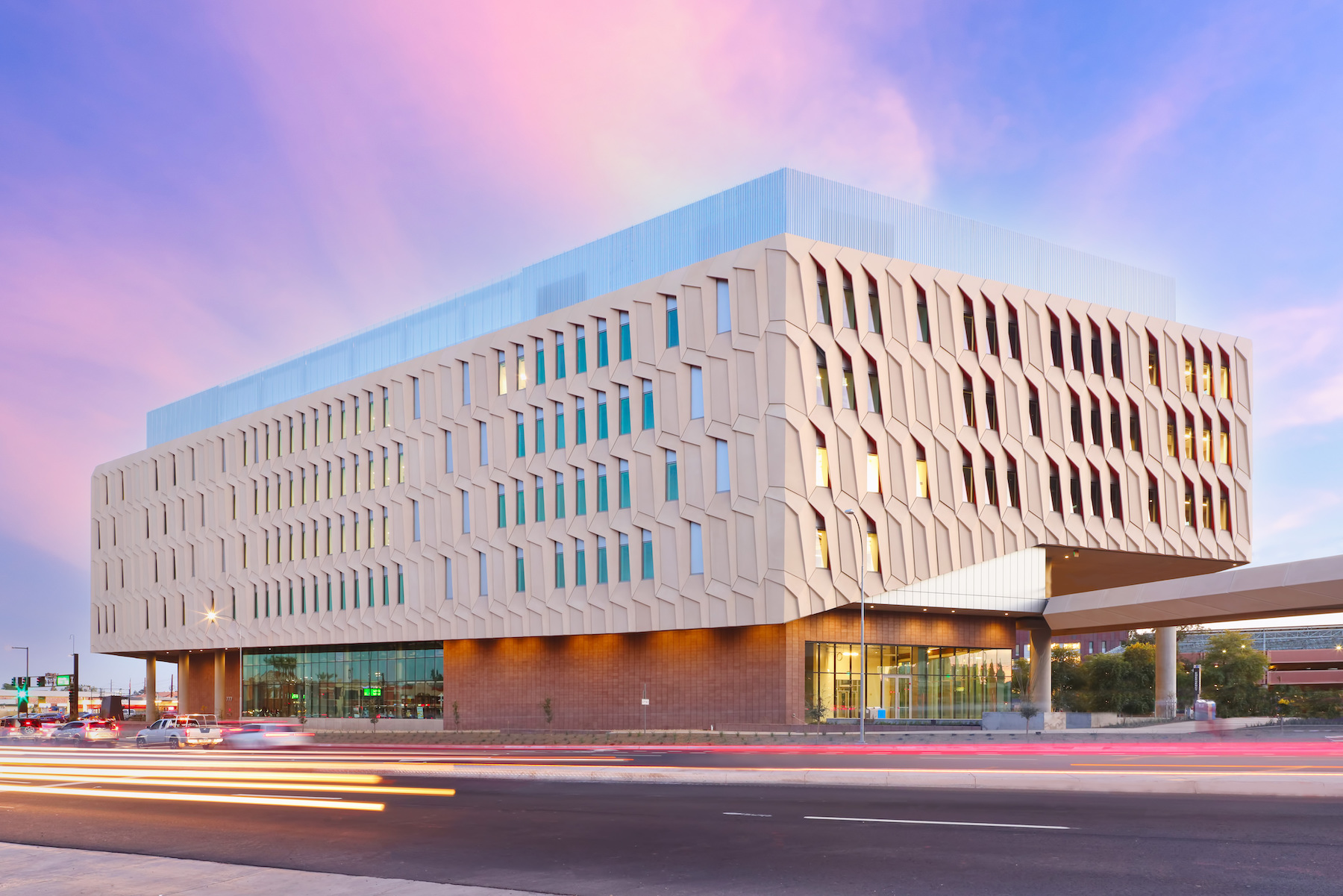
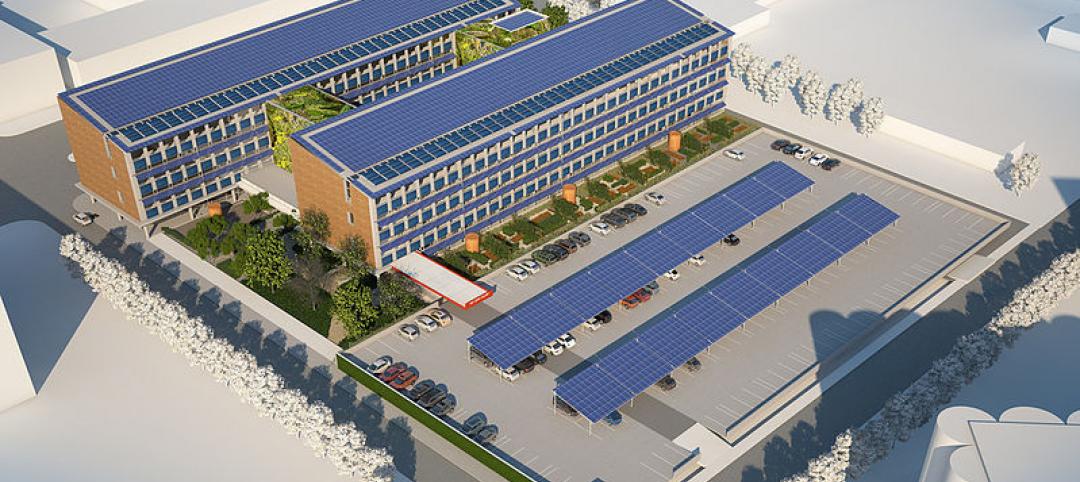
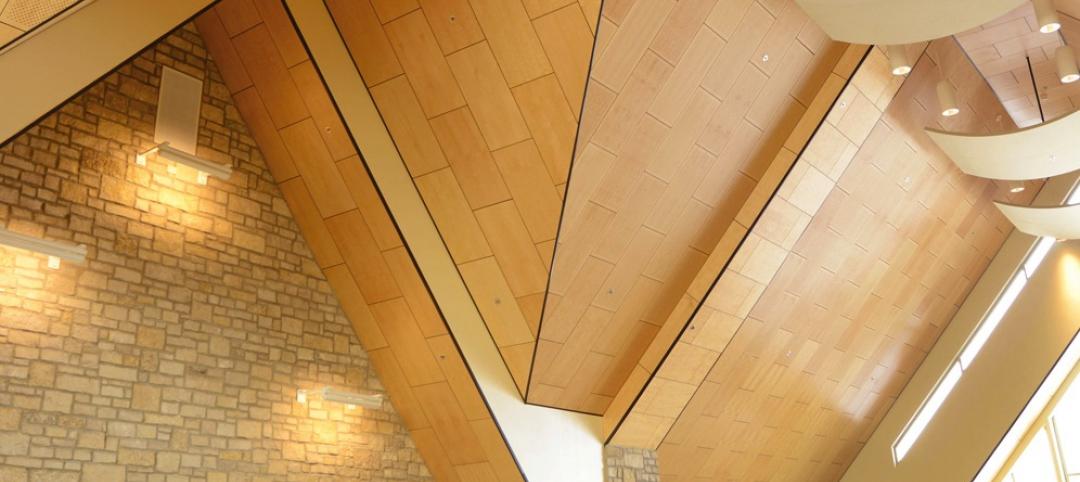
