The 65th Street Lincoln Center pavilion in New York, a multi-use project housing Lincoln restaurant, the new Elinor Bunin Munroe Film Center, and the Laurie Tisch Illumination Lawn, has earned national recognition in the 2011 Innovative Design in Engineering and Architecture with Structural Steel awards program (IDEAS2).
In honor of this achievement, members of the project team will be presented with awards from the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) during a ceremony in the Hauser Patron Salon on the second floor of Lincoln Center's Alice Tully Hall, just across 65th Street from the pavilion, on Wednesday, November 9.
Conducted annually by AISC, the IDEAS2 awards recognize outstanding achievement in engineering and architecture on structural steel projects around the country. The IDEAS2 award is the highest, most prestigious honor bestowed on building projects by the structural steel industry in the U.S.
The project team members include owner Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts, New York; design architect and interior designer of the restaurant, Diller Scofidio + Renfro, New York; executive architect, FXFOWLE, New York; and architect and interior designer of the film center, Rockwell Group, New York; structural engineer Arup (AISC Member), New York; and general contractor Turner Construction Company (AISC Member), New York.
The 65th Street Lincoln Center pavilion is a National award winner in the category of projects $15 Million to $75 Million, making it one of only eight projects around the country to receive the National honor. Each year, the IDEAS2 awards honor National and Merit award winners in three categories, based on constructed value: projects less than $15 million; projects $15 million to $75 million; and projects greater than $75 million. Each project is judged on its use of structural steel, with an emphasis on creative solutions to project requirements; design innovation; aesthetic and visual impact of the project; innovative use of architecturally exposed structural steel; technical or architectural advances in the use of steel; the use of innovative design and construction methods; and sustainable design.
Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts is one of the largest and best-known arts complexes in the world, with 12 independent companies and 15 venues bringing a wide range of events to five million visitors per year. Over the past decade, the center has undertaken an ambitious modernization of its midcentury campus. The central design challenge: reactivating the connection between the 16-acre campus and its Manhattan neighborhood, increasing the visibility of resident organizations and drawing in new audiences.
One of the key architectural solutions to emerge from the modernization project is the new 65th Street Lincoln Center pavilion. Topped by a striking warped green roof and housing a glass-walled restaurant, the pavilion is a distinctive yet accessible urban form that fulfills complex programmatic requirements while maintaining much-needed public space on the campus.
In addition to creating an iconic shape that stands out among its rectilinear neighbors, the pavilion's unique geometry addresses a number of practical concerns. The lowest point of the structure brings the roof flush with the plaza, extending a friendly invitation onto the grass to both Lincoln Center patrons and casual passerby. The twisting planes tilt the 7,200-sf lawn away from 65th Street, reducing visitors' exposure to noise and traffic.
"This pavilion is a substantial element delicately inserted into an existing urban space," commented Robert Theel, AIA, regional chief architect and director, Design & Construction Division, General Services Administration Great Lakes Region, Chicago, and a judge in the competition.
The open, serene atmosphere is carried into the 11,000-sf restaurant, called Lincoln, which features an exposed central kitchen flanked by four public dining areas. Glass walls and a contoured mahogany ceiling frame views to the outside and draw the public's gaze inward. Accessible from both plaza and street level, Lincoln has been praised as one of the nation's best new restaurants since its September 2010 launch.
The simple, streamlined form of the pavilion gives no indication of the complex, densely packed facilities beneath. In addition to three new subterranean Lincoln Center Film Society theaters, the restaurant sits atop the central utility plant, which provides chilled water and stream to the entire campus.
The layout for the geometry of the pavilion's steel superstructure follows the mathematical principals and main generating lines of a rectilinear hypar. As a result, straight steel members were able to be used for all floor beams. Thoughtful rationalization of the architectural form and use of steel for the primary structure simplified fabrication and enabled rapid construction. The latter was particularly important due to Lincoln Center's need to remain open throughout the design and construction process. The design team and contractors exchanged 3D models, further easing fabrication and aiding interdisciplinary coordination.
Arup's structural design thoughtfully addresses the requirements of each programmatic element. Metal decking with concrete poured on top forms the warped floor structure. Columns at regular intervals transfer vertical loading into the existing building. An additional layer of transfer beams underneath the columns transfers vertical loading around the movie theaters and the central mechanical plant into existing footings. On one end, the lower tip of the hypar sockets into the existing waffle slab of the plaza, allowing the transfer of lateral loading into the existing shear diaphragm. On the opposing side, braced frames transfer horizontal loading into the ground.
Throughout the five-year design and construction period, the project team created and coordinated multiple document packages corresponding to the logistical challenges and sequencing of the work, consistently exercising a high level of oversight to minimize conflicts and mitigate unforeseen field conditions.
The new pavilion and improved facilities will enable Lincoln Center to continue providing world-class performances to local, national and international audiences for decades to come. With its unique space-generating structure, complex interface of new and old, and challenging logistical and scheduling requirements, the pavilion pushed New York City's design and building community to the boundaries of existing construction technologies.
