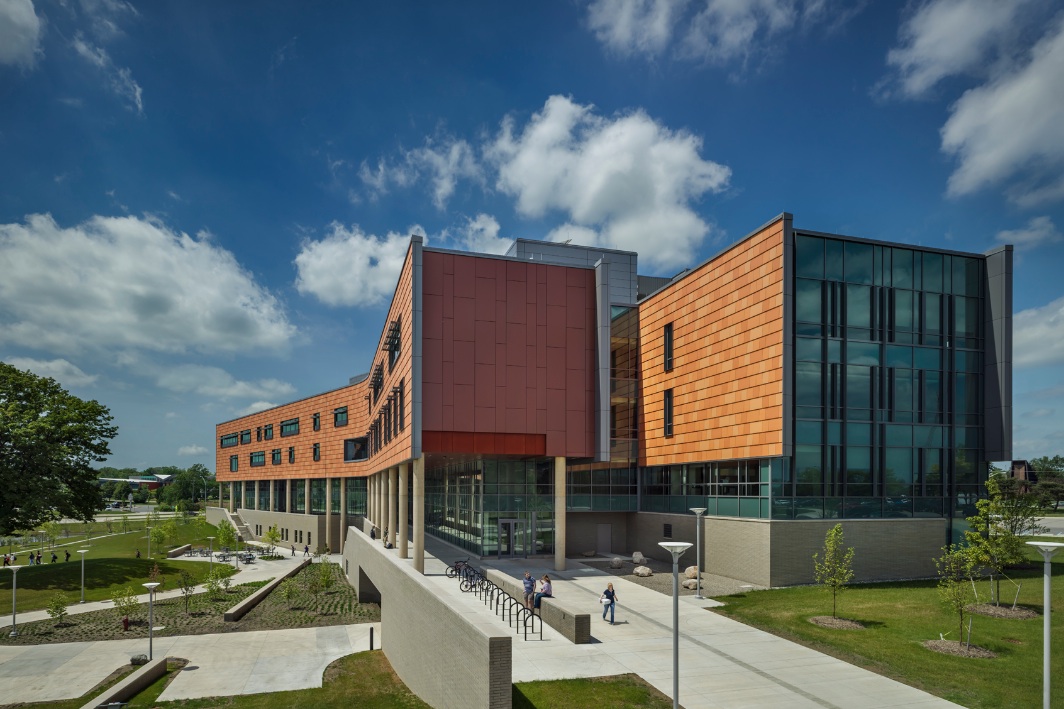
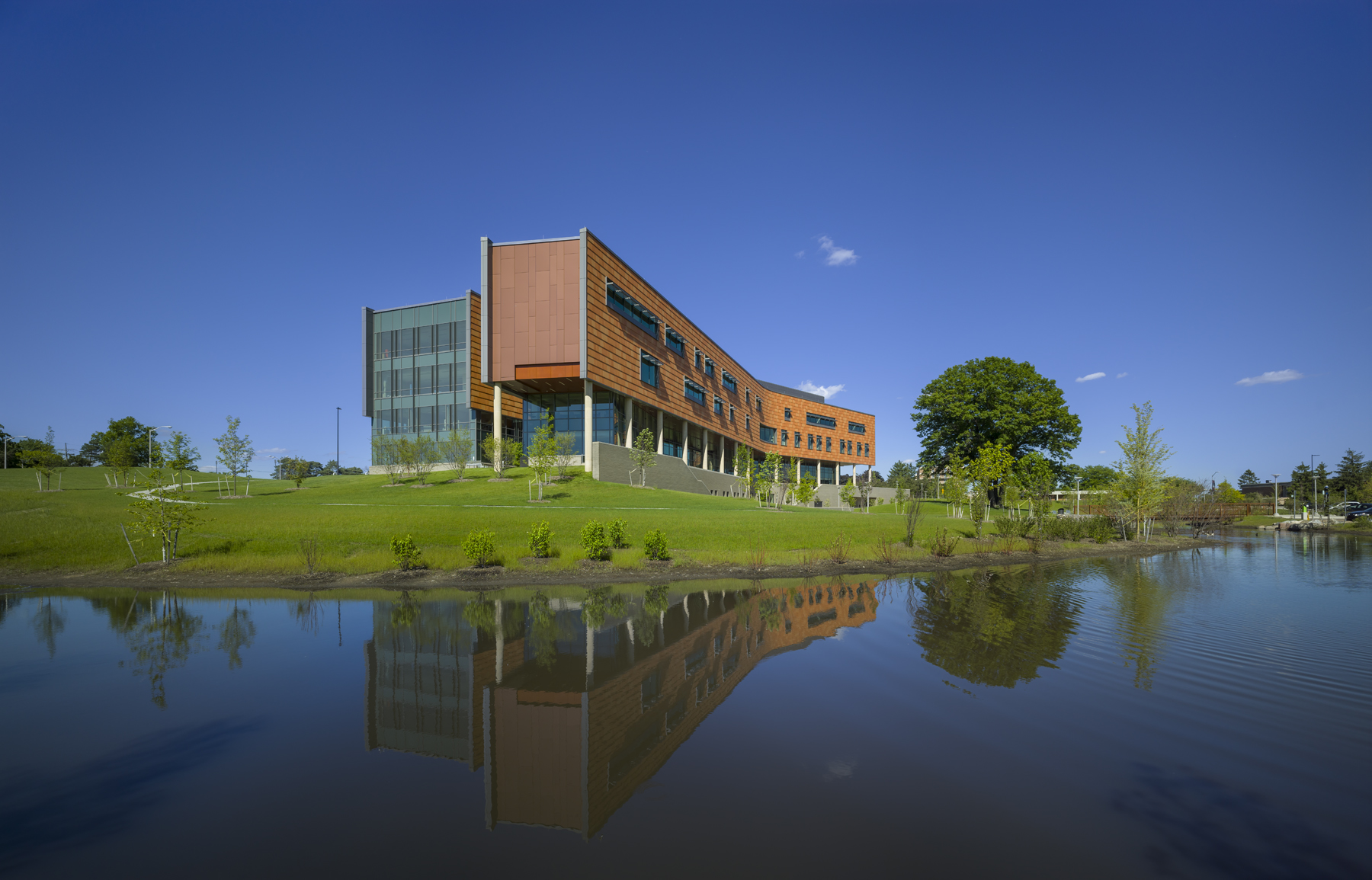
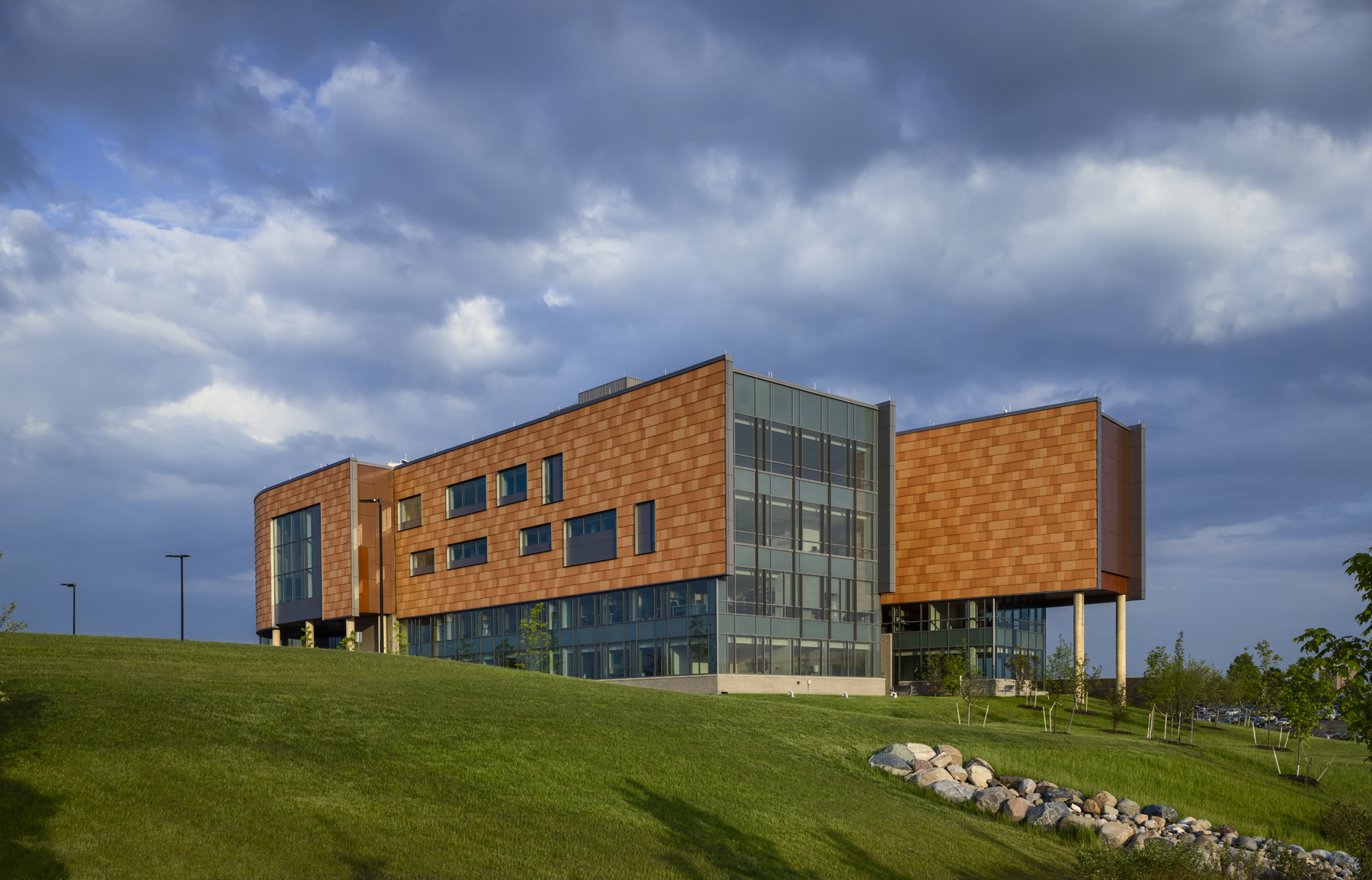
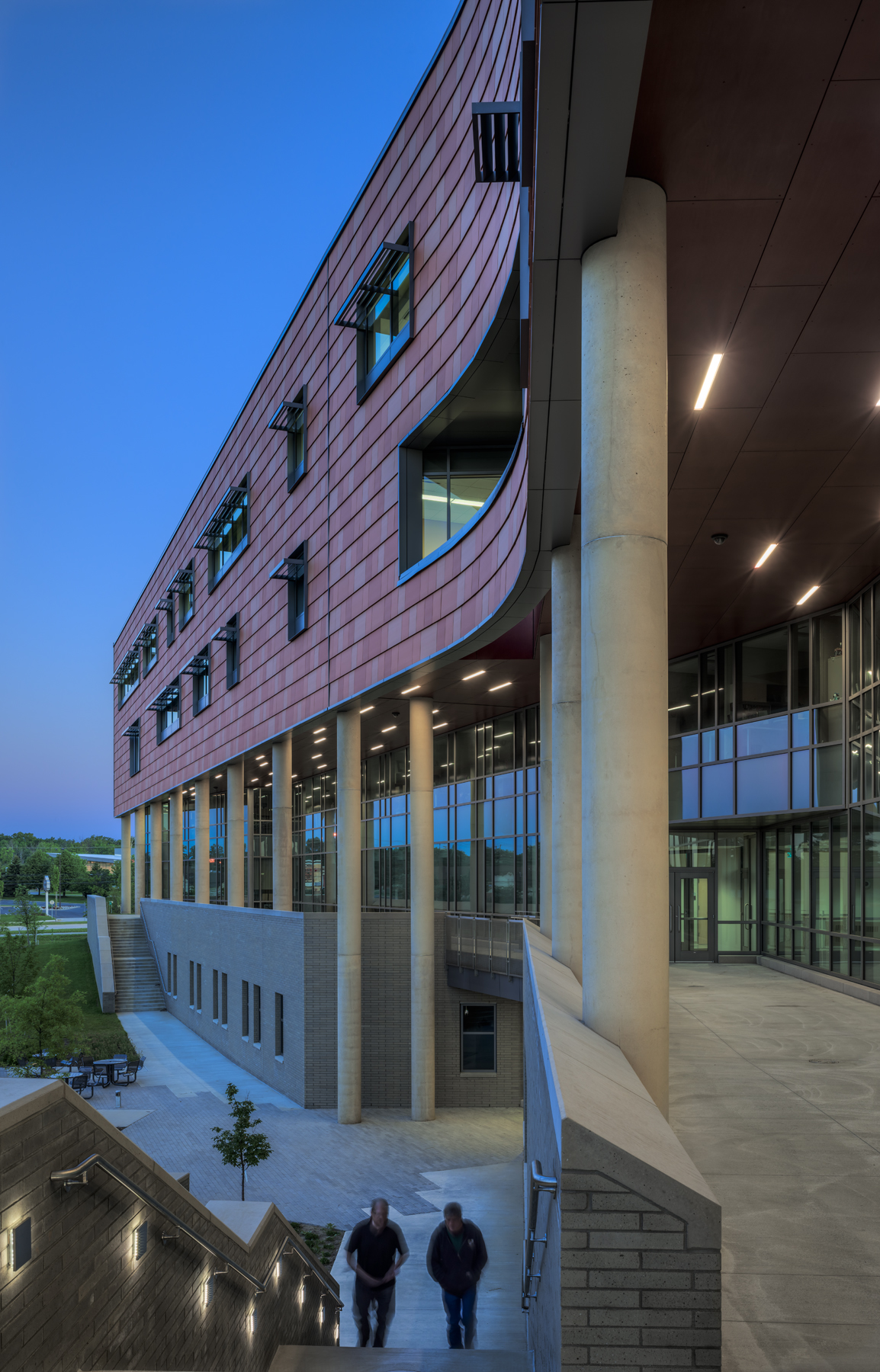
