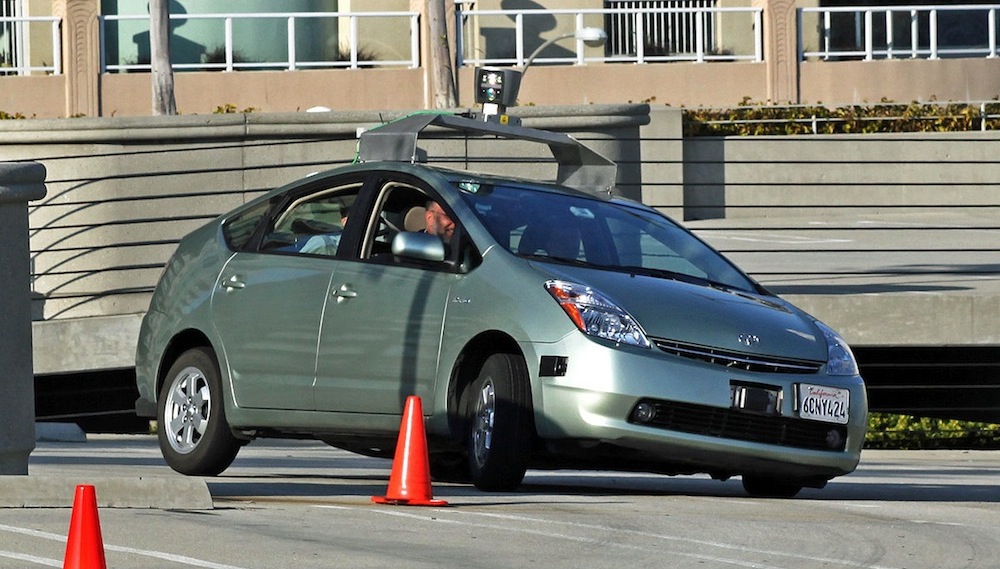
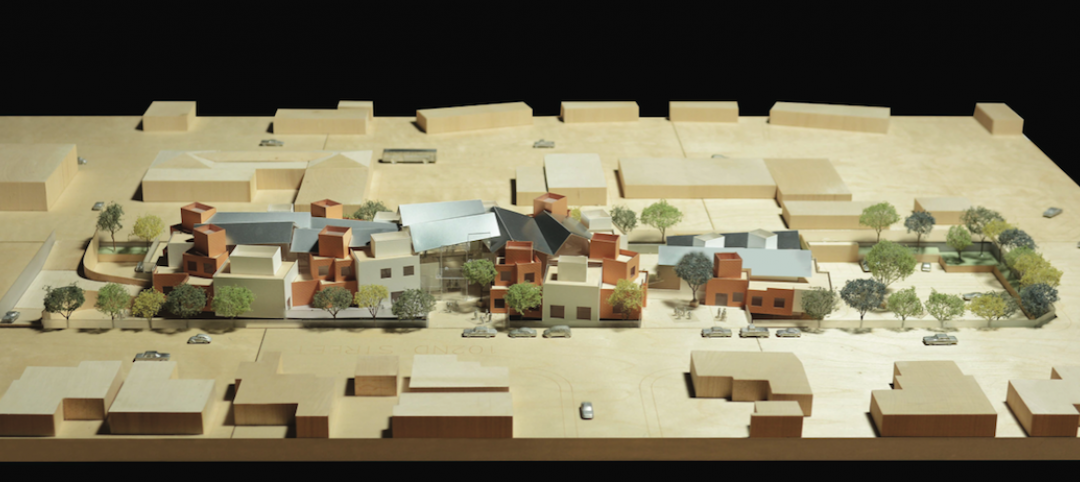
On July 20, the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor opened Mcity, a 32-acre simulated urban and suburban controlled environment, designed specifically to test the potential of connected and automated vehicle technologies.
The $6.5 million project comprises a five-mile stretch of roads, some of them up to five lanes. Mcity includes rearrangeable architecture such as buildings, streetlights, parked cars, traffic lights and stop signs, sidewalks, and other obstacles. Robotic pedestrians and mechanized bikes roam throughout Mcity.
The miniature city is developed and designed by the university’s two-year-old Interdisciplinary Mobility Transformation Center, a partnership of several automotive companies, the Michigan Department of Transportation, researchers from UM’s Transportation Research Institute, and its College of Engineering.
