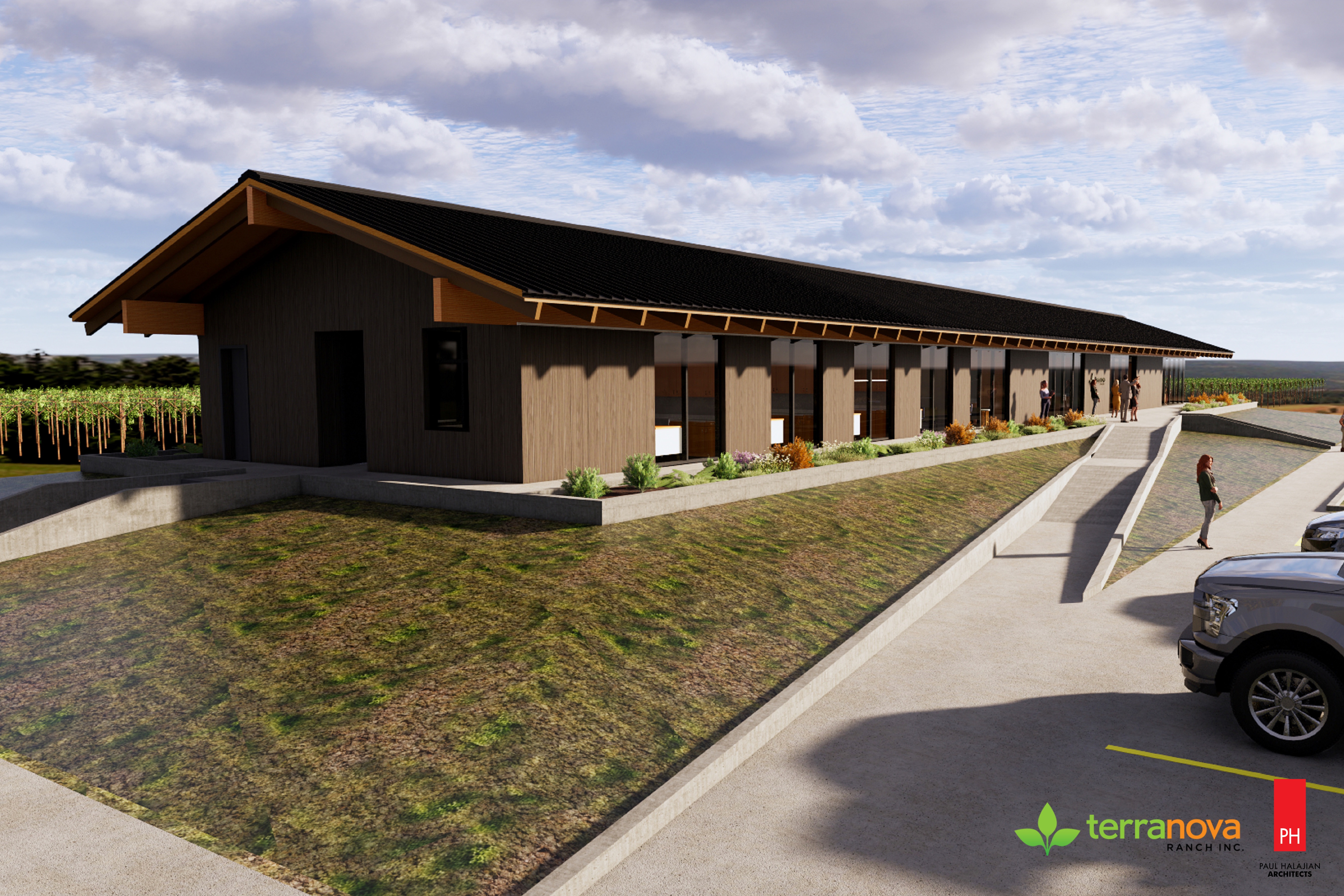
Terranova Ranch in Fresno, Calif., grows more than 25 different crops on 6,000 acres. The company, which started in 1981, has focused its attention lately on methods that keep its soil, water, and air quality as healthy and sustainable as possible.
The design for Terranova Ranch’s new office pavilion is the first net-zero carbon and net positive energy project by Paul Halajian Architects (PHA), and the client’s design choices were informed by the use of cove.tool’s web-based building performance app.
Terranova Ranch’s aimed for a 100 percent reduction in operational carbon emissions, and the architect provided several options toward meeting or exceeding that goal. (Cove.tool shared some of the details of this case study with BD+C.)
