When selecting replacement windows and doors for retrofits, Building Teams must consider aesthetics, cost, schedule, view, energy performance, accessibility, and durability. Then there are environmental and security considerations, such as vandal resistance, blast-hazard mitigation, and hurricane-impact protection. Fortunately, new technologies are making it easier to meet those requirements and upgrade the appearance and energy efficiency of a building, while keeping the project on budget.
Compared to the products available 15 years ago, new windows and doors offer greatly improved thermal performance, says John Bendt, sales/marketing vice president with Wausau Window and Wall Systems (www.wausauwindow.com). “That’s because better thermal separators, such as glass-reinforced nylon, provide superior insulation through increased aluminum separation and air space in the frames,” says Bendt.
Fabricated glass continues to improve in insulating value and controlling solar heat gain while letting an appropriate amount of natural light into the building. Triple-insulating glass is also being considered for more projects. “The biggest trend today is toward energy-efficient technologies, including aluminum-clad wood, fiberglass and vinyl frames, and high-performance, low-e glass,” says Terry Zeimetz, commercial marketing manager for Pella Corp. (www.pella.com).
“Aluminum cladding has come a long way in its ability to emulate wood profiles,” notes Jeff Hoffman, an architectural sales representative for Marvin Windows and Doors (http://commercial.marvin.com)
Older windows can be swapped out for new ones that offer similar sightlines and historical look. For example, aluminum-framed, projected windows can be made to look like old steel windows or double-hung windows but are easier to operate, says Bendt. Aluminum cladding is frequently used in historically influenced replacement windows because it’s durable and easy to customize. Factory-applied anodized and baked-on fluoropolymer paint finishes can be formulated to match existing color schemes or reproduce a building’s original colors. Such finishes are also eco-friendly.
Commercial doors can be specified with components and technologies to address constantly increasing thermal performance requirements. “Many types of high-performance glass, including those that withstand blasts and hurricane impact, can be incorporated without altering the overall look of a door,” says Mary Olivier, marketing manager for Tubelite Inc. (www.tubeliteinc.com), a manufacturer of architectural aluminum window, entrance storefront, and curtain wall systems.
Durability is a key factor in selecting a door/hardware combination and the size of the stiles (the vertical members of the door frame). But the most significant task in replacement projects, particularly for historic buildings, is to match the work of historic artisans using modern materials on a limited budget, Olivier says.
Deciding whether or not to use the existing window and door framing in a retrofit depends on such factors as the presence of wood rot and hazardous materials, the structural integrity of the existing frame, and the anchorage scheme of the replacement system, says Ken Brenden, CDT, of the American Architectural Manufacturers Association (www.aamanet.org), Schaumburg, Ill.
Bendt points out that older window frames don’t offer modern-day thermal technology and performance, so it’s worthwhile to evaluate new frames for their potential energy savings and reduced maintenance. Ultimately, the decision to keep or tear out existing framing should be based on energy modeling and budgeting information, he says.
Let’s take a look at a few instructive window/door retrofits.
[pagebreak]
UNIVERSITY RESIDENCE HALL UPGRADE: SAVE ENERGY, IMPROVE AESTHETICS
Eastern Michigan University, Ypsilanti, Mich., completed a $3.1 window renovation last year on its First-Year Center, a freshman residential hall that dates back to the 1960s. More than 675 operable, high-performance windows were installed.
Energy conservation and improved aesthetics were the primary goals, says architect Sandra Laux, AIA, of Detroit-based Hamilton Anderson Associates (www.hamilton-anderson.com). To replace the single-pane glazed windows with insulated units, Laux selected Wausau low-profile windows. Their aluminum frames have a copper anodized finish to contrast with the blond brick exterior. The low-maintenance, durable finish is expected to maintain its color over time without forming a patina.
The renovation also included replacement of the exterior doors and curtain wall system. “The stair towers had single-glazed curtain wall from the 1960s, which was failing,” says Hamilton Anderson’s Michael Decoster.
Decoster specified EFCO curtain wall and storefront framing systems for the stair towers and entry canopy. The existing concrete canopy rested on small steel columns and was “a really heavy mass” hanging over the entry. “We took that all off the structure and reclad the canopy in curtain wall framing, so on each side of the entry are two-foot-tall pieces of glass that are structurally glazed,” he says. The frosted glass is backlit at night.