The new $64 million Oakland University Human Health Building has become the first LEED Platinum certified building on a university campus in Michigan.
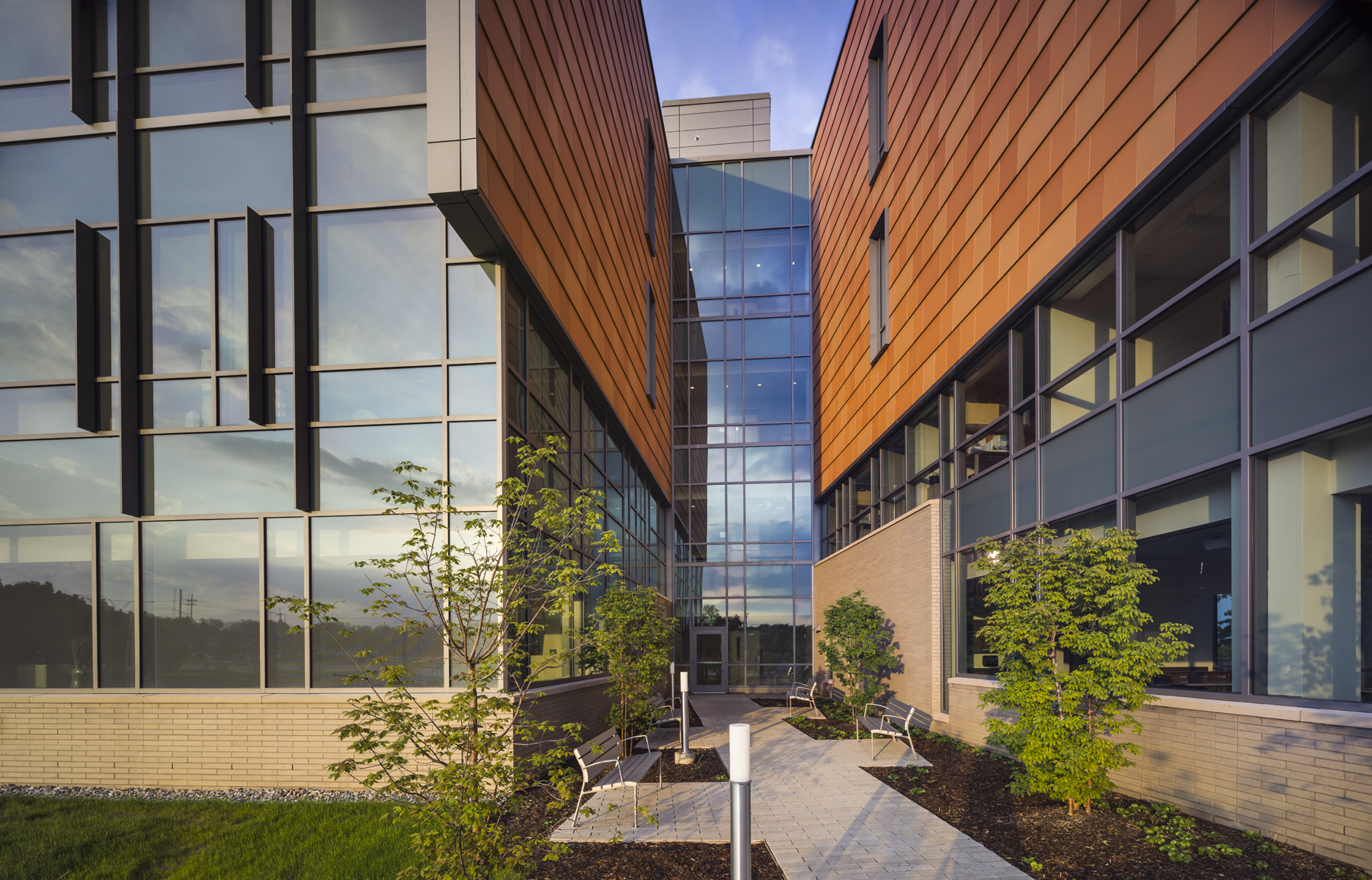