GOING BEYOND CODE MINIMUMS
Initially, the energy model for the 5,800-sf office building was designed to follow code minimum baseline assumptions from California’s Title 24, version 2019, which offered a carbon reduction of 12 percent. PHA’s project architect conducted several analyses on possible improvements to reduce the overall Energy Use Intensity (EUI), which in this model was 42.52 kBtu/sf/year.
These analyses measured the impacts of the building’s HVAC, lighting, equipment, hot water, fans, and pumps. The first proposed design change was an envelope upgrade, from the mandatory minimum of R-19 to R-30 by adding two inches of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam board to the exterior walls; and three inches of foam board insulation to the roof, which increased its R-value from 30 to 41. These changes would increase the building’s overall carbon reduction in base design to 20 percent and reduce the EUI to 38.
GLAZING’S BENEFITS DIDN’T PENCIL
The second option the architect investigated for Terranova Ranch combined the proposed envelope upgrade with improved glazing using Solarban 72 Acuity glass or Starphire glass with a u-value of 0.28 and solar heat coefficient of 0.28. (The baseline requirement is Solarban 60.) However, using cove.tool analysis tool, the architect determined that the whole-building EUI would have only reduced to 37, and only increased the carbon reduction by 2 percent from the first option. There were also cost considerations that made the glazing option less favorable.
The third upgrade option explored introduced 2,200 sf of monocrystalline solar panels, angled at a 15-degree incline atop a shaded parking structure. This option would reduce the building’s carbon emissions by 84 percent (from option No. 2’s 22 percent) and decrease the EUI to 7 form 37. Terranova Ranch was enthusiastic about this option.
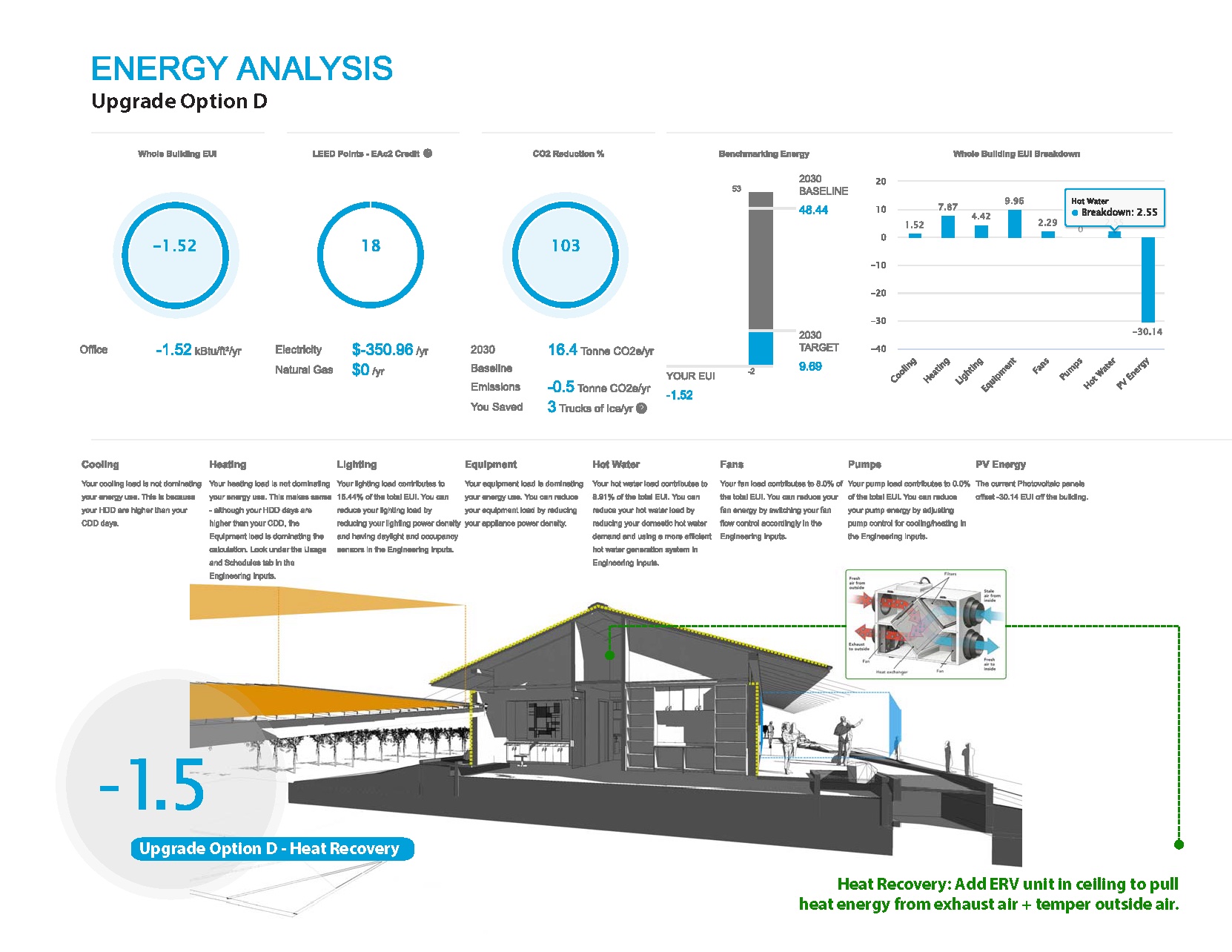
A fourth alternative explored introducing heat recovery by adding an energy recovery ventilator in the ceiling. This option allowed for a carbon reduction of 103 percent and an EUI score of negative 1.5. The client agreed to move forward in the building’s design with each option except the glazing upgrade.