The 14 IDEAS2 winners for 2011 were chosen from nearly 100 submissions received by architectural and engineering firms throughout the U.S. Each submission is reviewed and award winners are selected by a nationally recognized panel of design and construction industry professionals.
The IDEAS2 award dates back over 70 years to the earliest years of AISC's existence. Roger E. Ferch, P.E. president of AISC, said, "The entire 65th Street Lincoln Center pavilion project team has shown how structural steel can be used to create structures that combine beauty and practicality. The result is a pavilion that serves its patrons extremely well, while providing an example of what can be achieved when designing and constructing projects with steel." BD+C
Related Stories
| May 25, 2011
Developers push Manhattan office construction
Manhattan developers are planning the city's biggest decade of office construction since the 1980s, betting on rising demand for modern space even with tenants unsigned and the availability of financing more limited. More than 25 million sf of projects are under construction or may be built in the next nine years.
| May 25, 2011
Olympic site spurs green building movement in UK
London's environmentally friendly 2012 Olympic venues are fuelling a green building movement in Britain.
| May 25, 2011
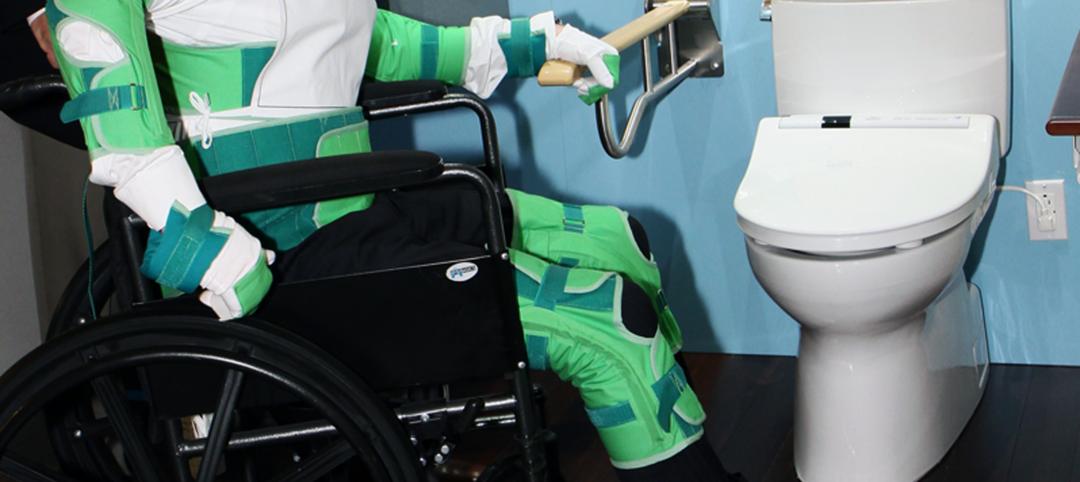
TOTO tests universal design at the AIA conference
If you could be 80 years old for 30 minutes—and have to readjust everything you think you know about your own mobility—would you do it?
| May 20, 2011
Hotels taking bath out of the bathroom
Bathtubs are disappearing from many hotels across the country as chains use the freed-up space to install ever more luxurious showers, according to a recent USAToday report. Of course, we reported on this move--and 6 other hospitality trends--back in 2006 in our special report "The Inn Things: Seven Radical New Trends in Hotel Design."
| May 19, 2011
BD+C’s "40 Under 40" winners for 2011
The 40 individuals profiled here are some of the brightest stars in the AEC universe—and they’re under the age of 40. These young architects, engineers, contractors, designers, and developers stood out among a group of 164 outstanding entrants in our sixth annual “40 Under 40” competition.
| May 18, 2011
Sanford E. Garner on the profitability of being diverse
Sanford E. Garner, AIA, NOMA, LEED AP ND, NCARB, founding partner and president of A2SO4 Architecture, LLC, Indianapolis, on gentrification, the profitability of being diverse, and his goals as NOMA president.
| May 18, 2011
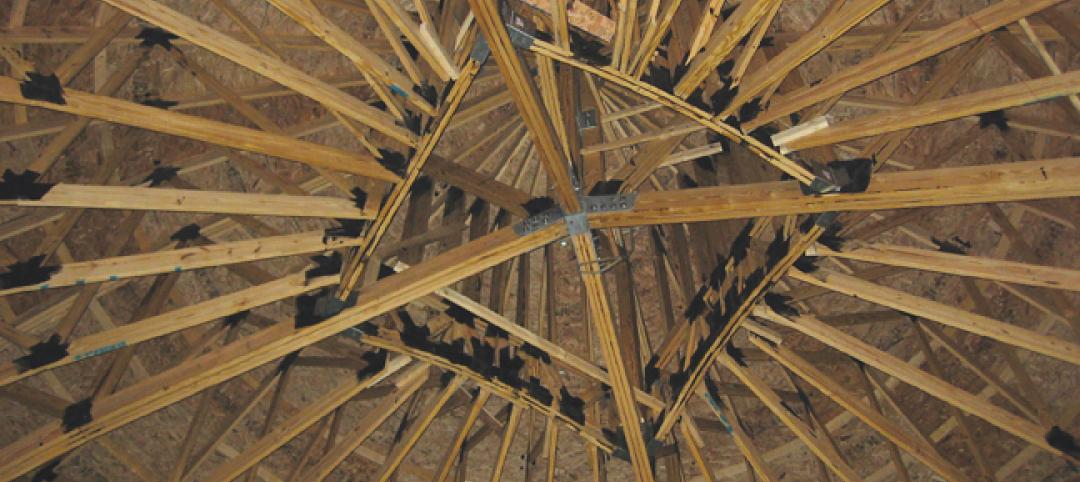
8 Tips for Designing Wood Trusses
Successful metal-plate-connected wood truss projects require careful attention to detail from Building Team members.