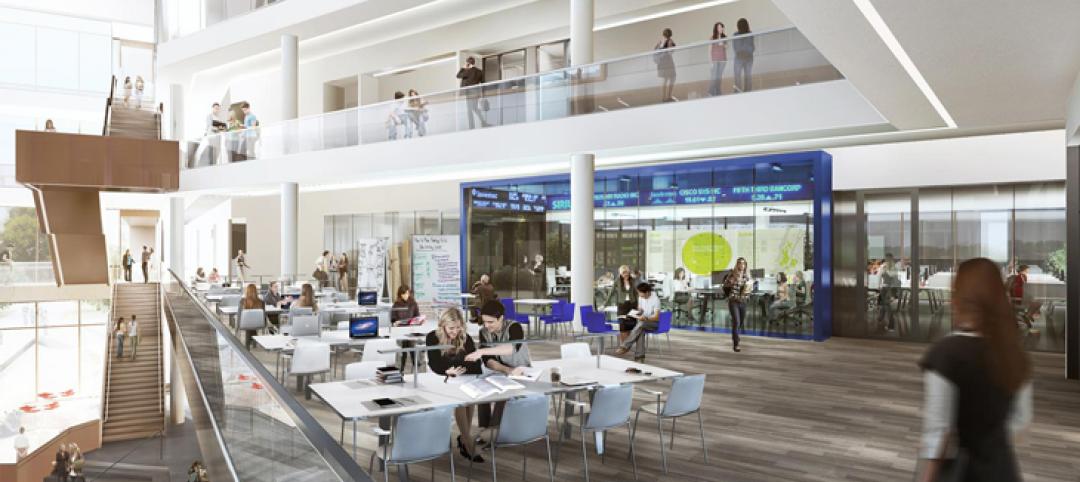
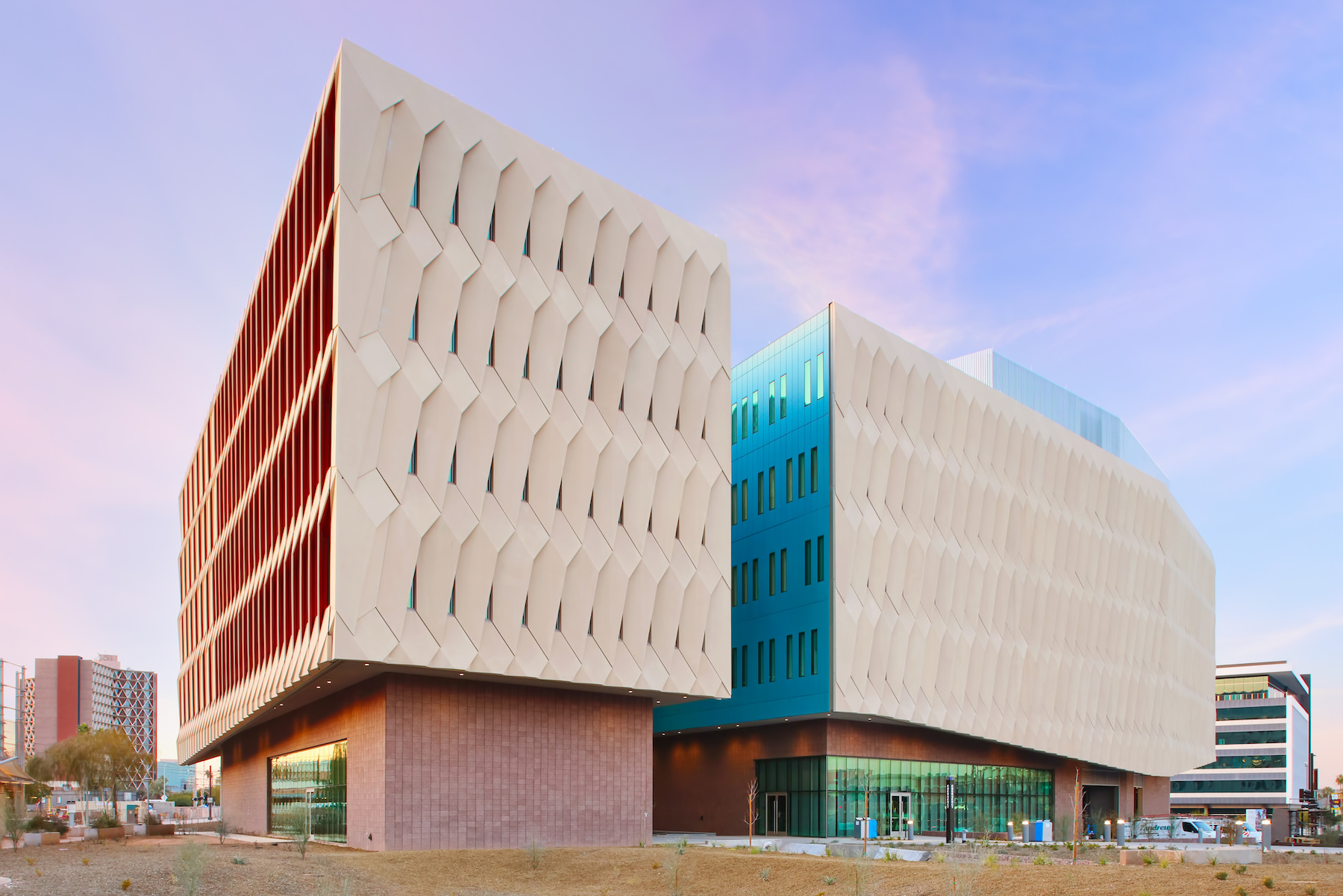
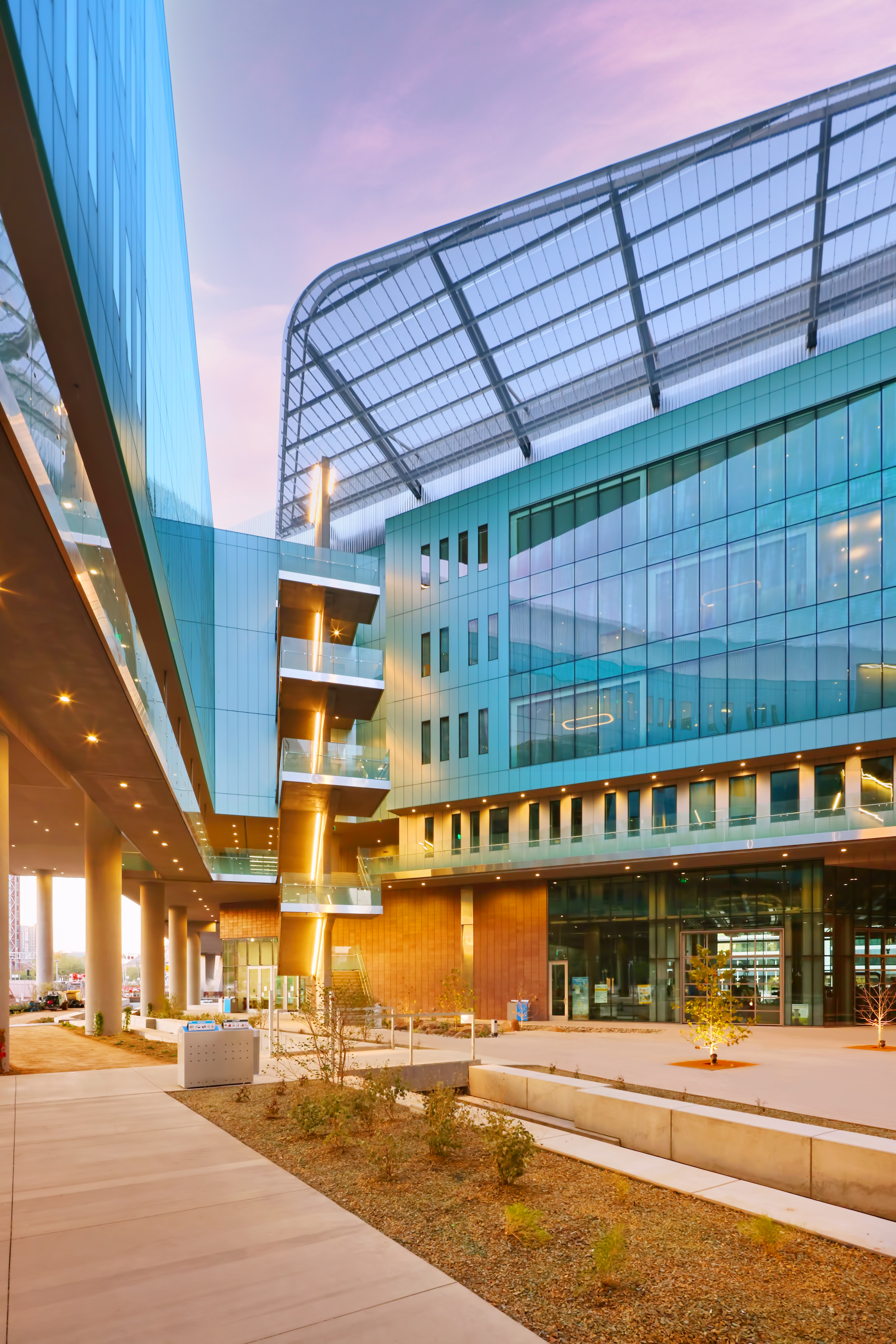
Arizona State University’s Interdisciplinary Science and Technology Building 7, completed in December 2021, was constructed with numerous innovative sustainability elements.