SUNLIGHT EXPOSURE WILL REDUCE BUILDING’S LIGHTING NEEDS
Along with the energy study, the architect conducted other analyses. Using cove.tool software, the architect observed that 85 percent of the office building’s interior would have access to “quality exterior views,” which in turn would earn the product LEED Views Credit. A daylight analysis of the architect’s design also showed that the building would be exposed to up to 12 hours of sunlight per day, reducing the design’s artificial lighting requirement.
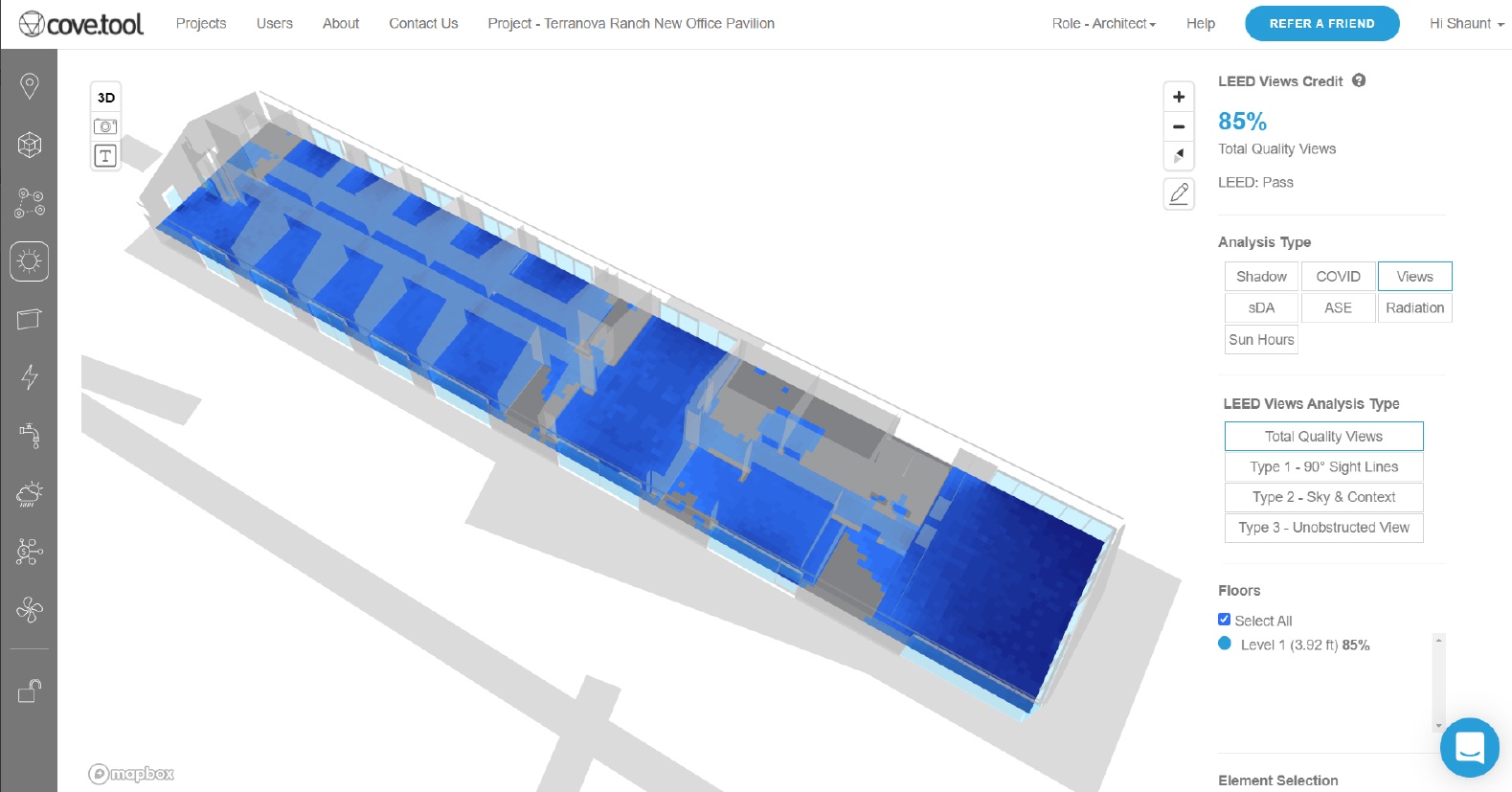
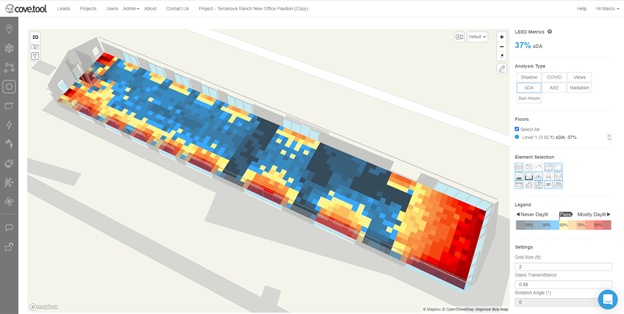
While most clients might not be as sustainably inclined as Terranova Ranch, conducting data-driven analyses can be fruitful as a common practice that allows the design team and client to delve into different design scenarios to achieve an intended performance goal.
Construction on the office pavilion was scheduled to begin in late spring. The architect and client did not disclose construction costs.
Related Stories
| Oct 18, 2010
World’s first zero-carbon city on track in Abu Dhabi
Masdar City, the world’s only zero-carbon city, is on track to be built in Abu Dhabi, with completion expected as early as 2020. Foster + Partners developed the $22 billion city’s master plan, with Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture, Aedas, and Lava Architects designing buildings for the project’s first phase, which is on track to be ready for occupancy by 2015.
| Oct 13, 2010
Editorial
The AEC industry shares a widespread obsession with the new. New is fresh. New is youthful. New is cool. But “old” or “slightly used” can be financially profitable and professionally rewarding, too.
| Oct 13, 2010
Prefab Trailblazer
The $137 million, 12-story, 500,000-sf Miami Valley Hospital cardiac center, Dayton, Ohio, is the first major hospital project in the U.S. to have made extensive use of prefabricated components in its design and construction.
| Oct 13, 2010
Campus building gives students a taste of the business world
William R. Hough Hall is the new home of the Warrington College of Business Administration at the University of Florida in Gainesville. The $17.6 million, 70,000-sf building gives students access to the latest technology, including a lab that simulates the stock exchange.