OREGON STATE HOSPITAL: RESPECT FOR HISTORY
In 2008, the Oregon State Hospital (OSH) campus, in Salem, was granted national historic landmark status. A complete structural renovation wasn’t an option, but J Building, an 1883-vintage four-story structure designed in the Kirkbride style of psychiatric facilities—and made famous as the setting of the film “One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest”—was restored and refurbished.
To bring the building up to 21st-century standards and seismic requirements, workers removed asbestos and lead paint, added steel rebar, layers of sprayed concrete, and new wood beams, and restored the original cupola.
But the grandest undertaking was the replacement of more than 500 windows on the street side of the building. “It was important to preserve as many historic features as possible,” says Patricia Feeny, communications manager for the OSH Replacement Project. “At the same time, we had to meet state-mandated energy and safety requirements.”
Wausau fabricated windows with sash muntins to match the originals in material and design. The psychiatric-grade windows were drop-tested for interior human impacts of up to 2,000 foot-pounds of energy. The aluminum frames have a resin-based coating that resists humidity, color change, chalking, gloss loss, and chemicals.
5 TIPS for a successful door and window retrofit
1. Analyze products on a level playing field using American Architectural Manufacturers Association and National Fenestration Rating Council (www.nfrc.org) standards and test sites. As you’re calculating ROI, be sure to factor in the savings that may come from being able to downsize the HVAC system, cut repair and maintenance costs, and trim energy costs due to better insulating value and more natural light.
2. Work with the manufacturer’s local architectural representative in the early stages of the project. Trained reps can help with site inspection, drawings, field measurements and testing, energy modeling, mockups, budgeting, detail support, and specification support.
3. Take advantage of AAMA publications on door and window selection criteria, design considerations, window and exterior door types, performance requirements and testing, and accessory items and special features: http://www.aamanet.org/general/1/45/publication-store.
4. Select an installer who will ensure a safe, hassle-free installation while minimizing disruptions to building occupants. Your manufacturer can assist you in finding the right installer.
5. Use moderate door heights and widths, especially when using insulated or specialty glass. Large entrances also have increased size and weight, which places additional strain on hinging hardware and can shorten the door’s longevity.
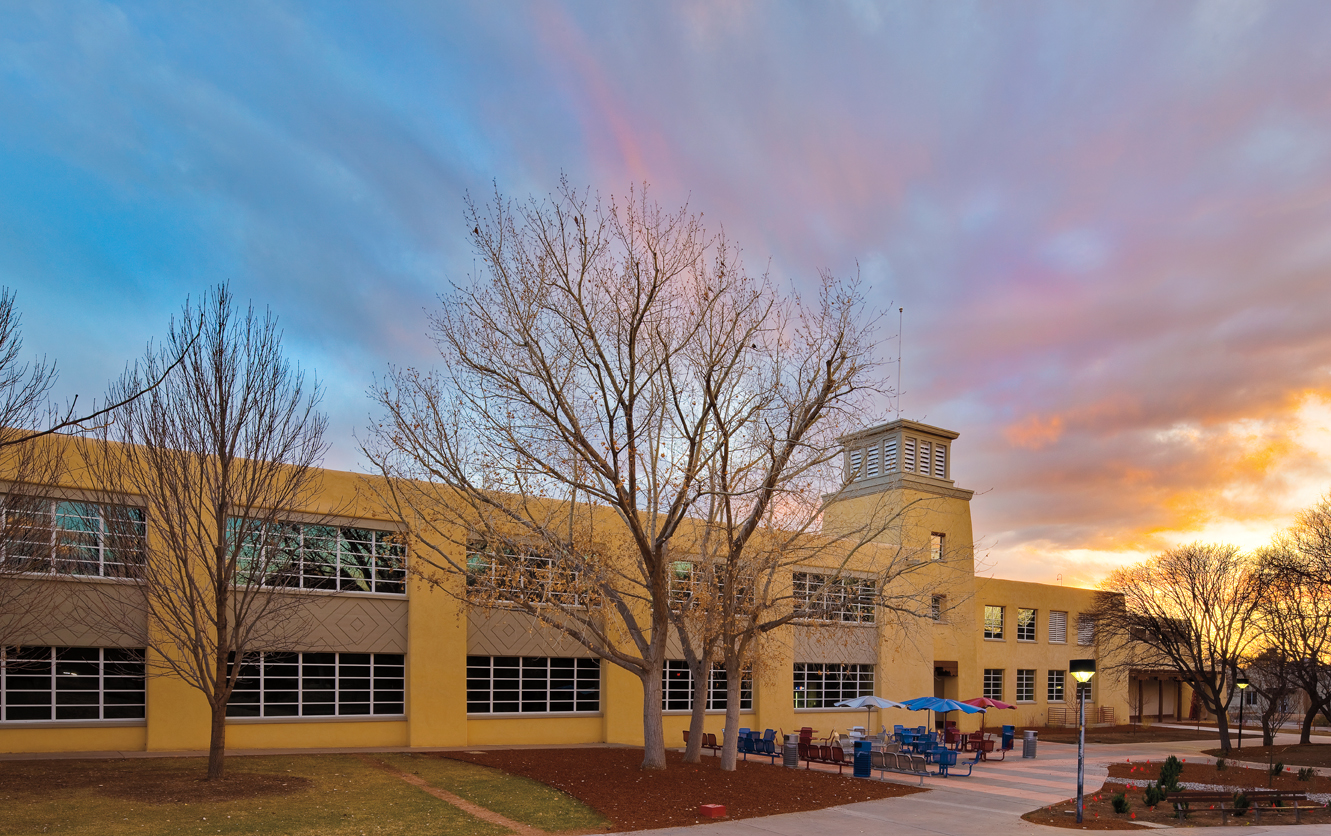
MITCHELL HALL AT UNM: HOMAGE TO THE PAST
Mitchell Hall, one of the oldest classroom buildings at the University of New Mexico, was built in 1954. While not a registered historic landmark, the building is noteworthy for its design by John Gaw Meem IV (1894-1983), one of the Southwest’s most influential architects.
In tackling the renovation, Albuquerque-based Hartman + Majewski Design Group (designgroupnm.com) sought to preserve the building’s historic integrity while improving its environmental sustainability. The original single-pane, steel-framed windows had narrow sightlines and were stacked vertically with one-inch widths between glazings.