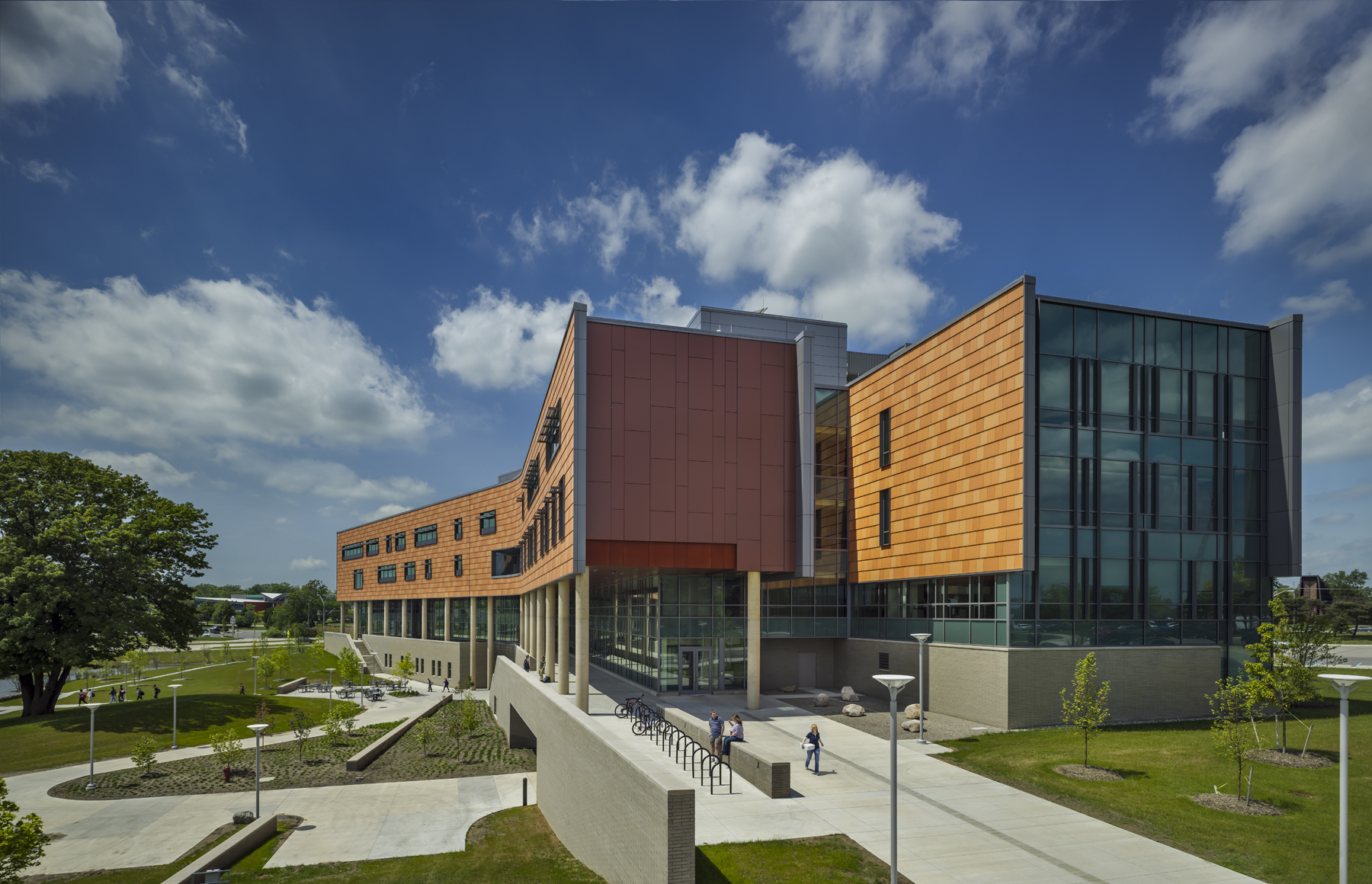
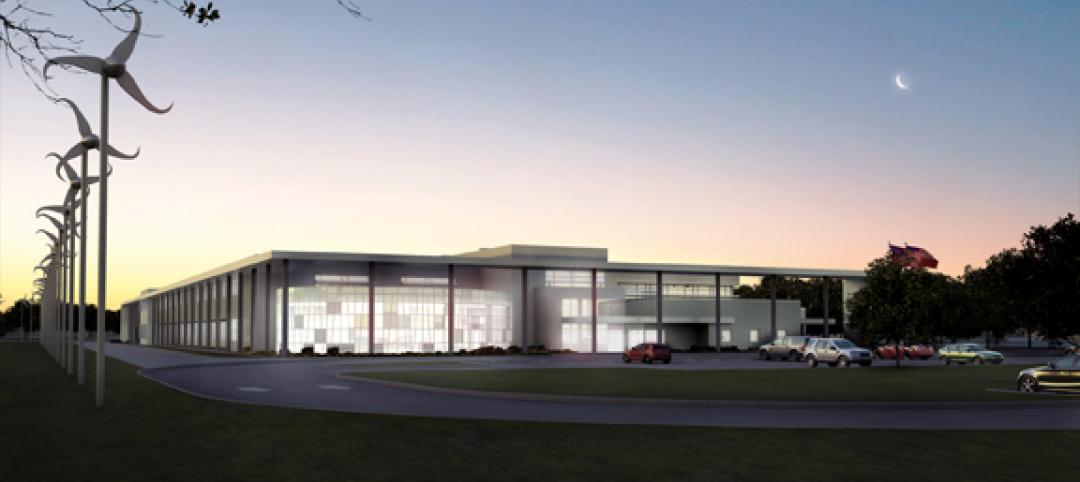
Designed by SmithGroupJJR, the 160,260-square-foot, five-story, terra cotta-clad building, built on the former site of a parking lot and an untended natural wetland, today features some of the industry’s most innovative, energy-efficient building systems and advanced sustainable design features.