“The initiative demonstrates the great potential in working with partners outside the University to address compelling issues of broad impact,” said UM’s president Mark Schlissel. NPR reports that 15 companies, which include Ford, GM, and Nissan, paid $1 million each to help build Mcity.
Companies like Google, Toyota, Uber, and Apple have been working on self-driving technologies that rely on GPS, radar and remote sensors known as LIDAR. So far the test results have been impressive, albeit in a limited sense. Experts anticipate that driverless streets and highways could be a common reality within the next 10 to 15 years. The real challenge, though, is getting driverless cars to react to and interact with how humans drive.
Google, which began its self-driving project in 2009, currently averages 10,000 autonomous miles per week on public streets. Over six years of testing through May 2015, its driverless vehicles had been involved in 12 minor accidents during more than 1.8 million miles of autonomous and manual driving combined. “Not once was the self-driving car the cause of the accident,” claims Google in a recent progress report. However, Google’s test cars rarely go beyond 25 miles per hour and so far have been limited to roads the car’s computers have already analyzed.
As the New York Times reported earlier this month, autonomous vehicles right now are programmed to drive overly cautiously, compared with humans’ typically aggressive driving habits. Autonomous cars “have to learn to be aggressive in the right amount, and the right amount depends on the culture,” Donald Norman, director of the Design Lab and the University of California, San Diego was quoted as saying.
Mcity, then, provides a testing ground for driverless cars in unpredictable conditions.
“There are many challenges ahead as automated vehicles are increasingly deployed on real roadways,” explains Peter Sweatman, director of the U-M Mobility Transformation Center. “Mcity is a safe, controlled and realistic environment where we are going to figure out how the incredible potential of connected and automated vehicles can be realized quickly, efficiently and safely.”
NPR quotes university researchers who are hoping to have 20 to 30 automated cars driving around Ann Arbor’s streets within the next six years.
Related Stories
Market Data | Jan 20, 2016
Nonresidential building starts sag in 2015
CDM Research finds only a few positive signs among the leading sectors.
Architects | Jan 15, 2016
Best in Architecture: 18 projects named AIA Institute Honor Award winners
Morphosis' Perot Museum and Studio Gang's WMS Boathouse are among the projects to win AIA's highest honor for architecture.
| Jan 14, 2016
How to succeed with EIFS: exterior insulation and finish systems
This AIA CES Discovery course discusses the six elements of an EIFS wall assembly; common EIFS failures and how to prevent them; and EIFS and sustainability.
University Buildings | Sep 21, 2015
6 lessons in campus planning
For campus planning, focus typically falls on repairing the bricks and mortar without consideration of program priorities. Gensler's Pamela Delphenich offers helpful tips and advice.
Designers | Sep 21, 2015
Can STEAM power the disruptive change needed in education?
Companies need entrepreneurial and creative workers that possess critical thinking skills that allow them to function in collaborative teams. STEAM (science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics) education might be the solution.
Education Facilities | Sep 14, 2015
Gehry unveils plan for Children's Institute, Inc. campus in LA
The new facility, which will have rooms for counseling, afterschool activities, and youth programs, will allow CII to expand its services to 5,000 local children and families.
Mixed-Use | Aug 26, 2015
Innovation districts + tech clusters: How the ‘open innovation’ era is revitalizing urban cores
In the race for highly coveted tech companies and startups, cities, institutions, and developers are teaming to form innovation hot pockets.
University Buildings | Aug 13, 2015
Best of Education Design: 9 projects named AIA Education Facility Design Award winners
Georgia Tech's Clough Commons, Boston's Berklee Tower, and seven other facilities were honored for aiding learning and demonstrating excellent architectural design.
Giants 400 | Aug 7, 2015
K-12 SCHOOL SECTOR GIANTS: To succeed, school design must replicate real-world environments
Whether new or reconstructed, schools must meet new demands that emanate from the real world and rapidly adapt to different instructional and learning modes, according to BD+C's 2015 Giants 300 report.
Giants 400 | Aug 7, 2015
UNIVERSITY SECTOR GIANTS: Collaboration, creativity, technology—hallmarks of today’s campus facilities
At a time when competition for the cream of the student/faculty crop is intensifying, colleges and universities must recognize that students and parents are coming to expect an education environment that foments collaboration, according to BD+C's 2015 Giants 300 report.