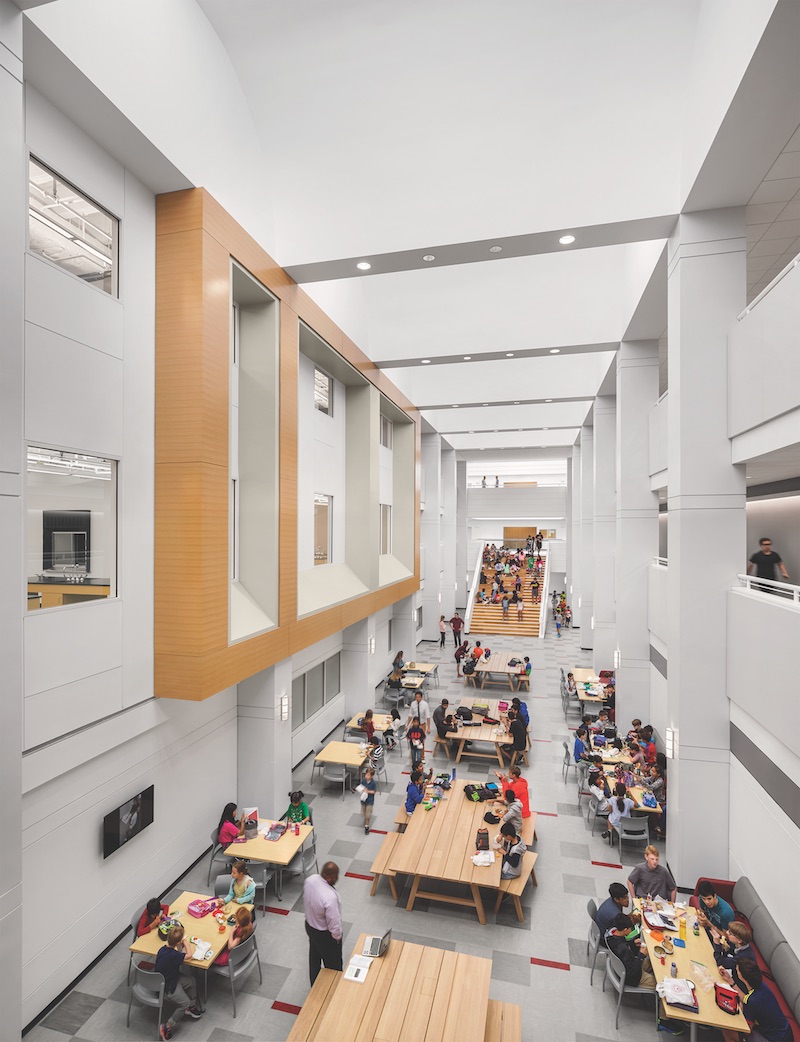
The average age of the 84,000 public elementary and secondary schools in the U.S. is 44 years since construction, and 12 years since a major renovation, according to the Department of Education. School districts, say AEC experts, are more inclined than ever to tear down old schools and build new with the latest technological and security systems.
Older schools, with their small windows and rooms and creaky infrastructure, are tough and expensive to retrofit. That may explain why more school districts, when they choose to renovate, are preferring to adapt vacant buildings in their communities for reuse as modern schools.
And boy, are there a lot of vacant buildings out there. In the greater Washington, D.C., region alone, there’s over 70 million sf of unused office space. In Dallas, 30 million sf of offices sit empty, and 17 million sf in Phoenix. To say nothing of the hundreds of millions of retail square footage that e-commerce has rendered superfluous.
For example, last February, a former Kmart in Waukegan, Ill., became home to the 53,000-sf Cristo Rey St. Martin College Prep, an $18.5 million adaptive reuse project that JGMA designed and McShane Construction built, with 18 classrooms, three science labs, a cafeteria, library, and administrative offices for 400 students.
See Also: Making schools more secure is imperative, but how best to do that isn't settled yet
Adaptive reuse “is becoming a more established option for educational program space,” say the authors of a new white paper from Perkins Eastman, “Commercial Conversion: Adaptive Reuse, A Catalyst for Educational Innovation.” One reason is that schools are scrambling to keep pace with growing student populations. More than 31% of school sites include temporary buildings.
Culling from its own K-12 portfolio, Perkins Eastman provides case studies of creative adaptive reuse. In New York’s Chelsea neighborhood, Avenues: The World School of New York took a 215,000-sf, 1920s-era warehouse with 20,000-sf floor plates and converted it into a pre-K-12 school for 1,600 students. The building already had abundant windows on all four sides. But the classrooms had to be smaller than is typical because of the interior columns’ 20x20-foot spacing.
Other case studies—in New Jersey, Dallas, northern California, and northern Virginia—offer various adaptive scenarios, such as:
• a multitenant office tower where the school occupies the lower floors
• a former Verizon call center to which 30,000 sf was added over two floors for a private school for children and young adults with learning and behavioral disabilities
• a former corporate headquarters, whose deep, 120,000-sf floor plates are arranged around a series of atrium spaces, became the central organizing feature of a school.