The project’s primary funding of $40 million came from the State of Michigan legislature’s Capital Outlay Program. Then, to achieve the highest LEED rating – Platinum -- while staying on budget, Oakland University, assisted by SmithGroupJJR, successfully pursued a $2.7 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy, allowing the project to proceed with a full geothermal and renewable energy system.
“The collaboration between Oakland University, SmithGroupJJR and The Christman Company truly benefitted our ability to design and build the most energy-efficient and sustainable building on any college campus in Michigan,” said Terry Stollsteimer, associate vice president, facilities management, Oakland University.
The facility’s energy systems are designed to save an estimated 35% in energy costs annually compared to the LEED prescribed “baseline” building.
A geothermal field, consisting of 340 wells built 320 feet underneath the university’s main parking lot, uses the earth as an energy source for heat pumps that efficiently provide heating and cooling for the building.
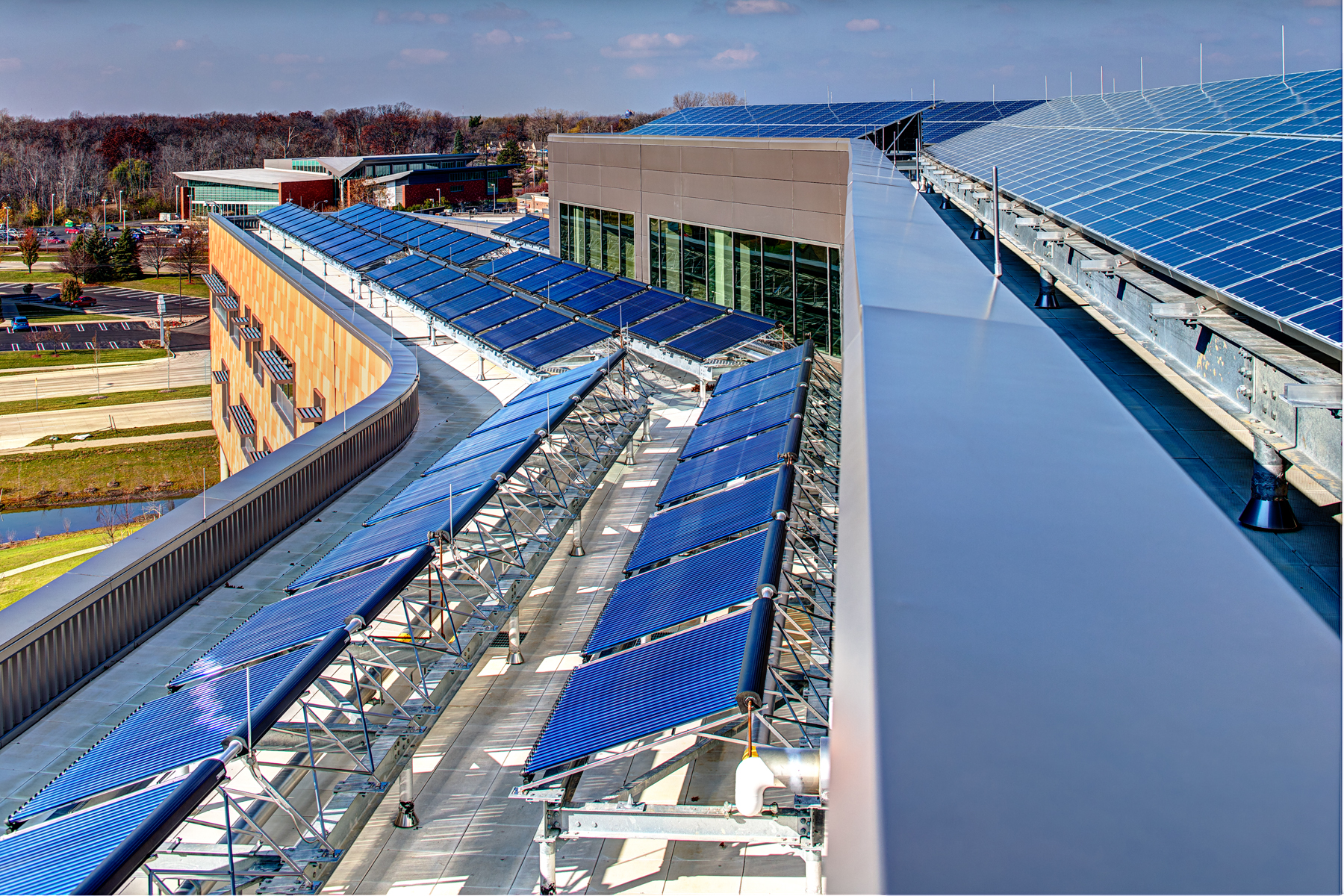
A total of 117 vacuum tube solar thermal panels provide “free” heat for the building in the wintertime, the desiccant dehumidification system in the summertime, and domestic water heating all year round. Four, 25,000-gallon underground tanks store any excess solar generated hot water until it’s needed.