The building team worked to support ASU’s carbon neutrality by 2035 goal. It took a holistic approach to sustainability and carbon neutrality on all decisions, according to GC McCarthy Building Companies. The result is a building with an Energy Use Intensity (EUI) that is roughly 50% below baseline.
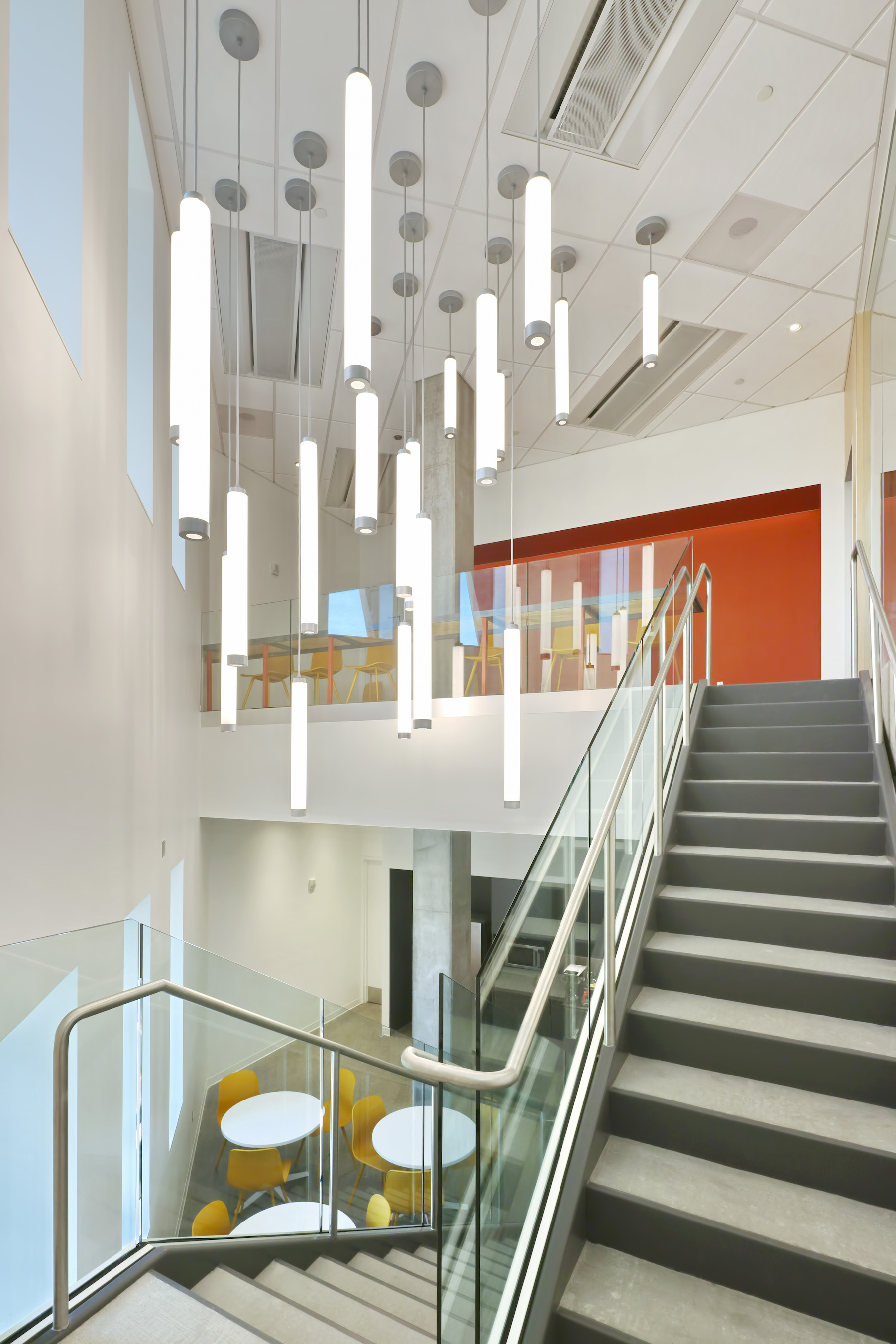
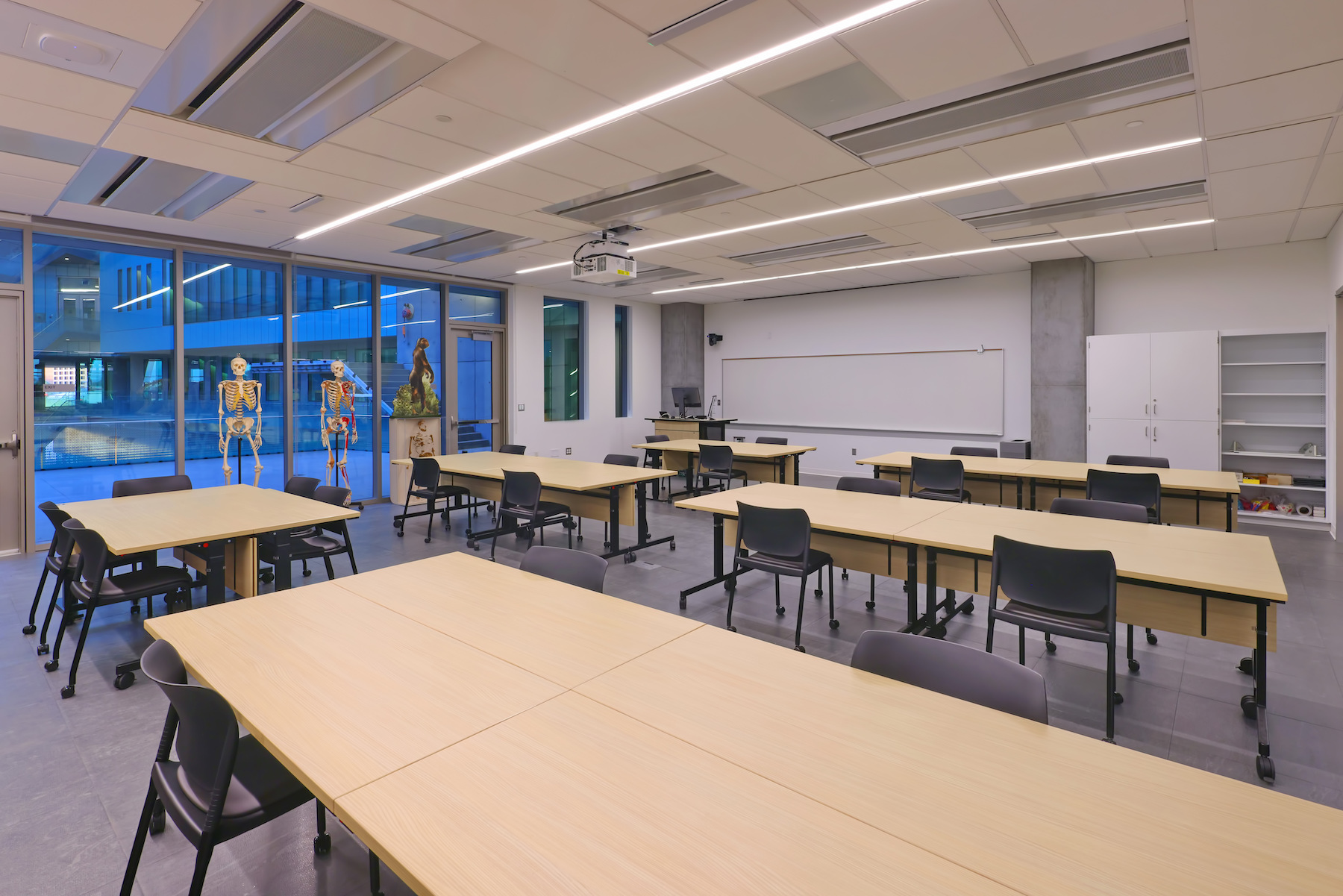
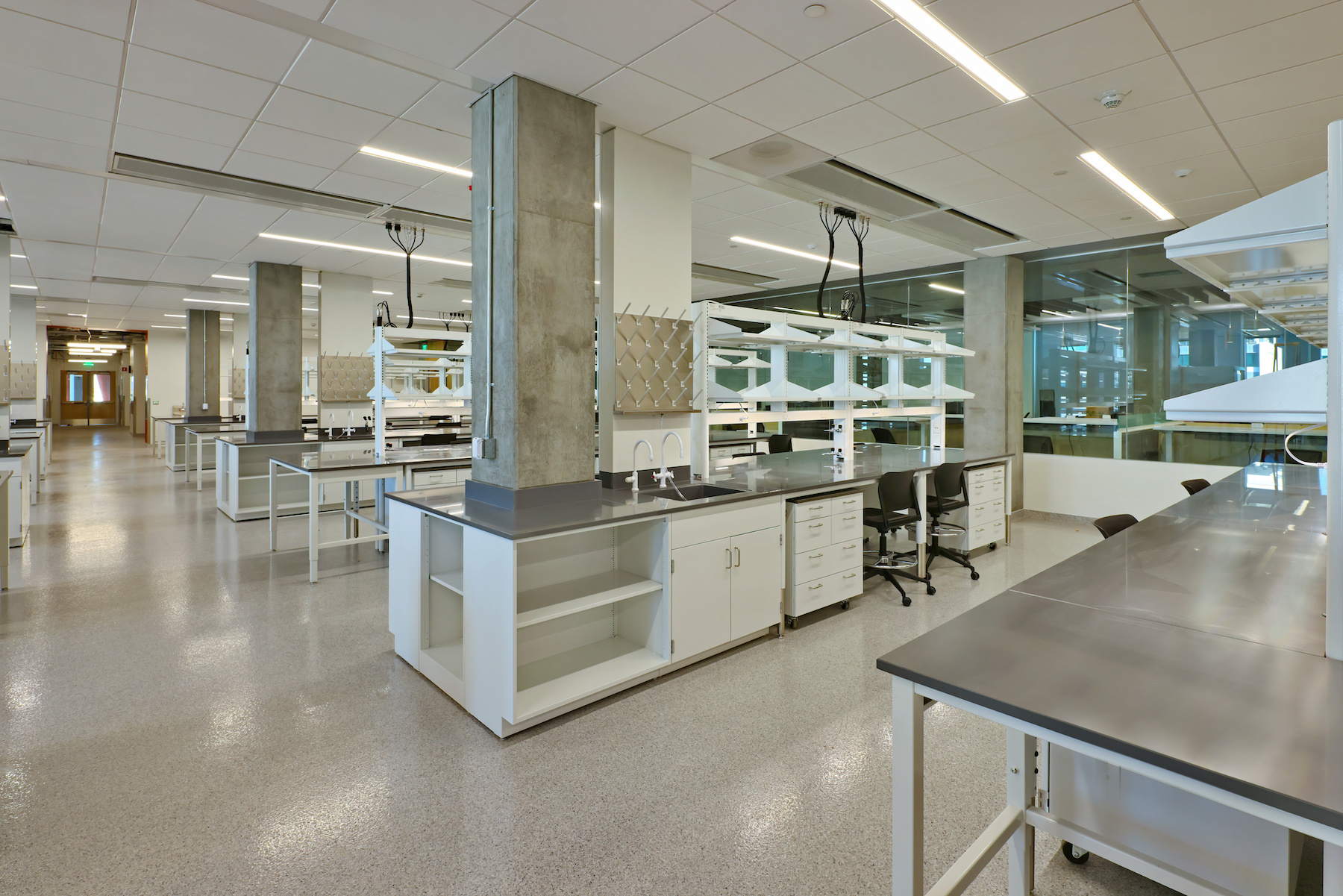
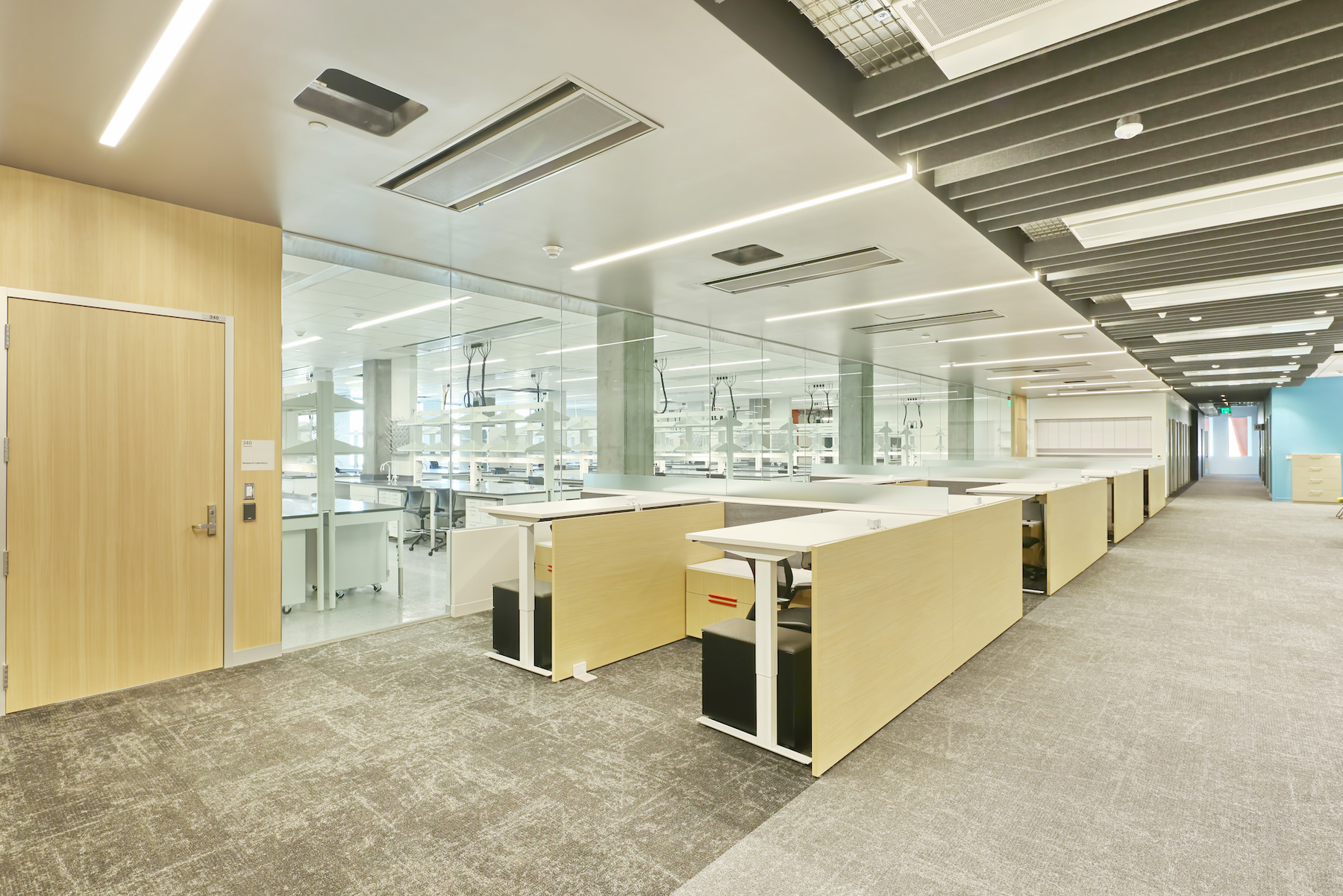
The $192 million, 281,000 sf, high-performance research facility fosters an interdisciplinary approach to knowledge generation and leading-edge research, including the sustainable use of food, water, and energy. Labs include spaces for biological sciences, engineering, life sciences, and sustainability, as well as dry lab space for computing, cyber-security, engineering design and fabrication, and robotics.