In El Segundo, Calif., Balfour Beatty Construction Services recently completed the construction of a Gensler-designed project for the Wiseburn Unified School District and Da Vinci Schools, which converted a 330,000-sf former Northrup Grumman aerospace facility on 14 acres into three charter schools—collectively known as Wiseburn High School—on three floors with 72 classrooms and 210,000 sf above administrative offices.
David Herjeczki, AIA, LEED AP, a Design Director and Principal with Gensler, told the Daily Breeze newspaper that this $160 million project, which opened in December 2017 and serves 1,350 students, was the first of its kind to make it through the Division of State Architect approval process. The project came about after Wiseburn, a former K-8 district, won unification in 2014 and chose to partner with Da Vinci rather than build its own high school.
Herjecki explained that the idea was to build a nontraditional school whose learning environments reflect the professional world. Da Vinci Science, on the second floor, includes an engineering lab; Da Vinci Design, on the top floor, has a fabrication lab. Da Vinci Communications is located on the third floor.
Each of the three high schools has a retractable door that rolls up onto an outdoor patio. There are no corridors or lockers, and many of the walls are movable. The classrooms have rearrangeable desks, a science lab, and collaborative spaces. The building’s floor-to-ceiling windows offer transparency and views of the surrounding city.
A gym, soccer fields, and shared aquatics center were scheduled for completion this summer.
Related Stories
| Nov 19, 2013
Top 10 green building products for 2014
Assa Abloy's power-over-ethernet access-control locks and Schüco's retrofit façade system are among the products to make BuildingGreen Inc.'s annual Top-10 Green Building Products list.
| Nov 18, 2013
ASSA ABLOY, CertainTeed team up to tackle classroom acoustics
The new alliance has uncovered easily accessible solutions to address these acoustical challenges and reduce the sound reverberation that further complicates noise issues.
| Nov 15, 2013
Greenbuild 2013 Report - BD+C Exclusive
The BD+C editorial team brings you this special report on the latest green building trends across nine key market sectors.
| Nov 15, 2013
Halls of ivy keep getting greener and greener
Academic institutions have been testing the limits of energy-conserving technologies, devising new ways to pay for sustainability extras, and extending sustainability to the whole campus.
| Nov 13, 2013
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Nov 8, 2013
S+T buildings embrace 'no excuses' approach to green labs
Some science-design experts once believed high levels of sustainability would be possible only for low-intensity labs in temperate zones. But recent projects prove otherwise.
| Nov 8, 2013
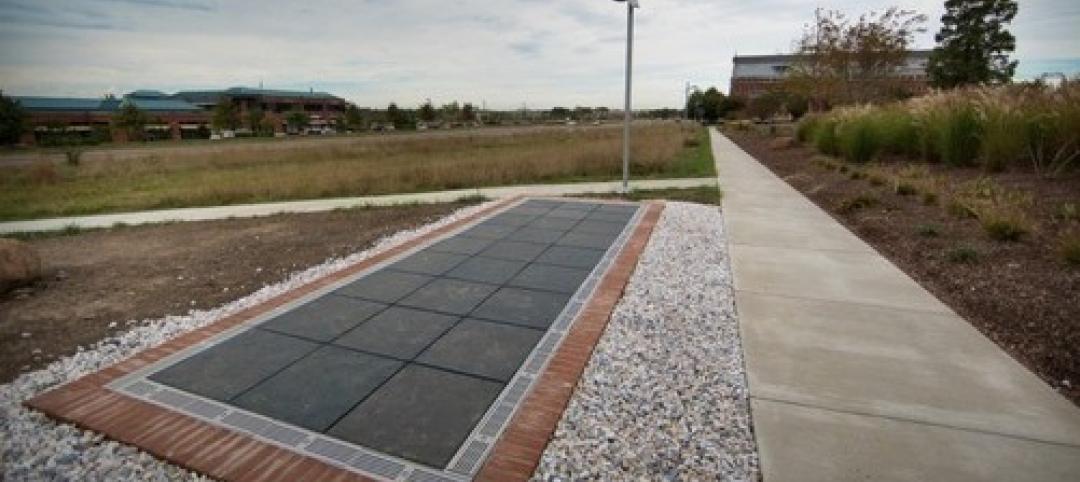
Walkable solar pavement debuts at George Washington University
George Washington University worked with supplier Onyx Solar to design and install 100 sf of walkable solar pavement at its Virginia Science and Technology Campus in Ashburn, Va.
| Nov 7, 2013
Fitness center design: What do higher-ed students want?
Campus fitness centers are taking their place alongside student centers, science centers, and libraries as hallmark components of a student-life experience. Here are some tips for identifying the ideal design features for your next higher-ed fitness center project.
| Nov 5, 2013
Net-zero movement gaining traction in U.S. schools market
As more net-zero energy schools come online, school officials are asking: Is NZE a more logical approach for school districts than holistic green buildings?
| Nov 5, 2013
Oakland University’s Human Health Building first LEED Platinum university building in Michigan [slideshow]
Built on the former site of a parking lot and an untended natural wetland, the 160,260-sf, five-story, terra cotta-clad building features some of the industry’s most innovative, energy-efficient building systems and advanced sustainable design features.