“Part of the goal was to maintain the exterior feel of the project so that the university could, in the future, pursue putting [the building] on the historic registry,” says principal architect Jeff Zellner, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP BD+C.
Hartman + Majewski analyzed the existing window systems and performed energy modeling as part of the LEED certification process. “We looked at improvements that would give us the biggest bang for the buck,” says Zellner.
The team considered a number of options, including true historic steel windows, storefront framing, and aluminum, but ultimately chose Pella fiberglass windows. “We were not familiar with fiberglass windows in commercial applications, but Pella did a pretty good sell on the performance characteristics as well as maintenance,” he says.
With the combined benefit of the new windows, a more efficient mechanical system, and enhanced lighting controls, Mitchell Hall is expected to earn LEED Silver.
THE ST. LOUIS ZOO: REPURPOSING THE ELEPHANT HOUSE
Peabody Hall, the oldest building at the St. Louis Zoo, was completed in 1917. The Renaissance Revival structure, designed by architect George Barnett, served for eight decades as the Elephant House. In 2009, Peabody Hall was renovated to house temporary exhibits in celebration of the zoo’s 100th anniversary. The project was a joint venture of two St. Louis-based design firms, Ottolino Winters Huebner (www.owh-inc.com) and the JCO LLC (www.thejco.com).
According to OWH, the original Elephant House’s masonry, stone, and terra cotta exterior had held up quite nicely over 95-plus years, but the windows and doors were well past their usable life—especially the ornate quatrefoil window in the attic. Finding durable, easy-to-use replacement products that allowed the necessary customization to replicate the form and appearance of the originals became the challenge.
Marvin Windows and Doors fabricated five large transoms, two sets of stationary awning windows, and seven commercial doors (three operating, four fixed) for the renovation. All windows and doors were glazed with black spandrel insulating glass that emulates the look of field-painted glass. To replicate the quatrefoil window, Marvin used five pieces of glass, with true divided lites in the rectangular center section and simulated divided lites surrounding the rectangle. +
Related Stories
| Jan 25, 2011
Bloomberg launches NYC Urban Tech Innovation Center
To promote the development and commercialization of green building technologies in New York City, Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg has launched the NYC Urban Technology Innovation Center. This initiative will connect academic institutions conducting underlying research, companies creating the associated products, and building owners who will use those technologies.
| Jan 25, 2011
Top 10 rules of green project finance
Since the bottom fell out of the economy, finding investors and financial institutions willing to fund building projects—sustainable or otherwise—has been close to impossible. Real estate finance prognosticators, however, indicate that 2011 will be a year to buy back into the real estate market.
| Jan 25, 2011
Chicago invented the skyscraper; can it pioneer sustainable-energy strategies as well?
