In the rush to slash energy consumption in power-hungry data centers, design teams, equipment manufacturers, and tech companies have been developing clever, low-energy cooling solutions—from Facebook’s open-rack server setup with exposed motherboards, to Skanska’s eOPTI-TRAX liquid refrigerant coil system, to Google’s evaporative cooling schemes.
Solutions like these have helped data center facility operators achieve unprecedented energy performance levels, with power utilization effectiveness (PUE) ratios dipping below 1.10 in some instances. This means that less than 10% of the total energy consumption in a facility is attributed to noncomputing functions, such as air-conditioning and lighting.
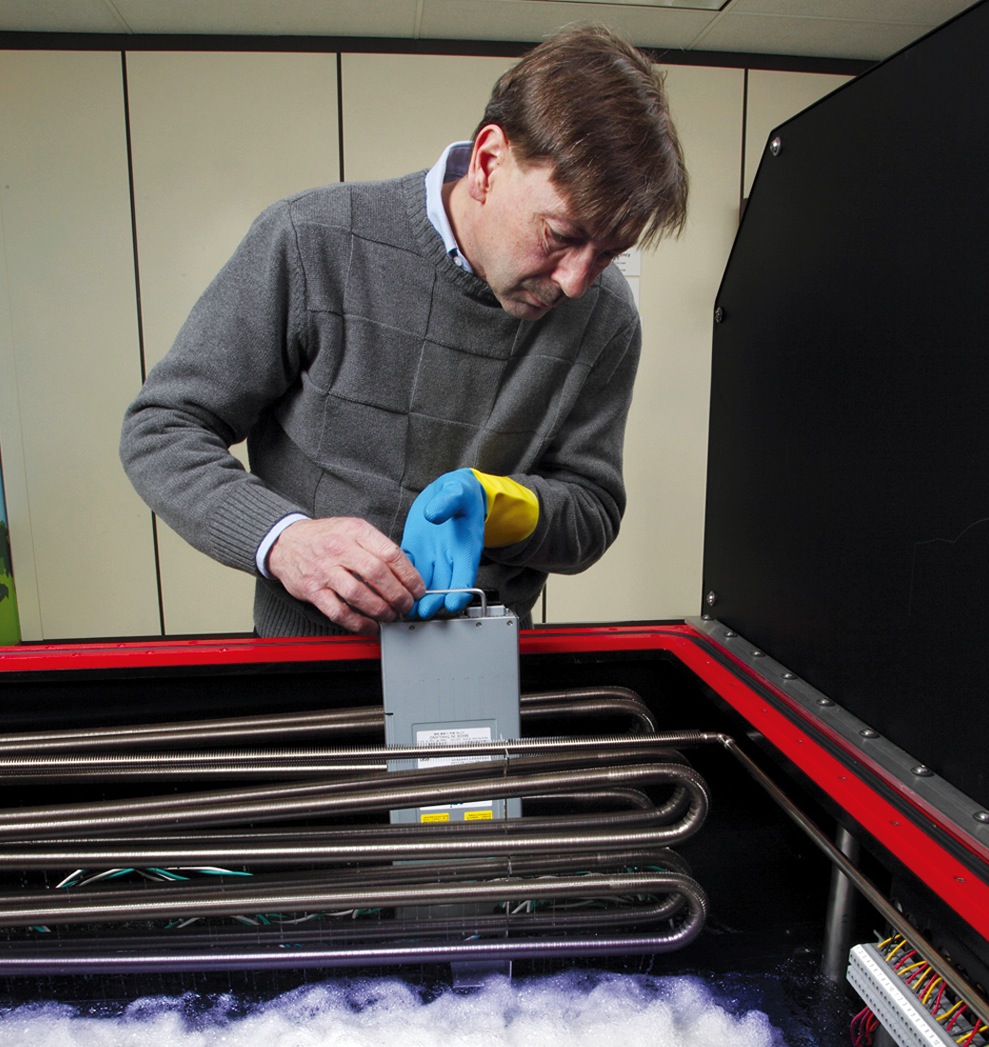
Now, a new technology promises to push the limits of data center energy efficiency even further. Called immersive cooling, it uses a liquid instead of air to cool the servers. LiquidCool Solutions, Green Revolution, and 3M are among the pioneers of this technology. Each system works a bit differently, but the basic idea is to submerge the motherboards in tanks filled with nonconductive fluid, which absorbs the heat generated by the processors.
LiquidCool Solutions, for example, uses an enclosed server module and pumps dielectric fluid through the server enclosure. Green Revolution uses a tub full of dielectric oil and circulates the liquid through the tubs. 3M also uses the tub approach, but the fluid boils and then is condensed to reject the heat.
By using liquid-based cooling at the server level, the need for air-conditioning is greatly reduced, or even eliminated in some climates. The same goes for traditional HVAC equipment and systems—chillers, fan units, raised floors, and so on.

