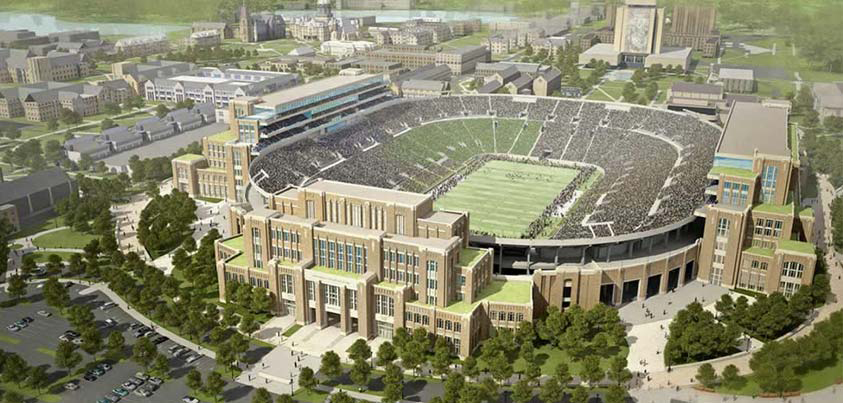
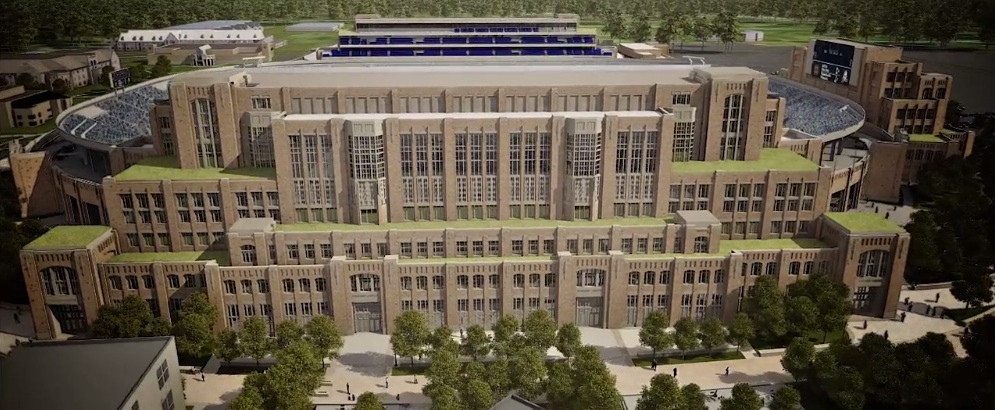
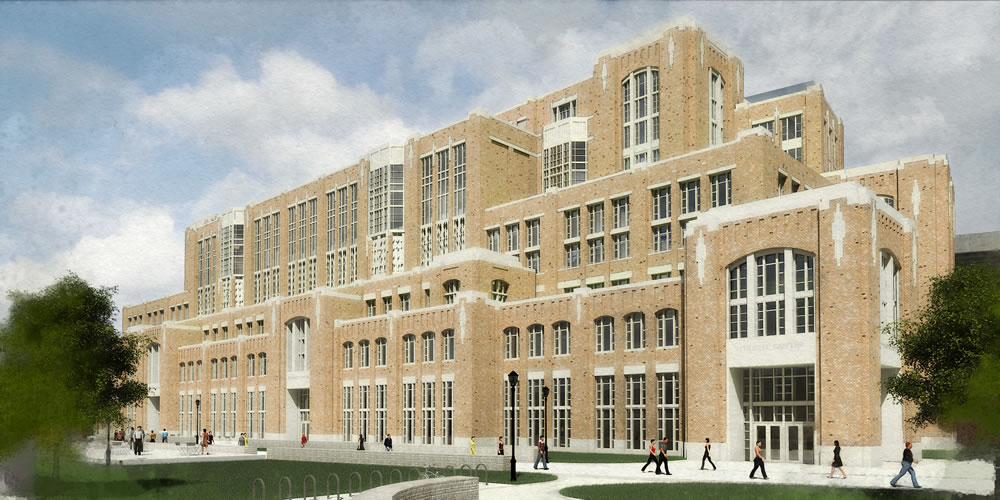
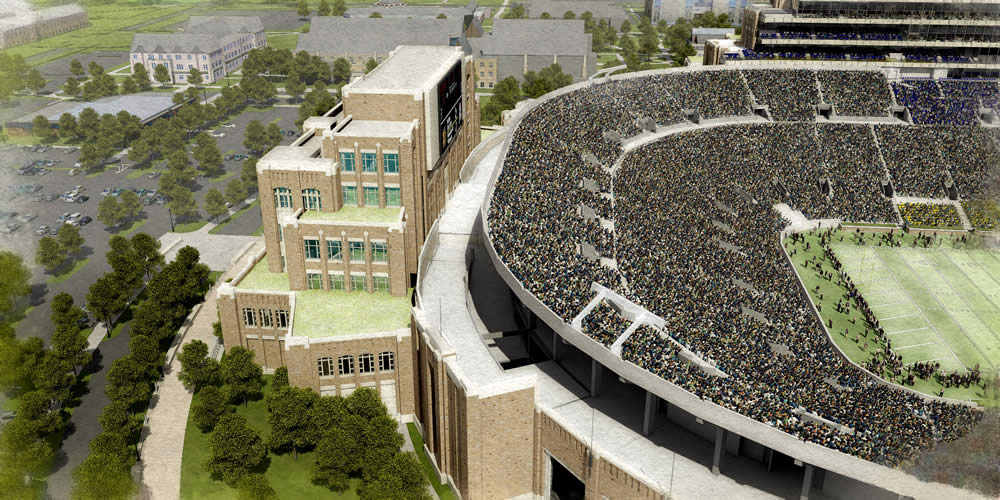
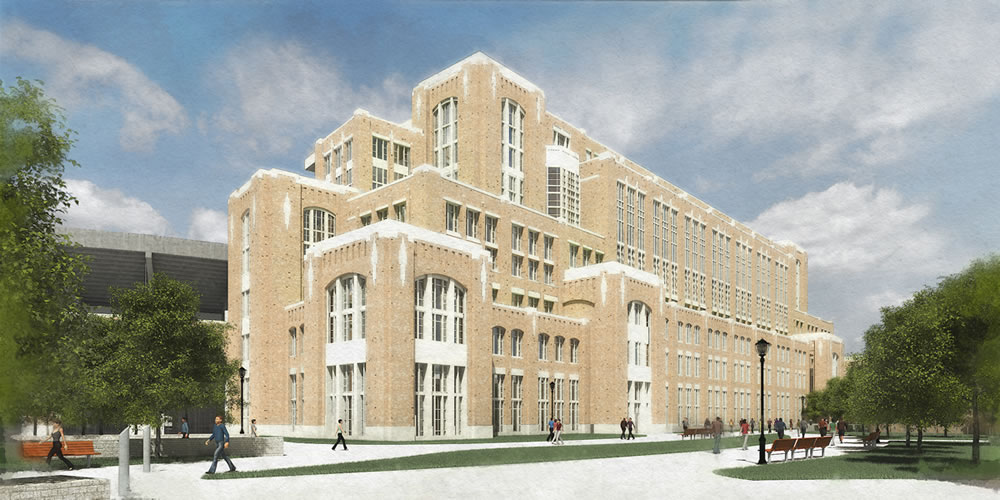
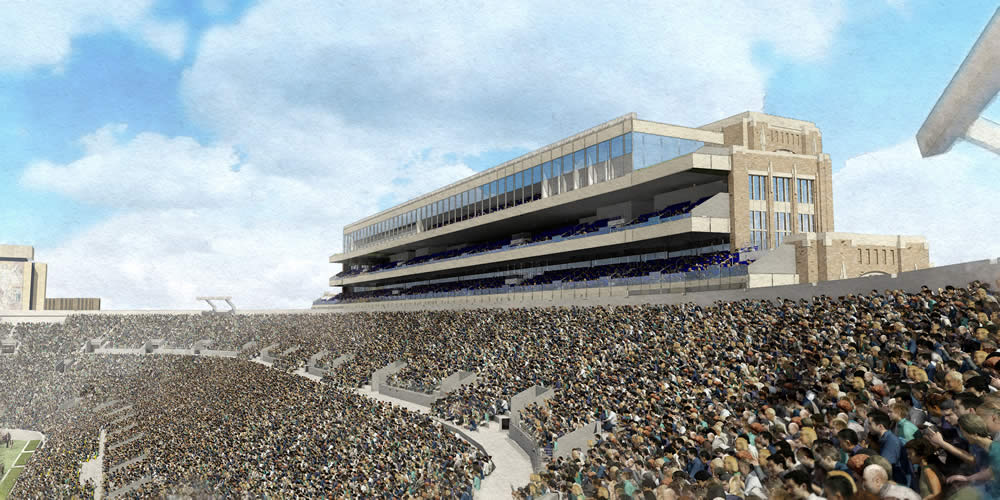
The University of Notre Dame announced this morning the largest building project in its 172-year history, integrating the academy, student life, and athletics with the construction of more than 750,000 sf in three new buildings attached to the west, east, and south sides of the school's iconic football stadium, at a projected cost of $400 million.
