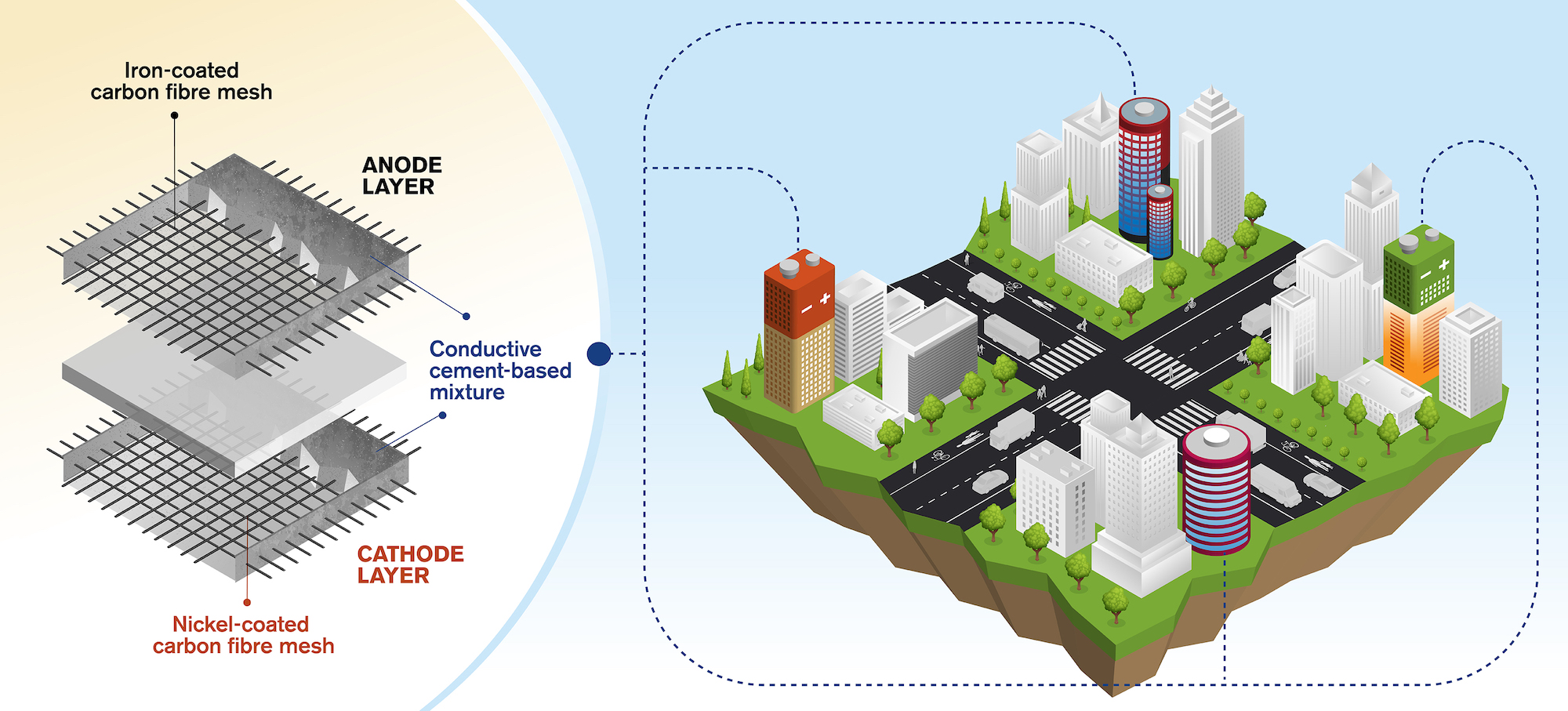
Researchers from the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering at Chalmers University of Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden, have created a concept for rechargeable batteries made of cement.