Chicago’s skyline has always been a source of pride. And while few new buildings are currently going up, building owners have developed a plan to capitalize on the latest advances: Smart-grid technologies that will convert the city’s iconic skyline into what backers call a “virtual green generator” by retrofitting high-rise buildings and the existing electrical grid to a new hyper-connected intelligent-communications backbone.
| Jan 25, 2011
AIA reports: Hotels, retail to lead U.S. construction recovery
U.S. nonresidential construction activity will decline this year but recover in 2012, led by hotel and retail sectors, according to a twice-yearly forecast by the American Institute of Architects. Overall nonresidential construction spending is expected to fall by 2% this year before rising by 5% in 2012, adjusted for inflation. The projected decline marks a deteriorating outlook compared to the prior survey in July 2010, when a 2011 recovery was expected.
| Jan 25, 2011
Jester Jones Schifer Architects, Ltd. Joins GPD Group
GPD Group is excited to announce that Jester Jones Schifer Architects, a Marion-based architectural firm, has joined our firm, now enabling GPD Group to provide architectural services to the Central-Ohio market.
| Jan 21, 2011
Combination credit union and USO center earns LEED Silver
After the Army announced plans to expand Fort Bliss, in Texas, by up to 30,000 troops, FirstLight Federal Credit Union contracted NewGround (as CM) to build a new 16,000-sf facility, allocating 6,000 sf for a USO center with an Internet café, gaming stations, and theater.
| Jan 21, 2011
Manufacturing plant transformed into LEED Platinum Clif Bar headquarters
Clif Bar & Co.’s new 115,000-sf headquarters in Emeryville, Calif., is one of the first buildings in the state to meet the 2008 California Building Energy Efficiency Standards. The structure has the largest smart solar array in North America, which will provide nearly all of its electrical energy needs.
| Jan 21, 2011
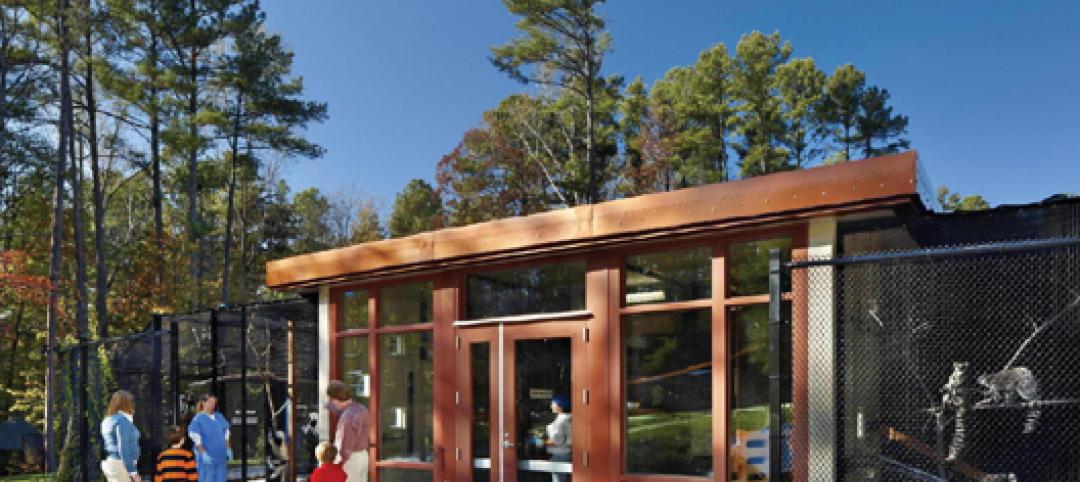
Primate research facility at Duke improves life for lemurs
Dozens of lemurs have new homes in two new facilities at the Duke Lemur Center in Raleigh, N.C. The Releasable Building connects to a 69-acre fenced forest for free-ranging lemurs, while the Semi-Releasable Building is for lemurs with limited-range privileges.
| Jan 21, 2011
Harlem facility combines social services with retail, office space
Harlem is one of the first neighborhoods in New York City to combine retail with assisted living. The six-story, 50,000-sf building provides assisted living for residents with disabilities and a nonprofit group offering services to minority groups, plus retail and office space.