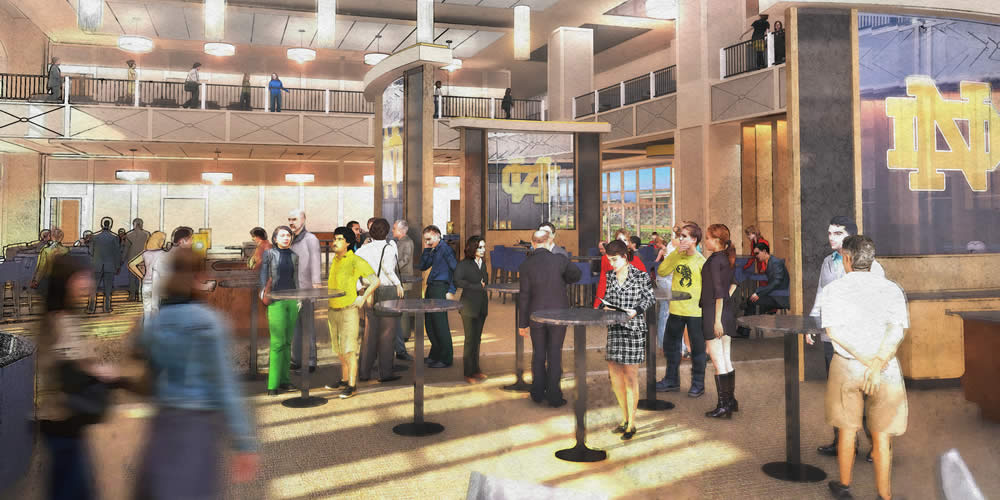
The plan, called the Campus Crossroads Project, features new structures attached to and serving the stadium: a west building for student life services, including space for student organizations, a recreation center and career center; an east building for the anthropology and psychology departments and a digital media center; and a south building for the Department of Music and the Sacred Music at Notre Dame program. The east and west buildings also will include some 3,000 to 4,000 premium seats for the football stadium with supporting club amenities.
The lead architectural firm for the Crossroads Project is The S/L/A/M Collaborative. RATIO Architects is the co-designer. Other consultants include Workshop Architects for the student center and 360 Architecture for the recreation, fitness, and hospitality areas. The contractor is Barton Malow Co.
Central components to the plan include the addition of meeting, research, and teaching venues, as well as facilities that do not currently exist on campus, such as a 500-person ballroom. The various new spaces also will be designed to accommodate multiple functions for multiple departments, such as the stadium club spaces, which also will be used for student services, academic event space, classrooms, conferences, career fairs, and other campus and community activities.
The exterior design of the Campus Crossroads Project is inspired by Knute Rockne’s original Notre Dame Stadium—which still stands today as the core of the facility—and is wed with materials, massing, and details taken from many of the Collegiate Gothic buildings on the campus.
The area between the stadium and the DeBartolo Hall classroom building will become a pedestrian plaza with walkways, trees, planters, and seating areas. The entire project will include sustainability practices consistent with other University projects.