The concept involves a cement-based mixture with small amounts of short carbon fibers added to increase conductivity and flexural toughness. Embedded within this mixture is a metal-coated carbon fiber mesh—iron for the anode and nickel for the cathode. Several combinations for the electrodes were tested before the iron anode and nickel-based oxide cathode were found to yield the best results. Additionally, researchers had to experiment with different ratios of carbon fiber before finding an optimal mixture of around 0.5% carbon fiber to improve the cement-based mixture’s conductivity for the electrolyte.
The resulting cement-based battery has an average density of 7 watt-hours per square meter during six charge and discharge cycles—low in comparison to commercial batteries, but still potentially very beneficial to the built environment considering the large volume at which the battery could be constructed when used in buildings, bridges, dams, and other concrete structures.
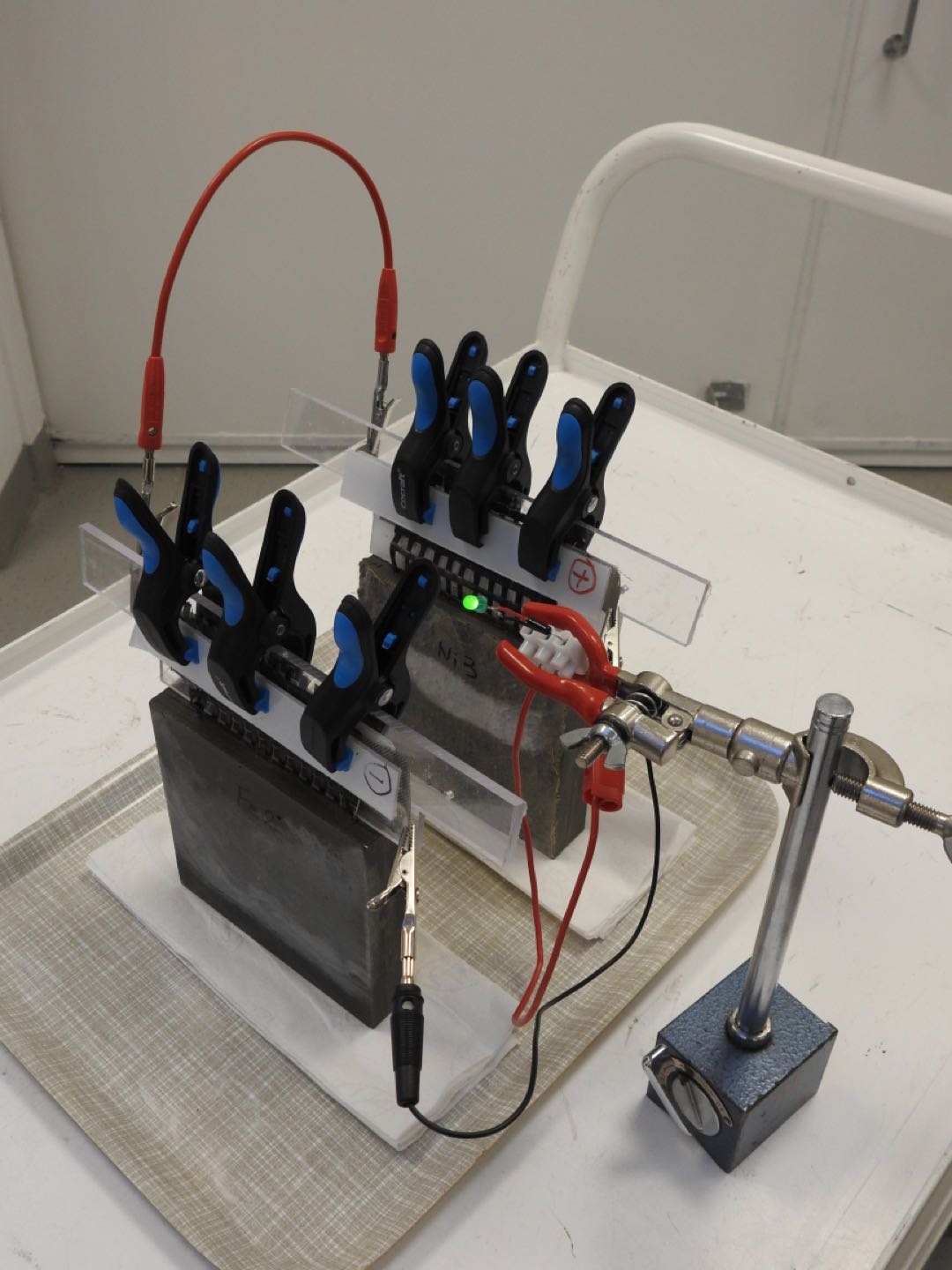
The research team—led by Chalmers Professor Luping Tang and Emma Zhang, PhD, formerly with the university, now Senior Development Scientist at Delta of Sweden—envisions possible applications for the concept that range from powering LEDs, providing 4G connections in remote areas, and cathodic protection against corrosion in concrete infrastructure.
