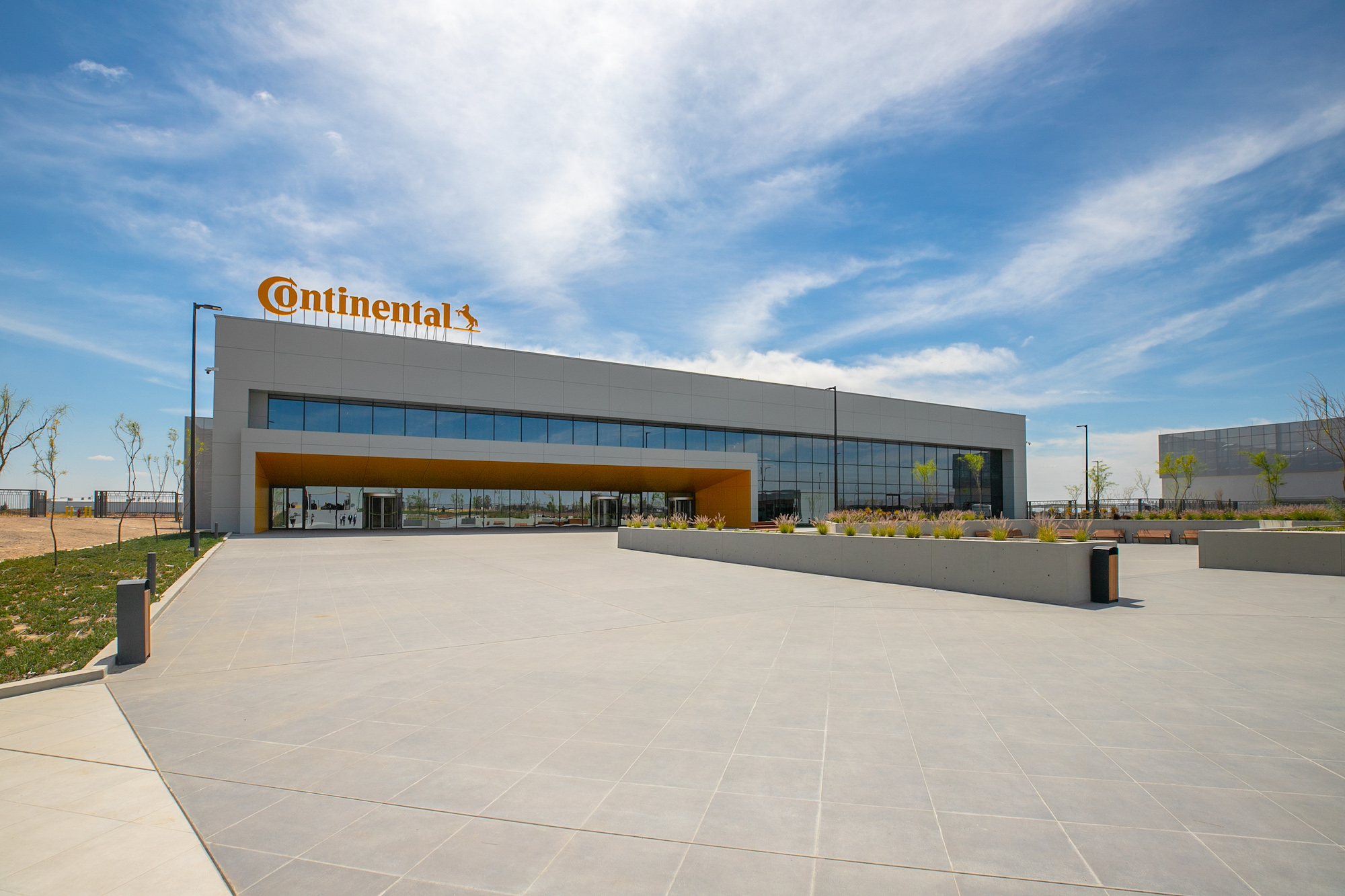

Ventilation codes must also adapt to multistory industrial buildings, even as AEC firms observe that demand for this typology is sporadic and mostly coastal. Ascione is seeing more demand for multistory industrial buildings “in our core markets,” although that choice increases construction costs substantially. Schell of Ryan Companies says multistory demand remains confined to dense urban areas where land availability leaves little other option.
One AEC firm that seems more enthusiastic about multistory industrial is Ware Malcomb, which developed its first design prototype in 2017. Di Roma says demand now extends beyond the East Coast to across the U.S. His firm has completed two multistory projects, in Vancouver, British Columbia, and in New York. It has four other projects under construction, six going through entitlements, and over 150 multistory site studies and test fits.
Di Roma says Ware Malcomb has also seen an increased demand for net-zero energy buildings, as sustainability in nonresidential design and construction has reached out to the industrial sector. “Some of our team members say they’ve been involved in more LEED projects in the past eight to 12 months than in the last eight years combined,” says Pepper Construction’s Peddicord. He adds that spec developers that are targeting Fortune 500 companies as tenants are more likely to invest in sustainability.
This trend isn’t surprising, given that more AEC firms and developers are making pledges to factor climate change into their projects. SSOE, for one, recently signed AIA 2030 and Science Based Target Initiative commitment letters that, says Brogley, “signify the important role and responsibility of the AEC industry to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.”