| May 18, 2011
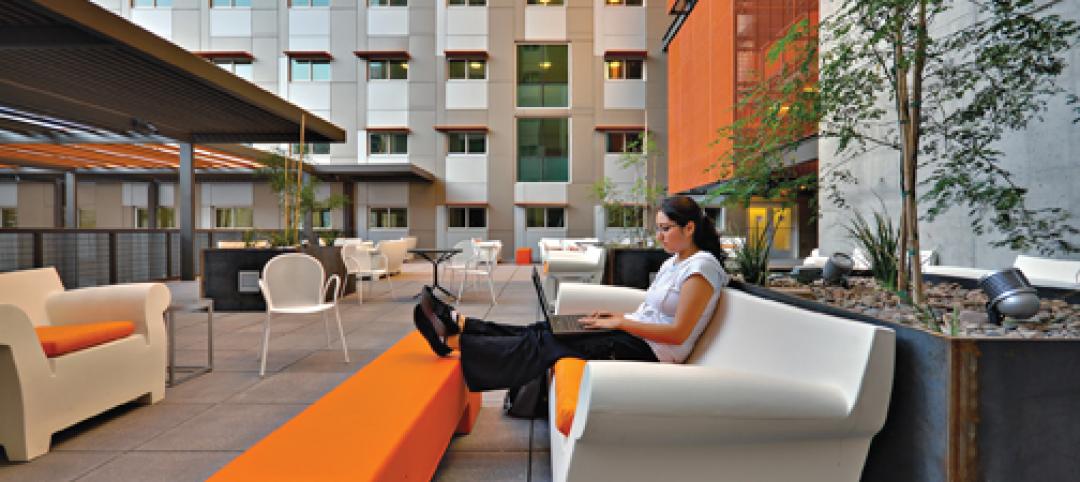
Major Trends in University Residence Halls
They’re not ‘dorms’ anymore. Today’s collegiate housing facilities are lively, state-of-the-art, and green—and a growing sector for Building Teams to explore.
| May 18, 2011
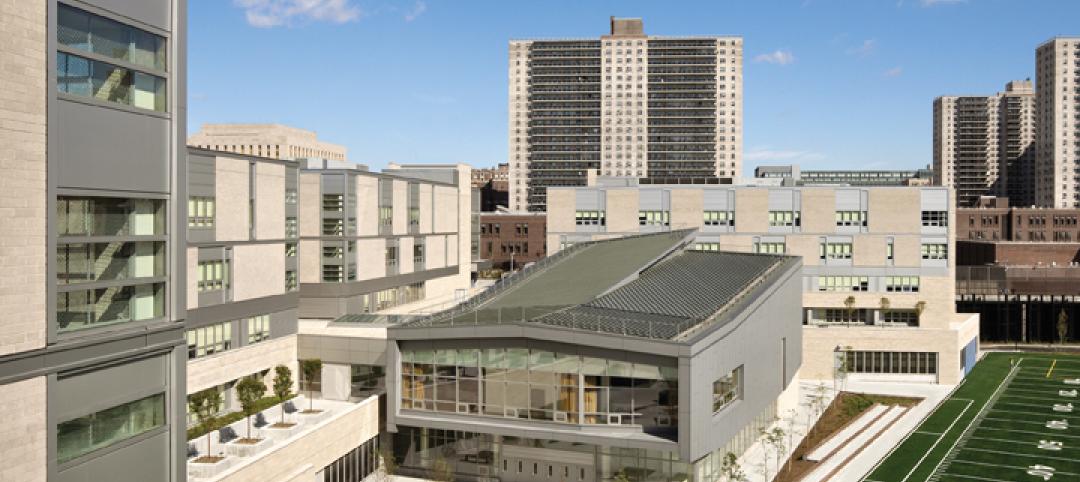
Former Bronx railyard redeveloped as shared education campus
Four schools find strength in numbers at the new 2,310-student Mott Haven Campus in New York City. The schools—three high schools and a K-4 elementary school—coexist on the 6.5-acre South Bronx campus, which was once a railyard.