“It could also be coupled with solar cell panels to provide electricity and become the energy source for monitoring systems in highways or bridges, where sensors operated by a concrete battery could detect cracking or corrosion,” said Zhang.
Technical questions that need to be answered before commercialization of the concrete technology include extending the service life of the battery and the development of recycling techniques. The batteries would need to either be able to match the 50-100 year life of a typical concrete building or be made easier to exchange and recycle when their service life is over.
Despite these obstacles, the researchers are optimistic the concept has plenty to offer as a future building material that contributes to additional functions such as renewable energy sources.
Related Stories
AEC Tech Innovation | Mar 9, 2022
Meet Emerge: WSP USA's new AEC tech incubator
Pooja Jain, WSP’s VP-Strategic Innovation, discusses the pilot programs her firm’s new incubator, Emerge, has initiated with four tech startup companies. Jain speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield about the four AEC tech firms to join Cohort 1 of the firm’s incubator.
Great Solutions | Nov 22, 2021
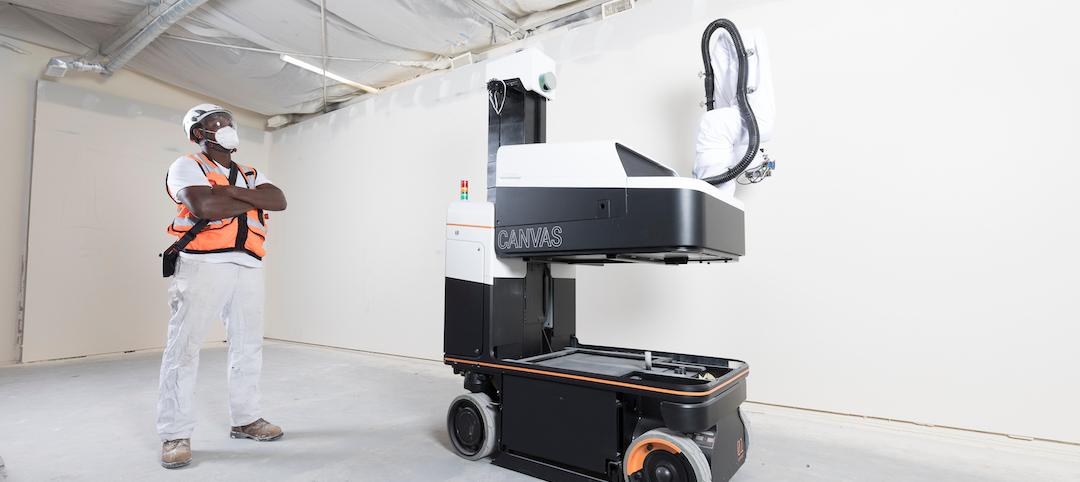
Drywall robots take the risk out of the finishing process
Canvas is using robots to complement the work already being done by drywall professionals.
