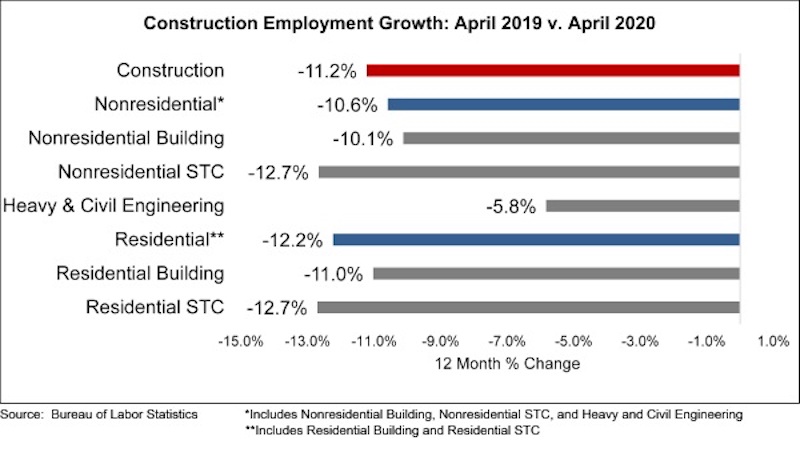
The construction industry lost 975,000 jobs on net in April, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data released today by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. This was the largest recorded decrease in construction jobs since the government began tracking employment in 1939, despite construction remaining an essential industry in much of the nation through April.
Nonresidential construction employment lost 560,500 jobs on net in April. There were job losses in all three nonresidential segments, with the largest decline registered among nonresidential specialty trade contractors, which lost 393,100 jobs. Nonresidential building lost 88,500 jobs, while heavy and civil engineering lost 78,900 jobs.
The construction unemployment rate was 16.6% in April, up 11.9 percentage points from the same time last year. Unemployment across all industries rose from 4.4% in March to 14.7% last month. This was the highest rate since the BLS started tracking unemployment in 1948. Because of technical reasons related to the BLS survey and a classification error in several responses, the unemployment rate is probably closer to 20%.
“The hope had been that construction activity would hold up well given the industry’s classification as an essential industry in much of the nation and the presence of substantial backlog coming into the crisis, which stood at 8.2 months in February, according to ABC’s Construction Backlog Indicator,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “But alas, in large measure, those hopes were not realized. The level of construction industry job loss in April easily surpassed that of the worst month sustained during the Great Recession, when 155,000 jobs were lost in March 2009. Between April 2006 and January 2011, construction industry employment declined by 2.3 million. The construction industry lost nearly a million jobs last month alone.
“Based on a combination of business confidence indicators, initial unemployment claims and other emerging data, May will represent another month of crushing construction employment loss,” said Basu. “Project postponements and cancellations are now commonplace, with construction backlog failing to be the protective shield that it normally is during the early stages of economywide recession.”


Related Stories
Market Data | Aug 13, 2018
First Half 2018 commercial and multifamily construction starts show mixed performance across top metropolitan areas
Gains reported in five of the top ten markets.
Market Data | Aug 10, 2018
Construction material prices inch down in July
Nonresidential construction input prices increased fell 0.3% in July but are up 9.6% year over year.
Market Data | Aug 9, 2018
Projections reveal nonresidential construction spending to grow
AIA releases latest Consensus Construction Forecast.
Market Data | Aug 7, 2018
New supply's impact illustrated in Yardi Matrix national self storage report for July
The metro with the most units under construction and planned as a percent of existing inventory in mid-July was Nashville, Tenn.
Market Data | Aug 3, 2018
U.S. multifamily rents reach new heights in July
Favorable economic conditions produce a sunny summer for the apartment sector.
Market Data | Aug 2, 2018
Nonresidential construction spending dips in June
“The hope is that June’s construction spending setback is merely a statistical aberration,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu.
Market Data | Aug 1, 2018
U.S. hotel construction pipeline continues moderate growth year-over-year
The hotel construction pipeline has been growing moderately and incrementally each quarter.
Market Data | Jul 30, 2018
Nonresidential fixed investment surges in second quarter
Nonresidential fixed investment represented an especially important element of second quarter strength in the advance estimate.
Market Data | Jul 11, 2018
Construction material prices increase steadily in June
June represents the latest month associated with rapidly rising construction input prices.
Market Data | Jun 26, 2018
Yardi Matrix examines potential regional multifamily supply overload
Outsize development activity in some major metros could increase vacancy rates and stagnate rent growth.