Federal and state incentives have sparked renewed interest in solar photovoltaic systems as a way for K-12 schools to lower their utility bills and, at the same time, educate students about the benefits of solar and other alternative energy sources.
Solar PV providers in California, Colorado, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Utah are partnering with school districts to install solar equipment and develop a teaching curriculum. Funding can come from a variety of government and private sources, with the bulk coming from the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act of 2009.
Some organizations are sponsoring their own solar-school initiatives in conjunction with the National Energy Education Development Project (NEED). The Walmart Foundation is partnering with NEED and the Foundation for Environmental Education to implement solar schools in five cities: Chicago, Los Angeles, Minneapolis, Seattle, and Washington, D.C.
UTAH PUTS THE SUN TO WORK
Utah’s Solar for Schools program was launched in 2010, after the state received ARRA funding to install and promote renewable energy. The Salt Lake City office of Johnson Controls, Inc. won a $3 million bid to install solar in 73 Utah schools. Thus far, 55 installations had been completed.
Oscar Rangel, JCI’s manager of public-sector solutions, based in Denver, says the company’s system will save $7.75 per watt, for a potential annual savings of $800-1,200. Rangel stresses that there’s more to the program than putting panels on the roof: “There’s also an educational component that involves the teachers, the kids, and the administration.”
In an intensive one-day workshop developed by Johnson Controls and the National Energy Foundation, teachers from around the Beehive State were exposed to curriculum materials that are correlated to state and national standards. NEF educators provide on-site teacher training geared to children from elementary school through high school.
“The labs are very hands-on, with activities that engage the students in learning not just about solar, but all different kinds of alternative energy,” says one participant, Laura Wheeler, who teaches middle school and high school in Morgan, Utah.
In one lab, students learn how to configure solar panels to generate the most power. (Another lab challenges them to see who can build the best wind generator.) There’s also a program where students patrol the building to monitor and report on energy usage. Johnson Controls is supplying software that links all the solar schools in Utah, allowing students to compare their school’s performance with that of others.
A typical installation consists of a 5.3-kW solar PV module, which can provide enough electricity to power the computer lab and a few classrooms or a library, Rangel says. That may not sound like much, but don’t tell that to teacher Laura Wheeler. “Even if we’re just lighting a library with solar, that’s a big deal to our school,” she says. “We’re in a very small, rural school district, so every penny we save goes a long way.”
CALIFORNIA RAMPS UP SOLAR IN SCHOOLS
With the California Solar Initiative, a statewide solar rebate program, California’s public sector is forecasted to save $2.5 billion from solar installations over the 30-year life of the systems. Educational institutions are expected to save approximately $1.5 billion of the total, according to SunPower Corp., a solar provider based in San Jose, Calif. The California School Boards Association recently announced Solar Schools, a program that supports school districts in developing efficient solar projects. Districts borrow ARRA funds and the federal government subsidizes the interest rate, meaning that loans are repaid at an average rate of 1.5%.
Interest in solar for schools has been accelerating due to a growing emphasis on energy conservation. “Currently, we have installations planned or under way in more than 90 schools,” says Bill Kelly, SunPower’s managing director. “It’s keeping us busy along with local electricians, steel fabricators, and erectors, so we’re also stimulating the local economy.”
The SunPower systems range from 100 kW to 1,000 kW. “The larger systems are for high schools,” Kelly says. “On average, in the schools we’re working with, 75-80% of the electric bill is offset or reduced by solar.”
Most solar panels are designed for parking lots rather than rooftops, he says. The panels form a canopy over the cars, with the secondary benefit of providing shade during hot weather.
As in Utah, California’s school districts want to not only invest in solar but also bring information about the technology into the classroom.
“Many of the school districts have engineering academies, and we’re working with them to develop a renewable energy curriculum,” says Kelly.
Recently, 16 high school students from the San Ramon Valley Unified School District completed a two-week course sponsored by SunPower.
“They learned everything about solar that you could cram into two weeks,” says SunPower’s Madeleine Maguire. “The idea is to create solar ambassadors so that they can teach their peers about this technology.”
CHECKING SOLAR’S AFFORDABILITY
With solar, first cost is still the issue for property owners and their Building Teams. The price of PV panels has fallen in the last two years due to greater efficiencies in manufacturing and technology, as well as increased competition among a growing number of suppliers.