Great Solutions | Sep 23, 2021
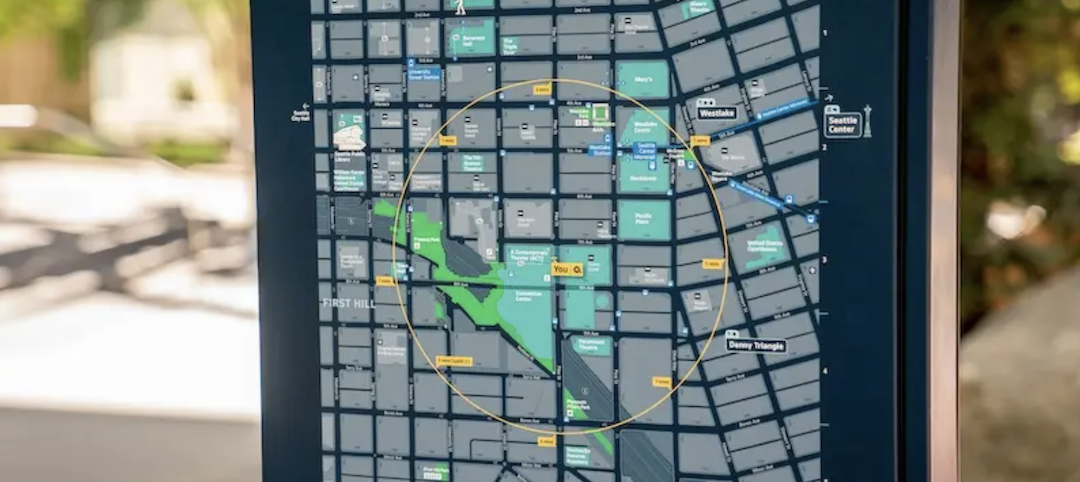
Seattle looks to become America’s most walkable city with a new citywide wayfinding system
Seamless Seattle will support the Seattle Department of Transportation’s commitment to increase the percentage of trips made by walking to 35% by 2035.
Great Solutions | Jul 9, 2021
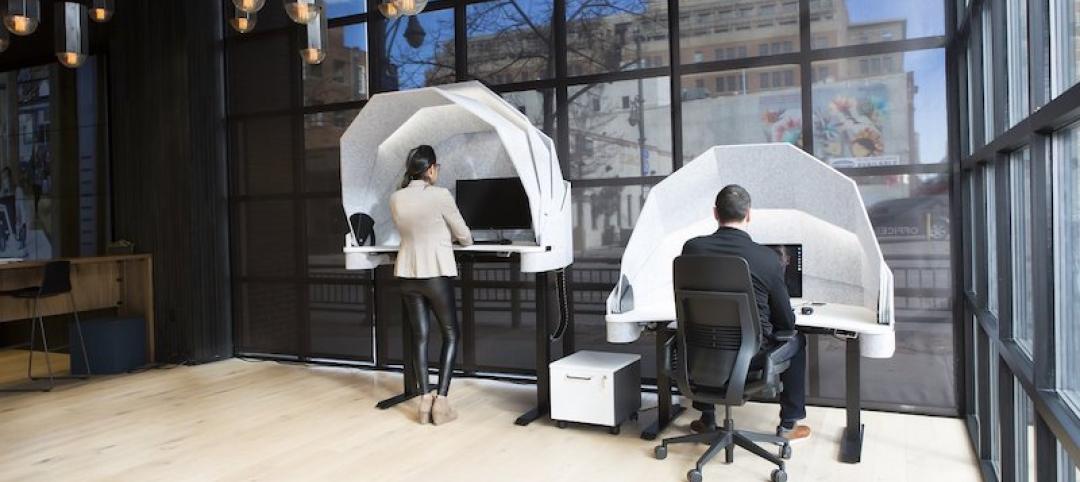
MojoDesk creates a new solution for managing open office distractions
The MojoDome allows for a private work space while also maintaining a collaborative environment.
Great Solutions | Mar 18, 2021
Follow the leader: New following technology better equips robots for the jobsite
New proof-of-concept from Piaggio Fast Forward and Trimble enables robots and machines to follow humans.