The Allied Control 500 kW immersion-cooled data center in Hong Kong is capable of delivering a PUE of just 1.02. The standard, 19-inch server racks use 3M Novec Engineered Fluids to enable tight component packaging for greater computing power in less space, according to Allied. Its open-bath design permits easy access to hardware and eliminates the need for pressure vessel enclosures and charging/recovery systems. PHOTO: COURTESY ALLIED CONTROL
“In most parts of the world, compressorized cooling would not be required with immersive cooling, since the liquid temperatures can be at a level where direct heat rejection using outdoor condensers or cooling towers would be sufficient,” says Thomas Squillo, PE, LEED AP, Vice President with Environmental Systems Design, who is currently researching the technology for the firm’s data center clients. “The fan energy is also eliminated, both in the HVAC system and in the server itself. Fluid pumping energy is very low.”
Other advantages of the cooling technology, according to Squillo:
• Increased performance and service life of the computer chips by eliminating heat buildup and problems related to contaminated air and dust.
• Ability to deploy data centers in extremely harsh environments without greatly impacting energy performance.
• Potential construction cost savings by downsizing or eliminating traditional HVAC systems.
Other than a few pilot projects, including a Bitcoin mining data center in Hong Kong and a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory-led installation in Chippewa Falls, Wis., immersive cooling technology is largely untested. A year into the Bitcoin pilot, the data center operator reported a 95% reduction in cooling costs.
AEC professionals are starting to realize the potential for immersive cooling, especially for high-performance computing centers and consolidated, high-density data centers.
“Large data centers that have many homogenous machines at high density—like those operated by Internet and cloud providers—are a good application,” says Squillo. “Small footprint and minimal energy use are very important due to the volume of servers. These can be deployed in remote areas where space and energy are cheap, but where air quality may be a concern, without having to worry about the data center air.”
TRICKY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Before the technology can be implemented, says Squillo, several nettlesome design factors specific to immersive cooling have to be addressed:
• Piping distribution to the racks and cooling units requires redundancy and valving to accommodate equipment maintenance without disrupting server performance.
• Additional equipment and space are needed to drain fluid from the tanks for server maintenance.
• Local code requirements may limit the amount of fluid that can be stored in a single room.
• For the foreseeable future, it’s unlikely that a large data center would be 100% liquid-immersion cooled. This means provisions will have to be made for both air- and liquid-cooling systems, which will require additional space in the data hall and mechanical room.
“I think that some form of this technology will definitely be the direction the data center market will take in the future,” says Squillo. “The market just needs to mature enough for owners to trust the technology and demand servers that are designed for a particular type of liquid cooling. In the short term, I see large companies and server manufacturers doing small-scale installations to test the concept, before wanting to implement it at a large scale.”
Related Stories
| Jan 6, 2012
Gensler unveils restoration and expansion of Houston's Julia Ideson building
The "new" building will serve as a repository of Houston memorabilia and rare archival material as well as the city's official reception space and a venue for exhibits, meetings and other special events.
| Jan 6, 2012
New Walgreen's represents an architectural departure
The structure's exterior is a major departure from the corporate image of a traditional Walgreens design.
| Jan 6, 2012
Summit Design+Build completes Park Place in Illinois
Summit was responsible for the complete gut and renovation of the former auto repair shop which required the partial demolition of the existing building, while maintaining the integrity of the original 100 year-old structure, and significant re-grading and landscaping of the site.
| Jan 4, 2012
Siemens acquires Pace Global Energy Services
Acquisition will enhance portfolio with new energy consulting and management services.
| Jan 4, 2012
Shawmut Design & Construction awarded dorm renovations at Brown University
Construction is scheduled to begin in June 2012, and will be completed by December 2012.
| Jan 4, 2012
Skanska acquires Industrial Contractors
Industrial Contractors Inc. is a contractor in the commercial, industrial and power markets of the Midwest. The company employs 2,400 people and in 2011 the revenues are estimated to be approximately $500 million.
| Jan 4, 2012
HDR to design North America’s first fully digital hospital
Humber River is the first hospital in North America to fully integrate and automate all of its processes; everything is done digitally.
| Jan 4, 2012
New LEED Silver complex provides space for education and research
The academic-style facility supports education/training and research functions, and contains classrooms, auditoriums, laboratories, administrative offices and library facilities, as well as spaces for operating highly sophisticated training equipment.
| Jan 3, 2012
Gilbane awarded $88M Contract for Ohio elementary school construction
The new award, which comprises the construction of five new elementary schools and demolition of 11 older facilities, is the latest K-12 building program managed by Gilbane for the Ohio School Facilities Commission since 1998.
| Jan 3, 2012
AIA's ABI November Index reaches 52.0
The Architecture Billings Index (ABI) reached its first positive mark since August.