According to the market intelligence firm IHS iSuppli, in 2009 the cost per watt for a PV solar panel was nearly $2.50. By 2015, that cost is expected to drop to as low as $1, or roughly $200 per panel. Installation prices, too, are expected to decrease about 10% a year—from $5 per watt to around $3 per watt by 2015, according to IHS. The worldwide PV market is poised to double by 2015, with the U.S. market growing steadily.
SunPower’s Kelly agrees that first cost is a constraint: “Even though solar has great economics for the long term, building owners need to watch their budgets.” Still, he urges Building Teams not to miss out on rebates by waiting for prices to go down. “In California, at least, the sooner you install it the bigger the incentive you get,” he says.
SIDEBAR: Science School Raises the Green Bar
The Walking Mountains Science Center in Avon, Colo., is on target to be certified LEED Platinum, but that wasn’t the Building Team’s primary goal. “We didn’t want to just talk the talk,” says Barry Monroe, LEED AP, project manager for local builder R.A. Nelson and Associates. “We wanted to do everything we could to make the building as green and as energy efficient as possible.” The facility will act as an experiential learning center for adults and children, as well as a model of sustainability.
Designed by Avon-based architects Zehren & Associates, the building produces 42% of its own electricity on site. PV solar panels on two south-facing roofs create energy, and a heat capture system harvests excess heat from the electrical equipment room and transfers it to domestic hot water. The sun also generates heat for the radiant in-floor system.
“Sun shades are part of the solar component and work in conjunction with daylighting to reduce heat gain inside the building,” Monroe says. The building is not air conditioned.
Students will monitor the building’s energy and water usage via a computerized dashboard. The solar system is expected to save about $6,000 a year in energy costs.
Related Stories
Multifamily Housing | Jun 28, 2023
Sutton Tower, an 80-story multifamily development, completes construction in Manhattan’s Midtown East
In Manhattan’s Midtown East, the construction of Sutton Tower, an 80-story residential building, has been completed. Located in the Sutton Place neighborhood, the tower offers 120 for-sale residences, with the first move-ins scheduled for this summer. The project was designed by Thomas Juul-Hansen and developed by Gamma Real Estate and JVP Management. Lendlease, the general contractor, started construction in 2018.
Architects | Jun 27, 2023
Why architects need to think like developers, with JZA Architecture's Jeff Zbikowski
Jeff Zbikowski, Principal and Founder of Los Angeles-based JZA Architecture, discusses the benefits of having a developer’s mindset when working with clients, and why architecture firms lose out when they don’t have a thorough understanding of real estate regulations and challenges.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Average U.S. apartment rent reached all-time high in May, at $1,716
Multifamily rents continued to increase through the first half of 2023, despite challenges for the sector and continuing economic uncertainty. But job growth has remained robust and new households keep forming, creating apartment demand and ongoing rent growth. The average U.S. apartment rent reached an all-time high of $1,716 in May.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Dallas high-rise multifamily tower is first in state to receive WELL Gold certification
HALL Arts Residences, 28-story luxury residential high-rise in the Dallas Arts District, recently became the first high-rise multifamily tower in Texas to receive WELL Gold Certification, a designation issued by the International WELL Building Institute. The HKS-designed condominium tower was designed with numerous wellness details.
University Buildings | Jun 26, 2023
Addition by subtraction: The value of open space on higher education campuses
Creating a meaningful academic and student life experience on university and college campuses does not always mean adding a new building. A new or resurrected campus quad, recreational fields, gardens, and other greenspaces can tie a campus together, writes Sean Rosebrugh, AIA, LEED AP, HMC Architects' Higher Education Practice Leader.
Standards | Jun 26, 2023
New Wi-Fi standard boosts indoor navigation, tracking accuracy in buildings
The recently released Wi-Fi standard, IEEE 802.11az enables more refined and accurate indoor location capabilities. As technology manufacturers incorporate the new standard in various devices, it will enable buildings, including malls, arenas, and stadiums, to provide new wayfinding and tracking features.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
Office Buildings | Jun 26, 2023
Electric vehicle chargers are top priority for corporate office renters
Businesses that rent office space view electric vehicle (EV) charging stations as a top priority. More than 40% of companies in the Americas and EMEA (Europe, the Middle East and Africa) are looking to include EV charging stations in future leases, according to JLL’s 2023 Responsible Real Estate study.