Great Solutions | Feb 11, 2021
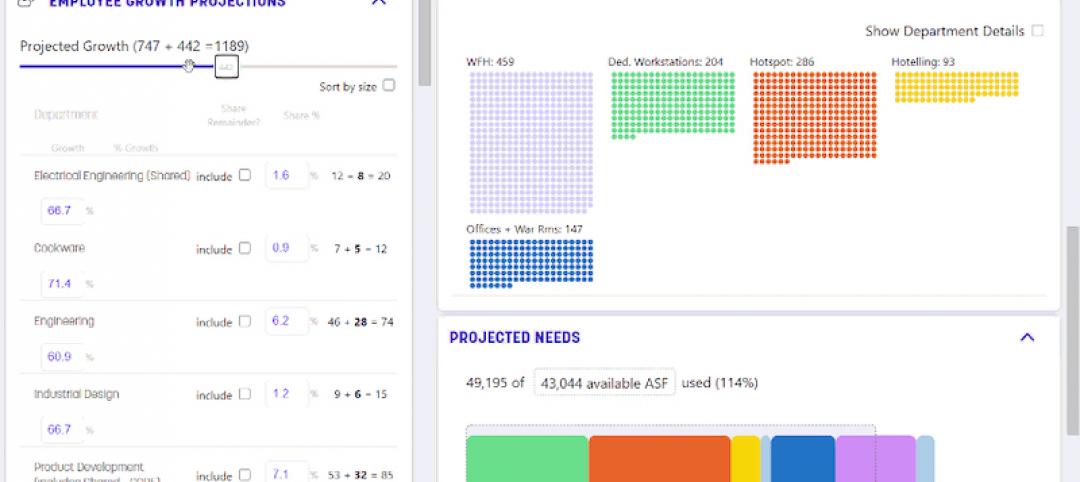
Simplifying the return to the office
A new web-based tool from Sasaki takes the guesswork out of heading back to the workplace.
Great Solutions | Oct 6, 2020
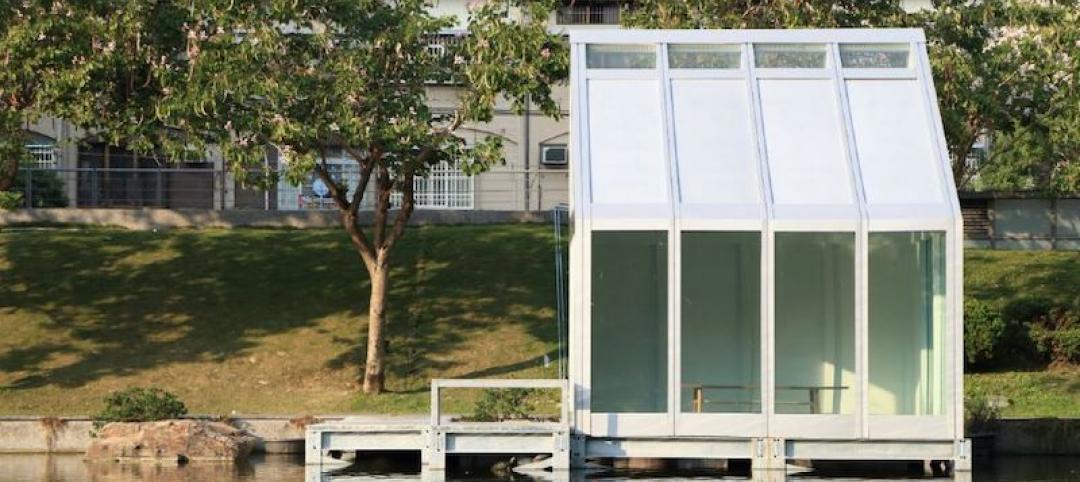
Could water-filled windows help buildings save energy?
New research shows how water-filled glass could help heat and cool buildings.