| Oct 13, 2010
Apartment complex will offer affordable green housing
Urban Housing Communities, KTGY Group, and the City of Big Bear Lake (Calif.) Improvement Agency are collaborating on The Crossings at Big Bear Lake, the first apartment complex in the city to offer residents affordable, eco-friendly homes. KTGY designed 28 two-bedroom, two-story townhomes and 14 three-bedroom, single-story flats, averaging 1,100 sf each.
| Oct 13, 2010
Residences bring students, faculty together in the Middle East
A new residence complex is in design for United Arab Emirates University in Al Ain, UAE, near Abu Dhabi. Plans for the 120-acre mixed-use development include 710 clustered townhomes and apartments for students and faculty and common areas for community activities.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community center under way in NYC seeks LEED Platinum
A curving, 550-foot-long glass arcade dubbed the “Wall of Light” is the standout architectural and sustainable feature of the Battery Park City Community Center, a 60,000-sf complex located in a two-tower residential Lower Manhattan complex. Hanrahan Meyers Architects designed the glass arcade to act as a passive energy system, bringing natural light into all interior spaces.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community college plans new campus building
Construction is moving along on Hudson County Community College’s North Hudson Campus Center in Union City, N.J. The seven-story, 92,000-sf building will be the first higher education facility in the city.
| Oct 13, 2010
Bookworms in Silver Spring getting new library
The residents of Silver Spring, Md., will soon have a new 112,000-sf library. The project is aiming for LEED Silver certification.
| Oct 13, 2010
County building aims for the sun, shade
The 187,032-sf East County Hall of Justice in Dublin, Calif., will be oriented to take advantage of daylighting, with exterior sunshades preventing unwanted heat gain and glare. The building is targeting LEED Silver. Strong horizontal massing helps both buildings better match their low-rise and residential neighbors.