Ascione says his firm’s industrial clients have been moving in this direction cautiously, with a focus on electric vehicles and embodied carbon. Choate’s Knudson notes, too, that investments in sustainability allow developers to promote their industrial buildings as healthier workplaces, which since the onset of the coronavirus pandemic “became a big selling point for attracting and retaining talent.”
Related Stories
Industrial Facilities | Oct 18, 2018
Tesla purchases 210 acres in Shanghai with plans to build Gigafactory 3
Construction is expected to begin soon.
Building Automation | Jul 13, 2018
Katerra has plans for a new advanced manufacturing factory in California
The building components facility will be located near rail, shipping ports, and freeways.
Industrial Facilities | Jul 11, 2018
AEC firms tap into the boom in logistics center construction
A Ryan Companies project in southern California is being built to meet its city’s rigorous green standards.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 27, 2018
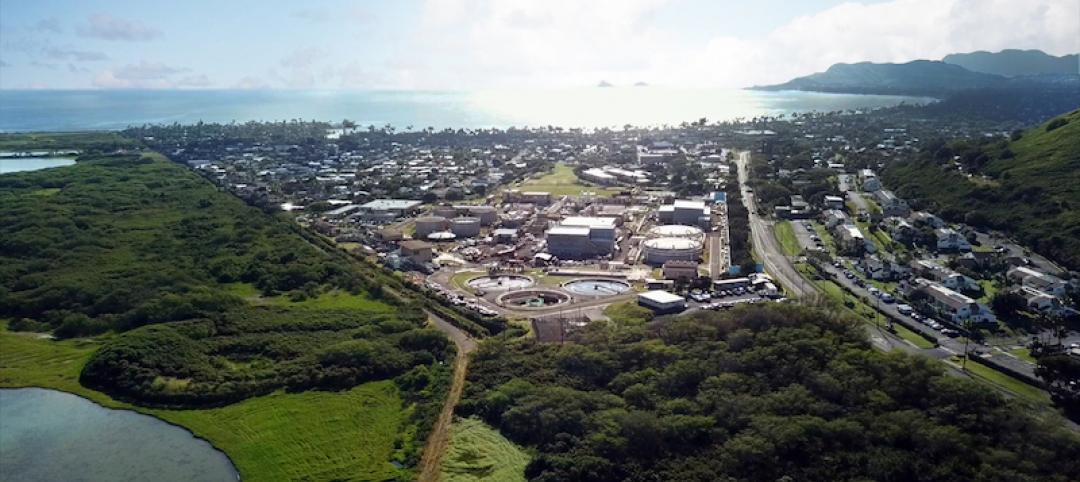
Hawaii announces completion of $375 million wastewater project
The new sewer tunnel and pump station help enhance Oahu’s utility infrastructure.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 25, 2018
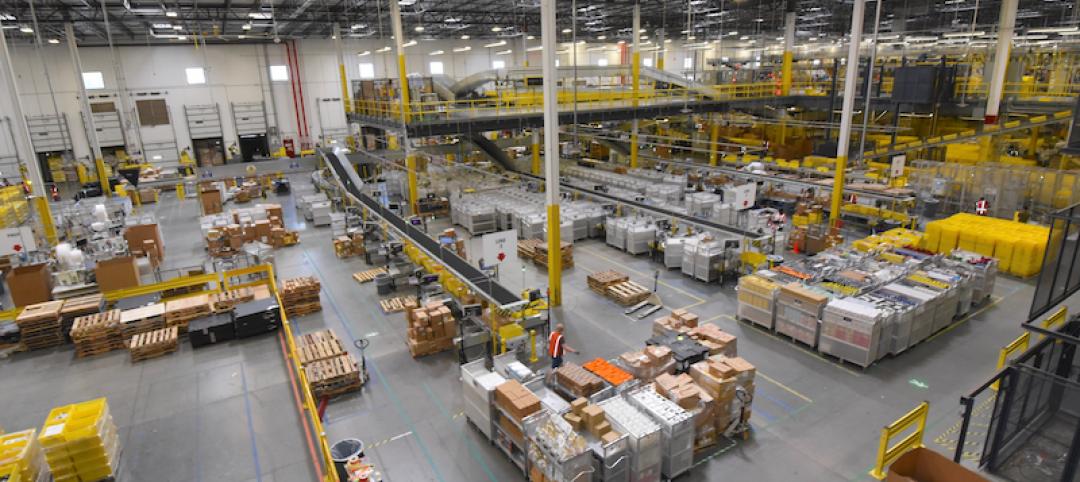
$150 million Amazon fulfillment center near Grand Rapids will be built on fast-paced 22-week schedule
The warehouse will be Amazon’s fourth in Michigan.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 15, 2018
Faraday Future selects GC for its 1 million-sf EV factory
Onsite construction has commenced in an effort to deliver the first FF91 by the year's end.
Market Data | Jun 12, 2018
Yardi Matrix report details industrial sector's strength
E-commerce and biopharmaceutical companies seeking space stoke record performances across key indicators.
Industrial Facilities | Apr 12, 2018
‘Next generation’ biomanufacturing plant will be the first of its kind in the U.S.
The plant will be located in Rhode Island.
Industrial Facilities | Apr 2, 2018
90,000-sf industrial facility will add needed manufacturing space in West Michigan
Vision Real Estate Investment recently broke ground on the building.
Industrial Facilities | Mar 26, 2018
thyssenkrupp’s new Zhongshan plant includes a high-speed test tower
The 813-foot test tower has 13 shafts.