Great Solutions | Aug 10, 2020
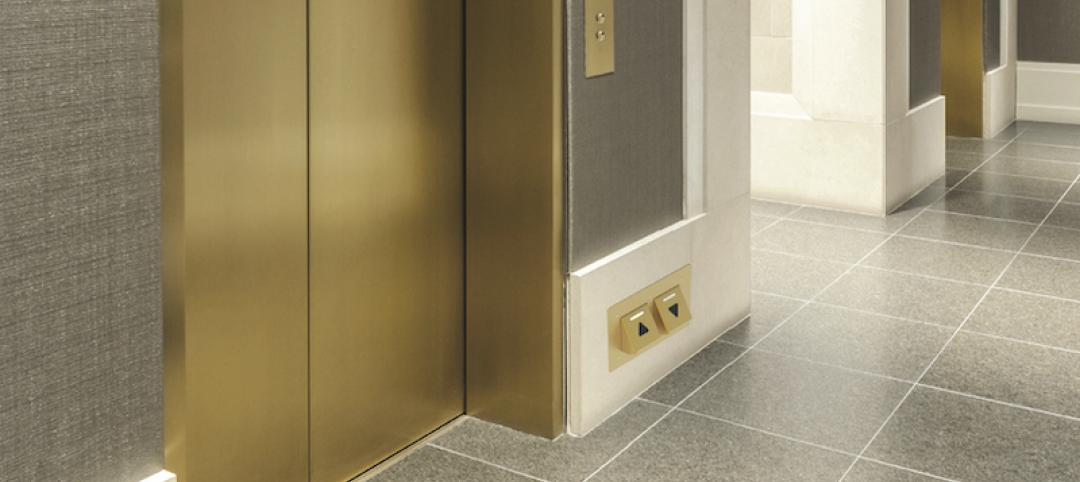
From lobby to penthouse, elevators can be a 100% touch-free experience
The Toe-To-Go elevator system allows riders to operate the elevator entirely with their feet.
Great Solutions | Jul 13, 2020
Essential protection for businesses
Custom protective barriers help keep essential business employees safe.
Great Solutions | Apr 13, 2020
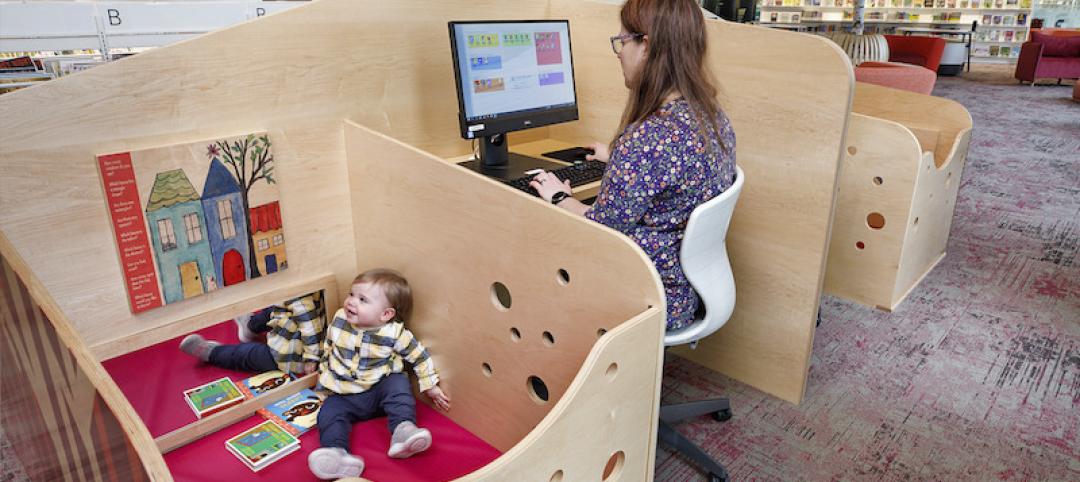
Family workstations highlight the new Fairfield Area Library
The workstations are the perfect remedy for squirming, restless children and toddlers.