A rooftop photovoltaic system, comprised of more than 200 solar panels covering 3,600 square feet, provides 45 kilowatts or 3% of the building’s power.
“Environmentally friendly buildings have shown to have positive effects on the quality of their occupants’ health, so it was easy for the university to decide that the new Human Health Building should be highly sustainable,” said Chris Purdy, AIA, LEED AP, SmithGroupJJR principal-in-charge for the project. SmithGroupJJR provided architectural design and development; mechanical, electrical, plumbing, structural and civil engineering; lab planning; interior design; landscape design and LEED certification and documentation.
The building’s environmental friendliness doesn’t end with the innovative, energy-efficient building systems. Outside, a grand porch created by the overhang of the upper floors protects faculty offices from the solar heat gain of a southern exposure. Exterior offices are outfitted with vertical sunshades and fritted glass to reduce glare and cut down on outside heat. Rainwater from the roof is collected and stored in a below-grade cistern, and used for site irrigation.
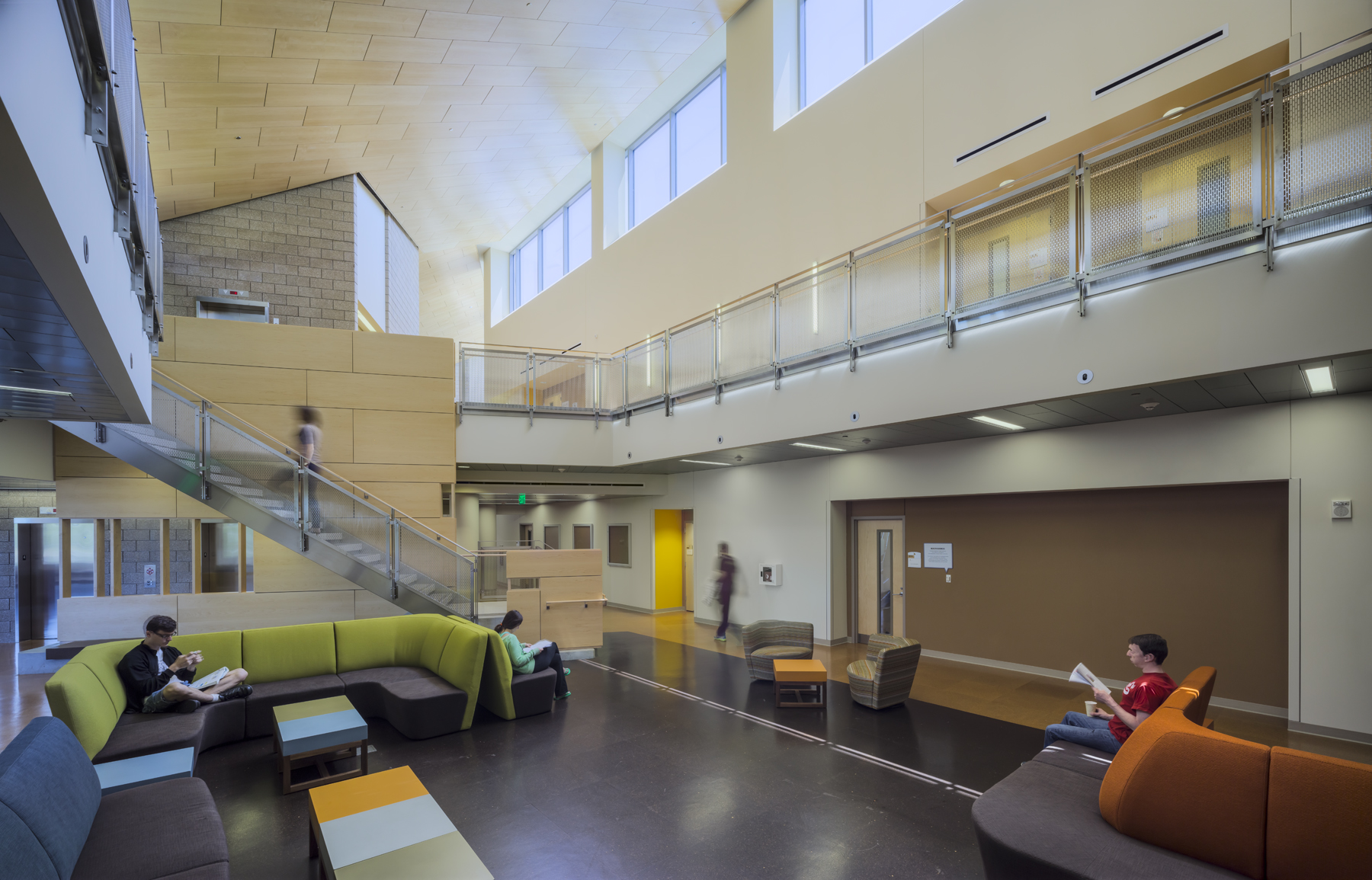
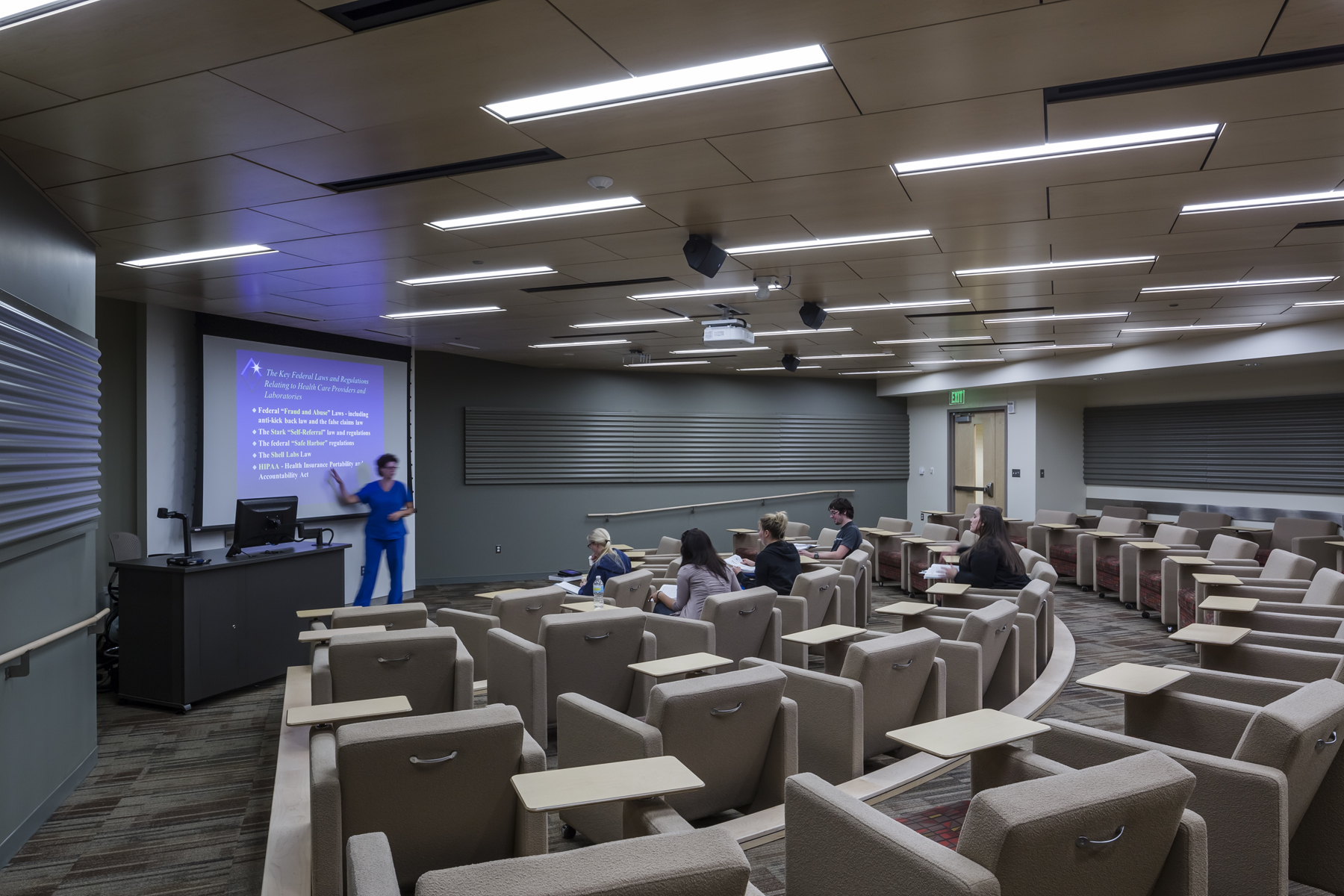
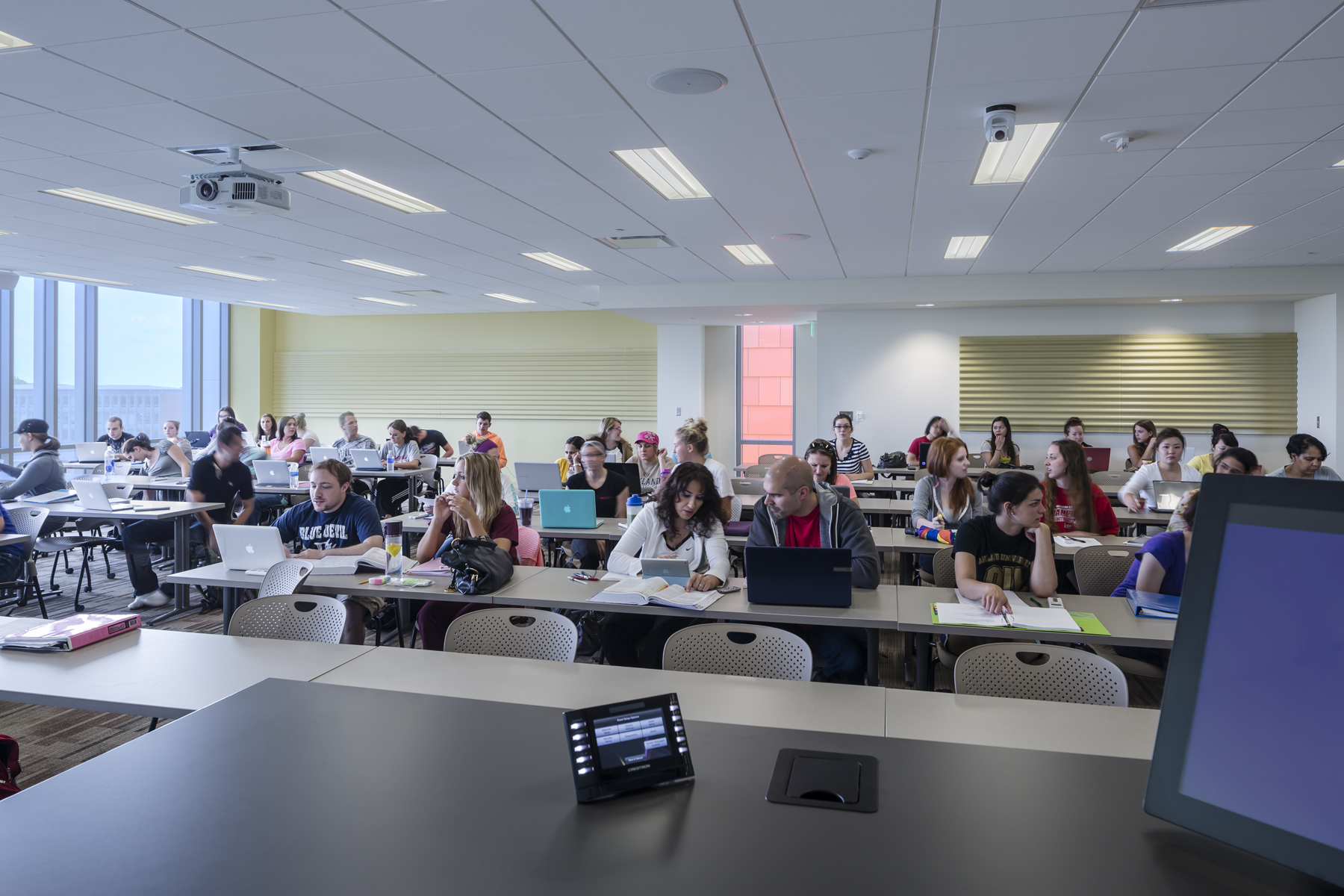
Inside the building, an elongated floor plan with floor-to-ceiling windows allows for abundant access to natural light and views of outdoor spaces. The interior’s use of recycled, regional and low-VOC materials includes sealed cork floors and bamboo cabinets, and walls are made with insulated cinderblock to reduce energy costs. Daylight and occupant sensors are used throughout the building to reduce energy use by occupants.