Notable sustainability features include:
- 42-foot architectural columns elevate the building entrance, creating significant shade areas and positioning the building to capture wind for natural ventilation.
- Radiant cooling system combines chilled beams, chilled ceilings, and chilled sails, providing comfort for occupants and supporting low-flow ventilation.
- Water efficiency strategies include: Use of Arizona’s Salt River Project non-potable canal water on the site’s landscape; water-saving drip irrigation and “smart” irrigation controls; hardscape designed so all rainfall conveys to planting areas; and the capture of mechanical system condensate water to irrigate plants.
- A 40% fly ash concrete mix that met structural integrity measures and provides a consistent aesthetic finish.
- First building in Arizona to use BubbleDeck, a void form structural deck system that uses a patented integration technique linking air, steel, and concrete in a two-way structural slab, resulting in less concrete and a lighter structure and foundation system.
- Inspired by self-shading pleats of the Sonoran cactus, the exterior skin takes shape in large GFRC rainscreen panels over a prefabricated building envelope. Skin sensors installed around the exterior track heat transfer throughout building’s lifecycle.
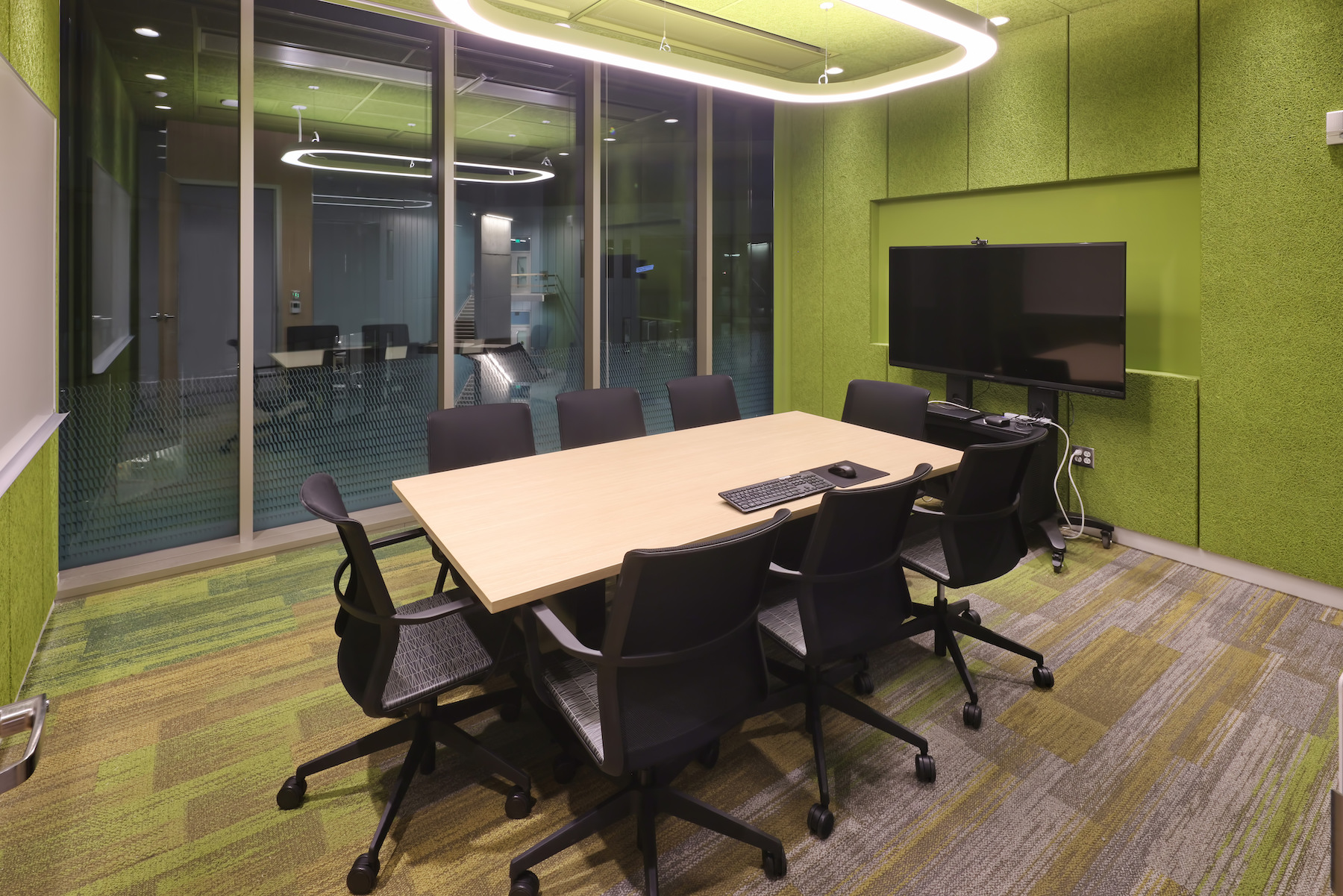
The structure now serves as the gateway to the Arizona State University Tempe campus and faces one of the busiest intersections in the Metro Phoenix area. The building will house Global Futures, the Julie Ann Wrigley Global Institute of Sustainability, the Rob and Melani Walton Sustainability Solutions Service, School of Sustainability, and the Institute of Human Origins, in addition to public outreach and exhibit space. The building will also include classrooms and a conference center with a 389-seat presentation hall.