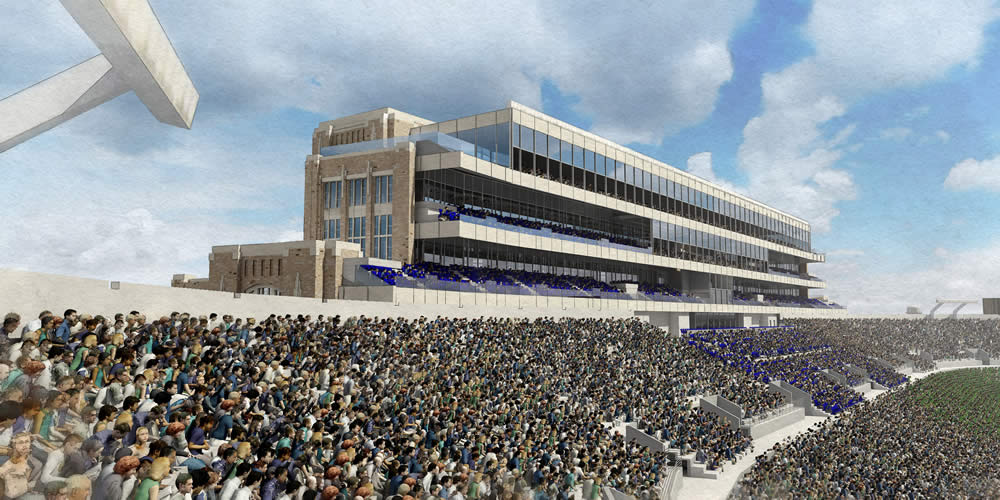
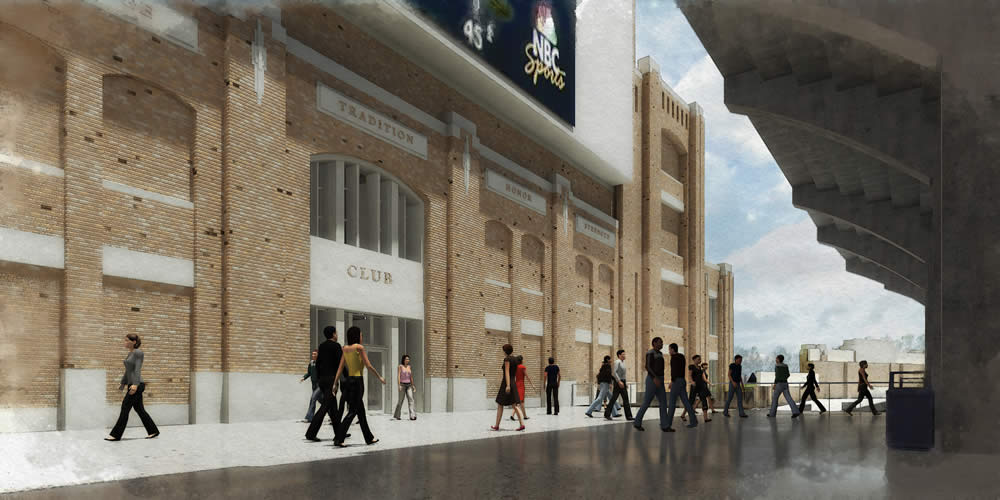
The project also will enhance the football fan experience on game days. A variety of premium seating options—both indoor and outdoor and mostly club seats—will be available on three upper levels on the east and west sides. A hospitality area also is planned for the new building on the south end of the stadium.
Football fans, especially younger ones, have expressed a clear desire to have better access to data and video when attending Notre Dame games. Some of that will be addressed through enhanced broadband connectivity and some by the introduction of video, though the shape that will take has not yet been finalized. However, to the extent the University provides video, whether in the concourse or in the stadium itself—similar to the philosophy in Purcell Pavilion and the Compton Family Ice Arena—there will be no commercial signage or advertising.
Notre Dame Stadium opened in 1930 and was expanded to its current configuration in 1997. One of the nation’s most iconic athletics venues, it is used for home football games, the University Commencement Ceremony and several other events.
Features of the three new buildings include:
West building
Space designed to enhance student development and formation will dominate the nine-story west building. Planning has ensured that the new facility will complement the student organization space and administrative offices located in the historic LaFortune Student Center.
Levels 1 and 2: Flexible, state-of-the-art meeting rooms, graduate and undergraduate student lounges, a dining area, student organization space and administrative offices.
Levels 3 and 4: Recreational sports and fitness facilities (the Rolfs Sports Recreation Center will become the practice home for the men’s and women’s varsity basketball teams).
Level 5: A career services center, centralized and expanded with more than 40 interview rooms, multiple training rooms and conference areas, an employer lounge and advising offices. The existing working press space on this level will be integrated into a premium seating area for the stadium.
