Planners are often asked to test a facilities concept, define how much space it will take, and determine how much it will cost to complete. These questions are useful in the early concept phase of a project, but the basis for planning is missing; what am I solving for, and how does this potential “bricks and mortar” solution meet a defined service, market, or strategic need of the organization? It’s all about scoping the right concept before getting too far down the facility planning phase.
Defining and documenting project scope (the project intention, goal, or purpose) at the outset and controlling scope throughout the planning and delivery process is essential to ensuring the project vision becomes reality.
Ask yourself:
● What strategies and goals are we trying to achieve?
● What is the scope of the envisioned project and how was it defined?
Clearly defining the project, then articulating the scope and rationale to the team is paramount prior to launch. Scope typically relates to:
● Meeting the demands of the organization’s patients (service area)
● Cultivating a new or expanded service line opportunity
● Helping to improve throughput and operations
● Fixing an infrastructure or standard-of-care issue
● Scope control/communicating clear scope of work
● Attaining successful project definition
Rushing into design and construction without clearly defining the project scope can lead to project delay and frustration later in the process. If each team member cannot clearly articulate the scope of the project, you should stop and get everyone on the same page. Establish measurable project goals early to stay on track.
Scope Definition and Documentation
A facility project is a tactical element of a strategic plan or the output of business plan; this plan is built on the mission, vision, and goals of the organization. An organization’s strategic plan should include:
● Mission and vision identification
● SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats)
● Internal and external environmental analysis
● Identification of gaps between mission/vision and internal/external needs
● Service needs identification
● Market-based needs and capacity analysis
● Strategic financial analysis
● Measurable strategic goals
● Tactics to meet the strategic goals of the organization
The needs identified in a strategic plan or focused business plan drive the tactical need for a project—not the other way around. A well-conceived scope guides facilities master planning and the detailed programming and design phases of a project. The scope of the project also acts as the base to define the project budget. Scope and budget are inextricably linked and need to be constantly checked against each other. It’s imperative that the two balance relative to a complete financial analysis of the project. If the project doesn’t “pencil” from a return-on-investment (ROI) perspective, then you’ll need to adjust scope and budget to get the project in line financially and still meet the market and service delivery goals of the organization.
If you conduct these analyses early, you have a better chance of making less costing changes if needed. As you move through the project delivery process, the ability to easily make changes decreases, and the cost of changes increases. Therefore, it’s important to appropriately define the scope, test it against the budget, and communicate and document it at the project outset.

Scope Control
Once scope is defined and clearly communicated to the project delivery team, it must be managed. Use scope control tools developed during the early planning phases and during each subsequent planning and design phase (master planning, space planning, schematic design, design development, and construction documents) to avoid scope creep. Scope creep refers to uncontrolled changes in a project’s defined scope. Typically, scope increases consist of new services, new features, or additional room elements without corresponding strategic or market demand justification. Avoid scope creep early by:
● Plan based on defined and justified needs rather than articulated wants
● Encourage stakeholder participation and plan based on facts and analysis to ensure buy-in from all parties
● Eliminate “pet” projects or elements with no financial strategic justification; this is “wish-casting” instead of “forecasting” and usually results in wasted finite resources at the expense of needed projects
● Clearly communicate scope to all key constituents and members of the project delivery team before embarking on detailed planning, design, and construction
● Track scope early and continue to track throughout the life of the project
Remember, you don’t need to eliminate scope changes all together. Sound strategic logic and rapidly changing market dynamics may dictate appropriate (controlled) changes to scope that are justified. Strong scope controls will identify acceptable variances and appropriately jump-start conversations as to the “why” for the changes.
Scope increases may require additional resources (e.g. staffing, space, equipment, capital costs, time, and operational costs) which must be justified or they could potentially put the project at risk. A few thousand square feet of scope creep could add millions to your total project cost, create delays if changed late in the design process, and cause a few headaches along the way. Allowing scope creep without correlating demand and revenue may require additional staffing resources, equipment, and furnishings, and carries the long-term operational cost without the requisite return on investment.
Interestingly scope can shrink too. Cutting revenue producing scope to make budget will have downward impact on potential ROI, the ability to meet service demand, and ability to offer services and recruit new staff. If a department is downsized to allow another area to grow and still remain within budget, make sure the downsized department is not rendered dysfunctional. If this happens, you may pay once the facility is operational.
There is great risk and cost to unfettered scope creep and a poorly defined project; therefore, proper planning and controls must be in place to prevent your project from being derailed. Items to consider:
● Thoroughly understand the project vision and involve all stakeholders in defining and documenting the project scope
● Utilize tools to monitor and control scope, and track the departmental “units” (e.g. number of rooms) and departmental space
● Expect changes; develop processes and criteria to evaluate proposed scope changes and to decide which changes are necessary to fulfill the intended vision
Start with acutely defining and documenting scope on the front end of the project. Control scope throughout the process to position yourself to control your project, instead of your project controlling you.