Laboratories | Jun 23, 2023
A New Jersey development represents the state’s largest-ever investment in life sciences and medical education
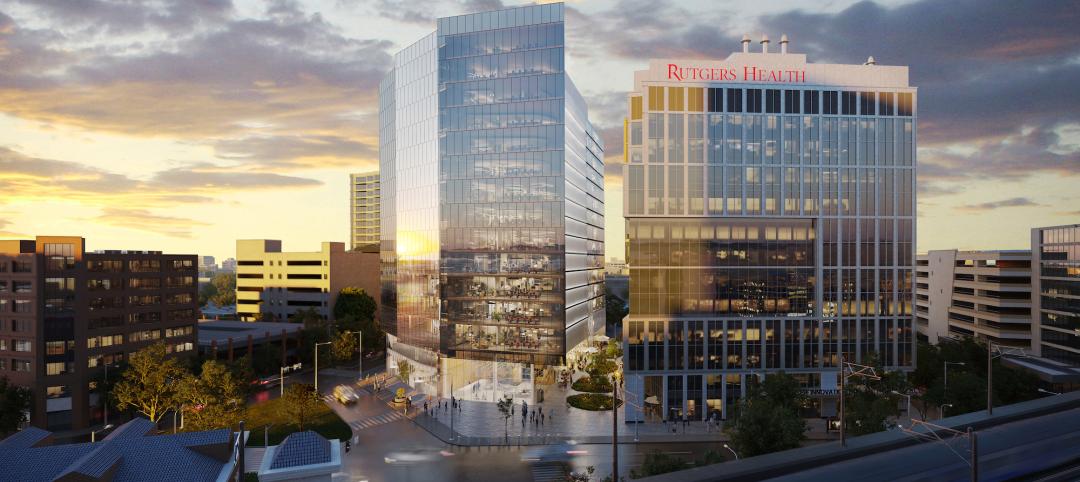
In New Brunswick, N.J., a life sciences development that’s now underway aims to bring together academics and researchers to work, learn, and experiment under one roof. HELIX Health + Life Science Exchange is an innovation district under development on a four-acre downtown site. At $731 million, HELIX, which will be built in three phases, represents New Jersey’s largest-ever investment in life sciences and medical education, according to a press statement.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Jun 22, 2023
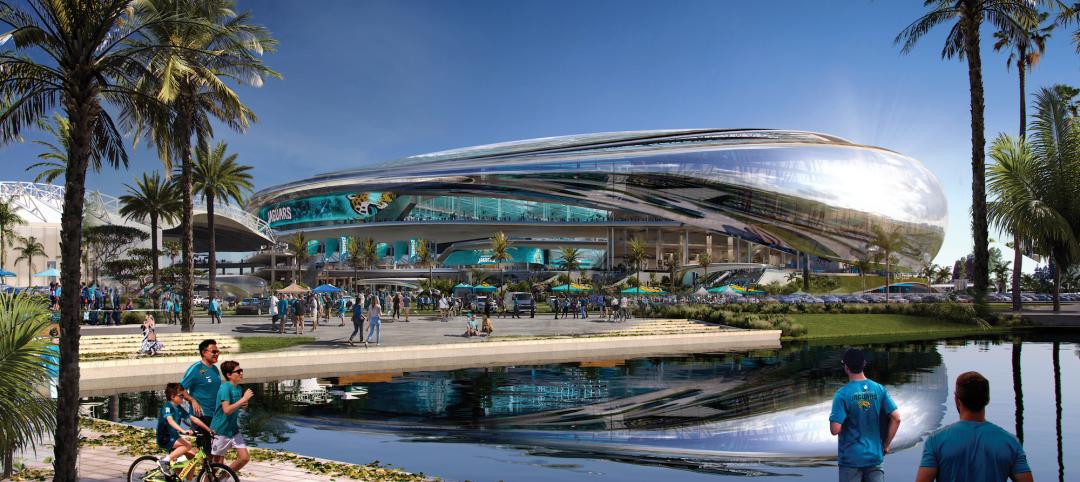
NFL's Jacksonville Jaguars release conceptual designs for ‘stadium of the future’
Designed by HOK, the Stadium of the Future intends to meet the evolving needs of all stadium stakeholders—which include the Jaguars, the annual Florida-Georgia college football game, the TaxSlayer.com Gator Bowl, international sporting events, music festivals and tours, and the thousands of fans and guests who attend each event.