Owner and/or developer: Arizona State University
Design architect: Architekton l Grimshaw
Architect of record: Architekton l Grimshaw
MEP engineer: BuroHappold Engineering
Structural engineer: BuroHappold Engineering
General contractor/construction manager: McCarthy Building Companies
Sustainability Consultants: Thornton Tomasetti






Related Stories
| Oct 9, 2014
Regulations, demand will accelerate revenue from zero energy buildings, according to study
A new study by Navigant Research projects that public- and private-sector efforts to lower the carbon footprint of new and renovated commercial and residential structures will boost the annual revenue generated by commercial and residential zero energy buildings over the next 20 years by 122.5%, to $1.4 trillion.
| Oct 2, 2014
Budget busters: Report details 24 of the world's most obscenely over-budget construction projects
Montreal's Olympic Stadium and the Sydney Opera House are among the landmark projects to bust their budgets, according to a new interactive graph by Podio.
| Sep 29, 2014
Living Building vs. LEED Platinum: Comparing the first costs and savings
Skanska USA's Steve Clem breaks down the costs and benefits of various ultra-green building standards and practices.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 24, 2014
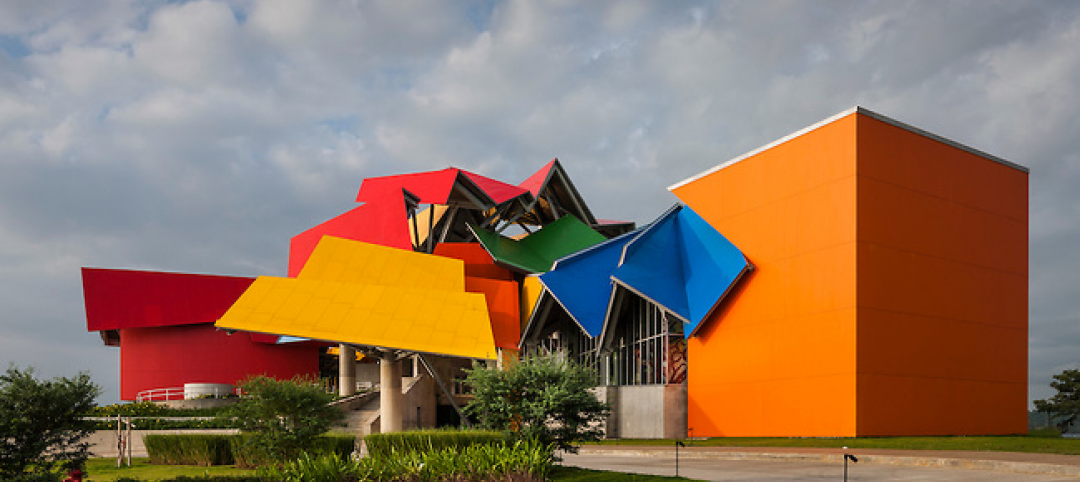
Frank Gehry's first building in Latin America will host grand opening on Oct. 2
Gehry's design for the Biomuseo, or Museum of Biodiversity, draws inspiration from the site's natural and cultural surroundings, including local Panamaian tin roofs.
| Sep 22, 2014
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 17, 2014
New hub on campus: Where learning is headed and what it means for the college campus
It seems that the most recent buildings to pop up on college campuses are trying to do more than just support academics. They are acting as hubs for all sorts of on-campus activities, writes Gensler's David Broz.
| Sep 15, 2014
Ranked: Top international AEC firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Parsons Brinckerhoff, Gensler, and Jacobs top BD+C's rankings of U.S.-based design and construction firms with the most revenue from international projects, as reported in the 2014 Giants 300 Report.
| Sep 15, 2014
Argentina reveals plans for Latin America’s tallest structure
Argentine President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner announces the winning design by MRA+A Álvarez | Bernabó | Sabatini for the capital's new miexed use tower.