Level 6: Mechanical support.
Level 7: A 500-seat student ballroom, club seating for football and booths for NBCSports telecasts of home football games. Student-oriented programming will have priority booking for non-game weekends.
Level 8: Premium stadium seats and terraces that will look onto the campus and the playing field.
Level 9: Club seating, boxes for home and visiting coaches, security booths and boxes for administrative and athletic department leaders.
Basement: Food service space for the three new buildings and the stadium.
South building
The relocation of the Department of Music and Sacred Music Program will provide much needed new and state-of-the-art space for these growing programs. It also will put music into close proximity to other performing arts departments and programs.
Level 1: Recital and rehearsal halls and the Leahy gate grand entrance to the stadium.
Level 2: A large music library, to be relocated from the Hesburgh Library, classrooms and rehearsal and tutoring rooms.
Level 3: A 350-person club/lounge.
Level 4: Department of Music offices, practice rooms and storage.
Level 5: The Sacred Music Program, offices, organ practice rooms and storage.
Level 6: Mechanical, with a scoreboard on the exterior.
East building
Offices and laboratories for the Departments of Anthropology andPsychology, which are housed in a variety of buildings on campus, now will be in one place and located closer to other social sciences departments, the College of Scienceand international institutes.
Level 1: A digital media center with a 2,000-square-foot studio and production, teaching, learning, research and scholarship facilities for use by faculty, students, University Communications, athletics and information technology will position Notre Dame as a national leader in what is a rapidly expanding and increasingly important component of higher education. A control room will support faith-based programming, such as Masses at the Basilica of the Sacred Heart, as well as athletics events, performing arts presentations and academic lectures and speeches.
Level 2: Anthropology offices, administrative space, conference and tutoring areas and multifunction research and teaching labs.
Levels 3, 4 and 5: Psychology offices, classrooms, labs, computer rooms and a student lounge.
Level 6: Mechanical support.
Level 7: Outdoor club seating for football, outdoor terraces and a large space that will double as a club area and flexible classroom.
Level 8: Outdoor club seating for football.
Level 9: Working press box, radio booths and a club area with indoor and outdoor premium seating for football.
For more on the Campus Crossroads Project, visit: http://crossroads.nd.edu.
Related Stories
| Sep 21, 2022
Demand for design services accelerates
Demand for design services from U.S. architecture firms grew at an accelerated pace in August, according to a new report today from The American Institute of Architects (AIA).
K-12 Schools | Sep 21, 2022
Architecture that invites everyone to dance
If “diversity” is being invited to the party in education facilities, “inclusivity” is being asked to dance, writes Emily Pierson-Brown, People Culture Manager with Perkins Eastman.
| Sep 20, 2022
NIBS develops implementation plan for digital transformation of built environment
The National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS) says it has developed an implementation and launch plan for a sweeping digital transformation of the built environment.
| Sep 20, 2022
New Long Beach office building reflects Mid-Century Modern garden-style motif
The new Long Beach, Calif., headquarters of Laserfiche, a provider of intelligent content management and business process automation software, was built on a brownfield parcel previously considered undevelopable.
| Sep 19, 2022
New York City construction site inspections, enforcement found ‘inadequate’
A new report by the New York State Comptroller found that New York City construction site inspections and regulation enforcement need improvement.
| Sep 16, 2022
Fairfax County, Va., considers impactful code change to reduce flood risk
Fairfax County, Va., in the Washington, D.C., metro region is considering a major code change to reduce the risk from floods.
Multifamily Housing | Sep 15, 2022
Heat Pumps in Multifamily Projects
RMI's Lacey Tan gives the basics of heat pumps and how they can reduce energy costs and carbon emissions in apartment projects.
| Sep 15, 2022
Monthly construction input prices dip in August
Construction input prices decreased 1.4% in August compared to the previous month, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Producer Price Index data released today.
| Sep 15, 2022
First LEED Platinum, net zero and net zero water synagogue opens
Kol Emeth Center, the world’s first LEED Platinum, net zero and net zero water synagogue, opened recently in Palo Alto, Calif.
| Sep 14, 2022
Fires on Amazon warehouse roofs seemingly caused by faulty PV installations
Amazon has made installing solar panels on rooftops a key part of its ESG strategy, but a series of events last year show how challenging greening up major facilities can be.