If you build it, will they come?
In summary, too often healthcare executives employ an “If you build it, they will come” mentality to a project. Sure, a new facility or space frequently have a halo effect and activity may spike initially. But if the services aren’t what the patient, caregivers, and physicians require, then they will stop coming. The analyses conducted in the planning phase will help to accurately define project scope; meet the strategic, market, and financial goals of leadership; and meet the needs of the healthcare organization’s community.
Related Stories
| Nov 19, 2013
Pediatric design in an adult hospital setting
Freestanding pediatric facilities have operational and physical characteristics that differ from those of adult facilities.
| Nov 19, 2013
Top 10 green building products for 2014
Assa Abloy's power-over-ethernet access-control locks and Schüco's retrofit façade system are among the products to make BuildingGreen Inc.'s annual Top-10 Green Building Products list.
| Nov 18, 2013
6 checkpoints when designing a pediatric healthcare unit
As more time and money is devoted to neonatal and pediatric research, evidence-based design is playing an increasingly crucial role in the development of healthcare facilities for children. Here are six important factors AEC firms should consider when designing pediatric healthcare facilities.
| Nov 15, 2013
Greenbuild 2013 Report - BD+C Exclusive
The BD+C editorial team brings you this special report on the latest green building trends across nine key market sectors.
| Nov 15, 2013
Pedia-Pod: A state-of-the-art pediatric building module
This demonstration pediatric treatment building module is “kid-friendly,” offering a unique and cheerful environment where a child can feel most comfortable.
| Nov 14, 2013
Behind the build: BD+C's 'Pedia-Pod' modular pediatric patient unit at Greenbuild 2013 [slideshow]
Next week at Greenbuild, BD+C will unveil its demonstration pediatric patient unit, called Pedia-Pod. Here's a behind-the-scenes look at the construction of this unique modular structure.
| Nov 13, 2013
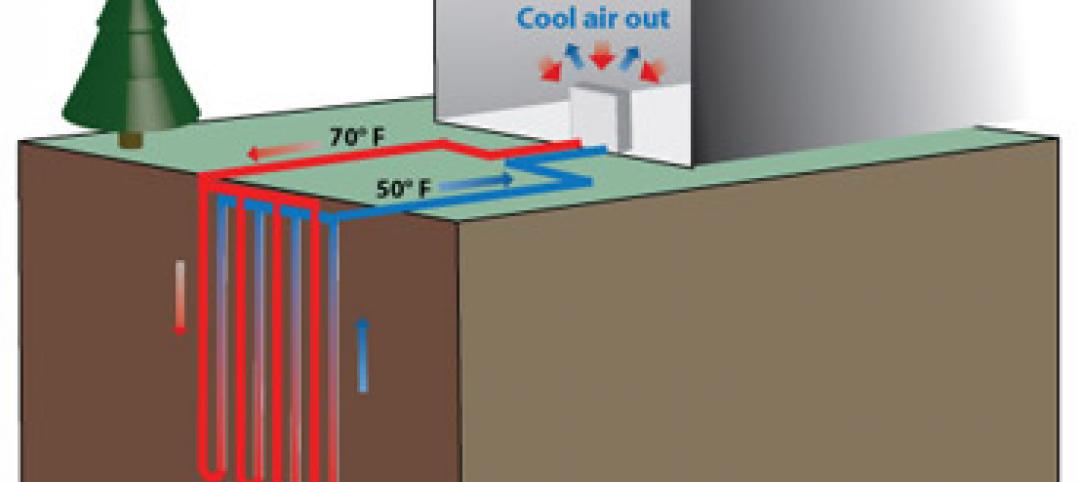
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Nov 8, 2013
Oversized healthcare: How did we get here and how do we right-size?
Healthcare facilities, especially our nation's hospitals, have steadily become larger over the past couple of decades. The growth has occurred despite stabilization, and in some markets, a decline in inpatient utilization.
| Nov 1, 2013
CBRE Group enhances healthcare platform with acquisition of KLMK Group
CBRE Group, Inc. (NYSE:CBG) today announced that it has acquired KLMK Group, a leading provider of facility consulting, project advisory and facility activation solutions to the healthcare industry.
| Oct 30, 2013
15 stellar historic preservation, adaptive reuse, and renovation projects
The winners of the 2013 Reconstruction Awards showcase the best work of distinguished Building Teams, encompassing historic preservation, adaptive reuse, and renovations and additions.