Directly south of the building is a towering, 100-year-old Oak tree that was integrated into the site design, rather than cleared. The site’s natural wetland was rehabilitated with native vegetation and invasive species were removed, thereby creating an outdoor lounge and gathering place for students.
About the Human Health Building, Oakland University
The Human Health Building (HHB) was conceived after increased student enrollment caused the university’s School of Nursing and School of Health Sciences to outgrow their separate facilities. The university envisioned a new building on the northwest corner of its 1,441-acre campus to allow the two schools a collaborative setting and an unprecedented opportunity for interaction among students, facility and community partners. Completed in August 2012, the HHB is the first structure constructed as part of the university’s proposed Health Quadrant Campus Master Plan, developed by SmithGroupJJR.
The HHB pairs advanced classrooms and hands-on instructional spaces with amenities that replicate those found in hospitals and community health centers – including a public clinic, simulation labs, and clinical and physical therapy labs. An emphasis was placed on student spaces; two-story, natural light-filled, “living room” areas on the fourth floor give students a place to gather before or after class. To learn more about the HHB from the design and construction team, go to: http://www.oakland.edu/?id=26078&sid=228
About SmithGroupJJR
SmithGroupJJR (www.smithgroupjjr.com) is a national leader in sustainable design, with 361 LEED Accredited Professionals on staff. The Oakland University HHB marks SmithGroupJJR’s 90th LEED certified project and its 11th LEED Platinum certification. The firm’s nationally recognized Learning Practice has completed the planning and design of educational facilities on over 350 campuses worldwide.
About LEED
The U.S. Green Building Council's LEED green building certification system is the foremost program for the design, construction and operation of green buildings. By using less energy, LEED-certified buildings save money for families, businesses and taxpayers; reduce greenhouse gas emissions; and contribute to a healthier environment for residents, workers and the larger community. For more information, visit www.usgbc.org.
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
Carnegie Hall vaults into the 21st century with a $200 million renovation
Historic Carnegie Hall in New York City is in the midst of a major $200 million renovation that will bring the building up to contemporary standards, increase educational and backstage space, and target LEED Silver.
| May 17, 2011
Redesigning, redefining the grocery shopping experience
The traditional 40,000- to 60,000-sf grocery store is disappearing and much of the change is happening in the city. Urban infill sites and mixed-use projects offer grocers a rare opportunity to repackage themselves into smaller, more efficient, and more convenient retail outlets. And the AEC community will have a hand in developing how these facilities will look and operate.
| May 17, 2011
Architecture billings index fell in April, hurt by tight financing for projects
The architecture billings index, a leading indicator of U.S. construction activity, fell in April, hurt by tight financing for projects. The architecture billings index fell 2.9 points last month to 47.6, a level that indicates declining demand for architecture services, according to the American Institute of Architects.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 17, 2011
Gilbane partners with Steel Orca on ultra-green data center
Gilbane, along with Crabtree, Rohrbaugh & Associates, has been selected to partner with Steel Orca to design and build a 300,000-sf data center in Bucks County, Pa., that will be powered entirely through renewable energy sources--gas, solar, fuel cells, wind and geo-thermal. Completion is scheduled for 2013.
| May 17, 2011
Should Washington, D.C., allow taller buildings?
Suggestions are being made that Washington revise its restrictions on building heights. Architect Roger Lewis, who raised the topic in the Washington Post a few weeks ago, argues for a modest relaxation of the height limits, and thinks that concerns about ruining the city’s aesthetics are unfounded.
| May 17, 2011
The New Orleans master plan
At an afternoon panel during last week's AIA National Conference in New Orleans, Goody Clancy Principal David Dixon and Manning Principal W. Raymond Manning shared their experiences creating the New Orleans Master Plan, a document that sets a new course for the city, from land use and transportation planning to environmental protection.
| May 17, 2011
Do these buildings look like buffalo to you?
It’s hard to contemplate winter now that we’re mid-spring, but when the seasons change, ice skaters in Winnipeg will be able to keep warm in plywood shelters designed by Patkau Architects. The designers created temporary shelters inspired by animal behavior—specifically, buffalo bracing against the wind. Check them out.
| May 16, 2011
USGBC and AIA unveil report for greening K-12 schools
The U.S. Green Building Council and the American Institute of Architects unveiled "Local Leaders in Sustainability: A Special Report from Sundance," which outlines a five-point national action plan that mayors and local leaders can use as a framework to develop and implement green schools initiatives.