Last January, a survey of 10,237 U.S. adults, conducted by Pew Research Center, found that 8% had installed solar panels on their homes, and another 39% had given serious thought to installing solar panels within the previous 12 months.
However, the growth in solar energy alternatives has been mostly confined to commercial buildings and to single-family detached households. Lower-income households, which represent 43% of the U.S. population, are more likely to reside in multifamily buildings that don’t have the mechanical/electrical infrastructure to distribute rooftop-captured solar energy to individual apartments.
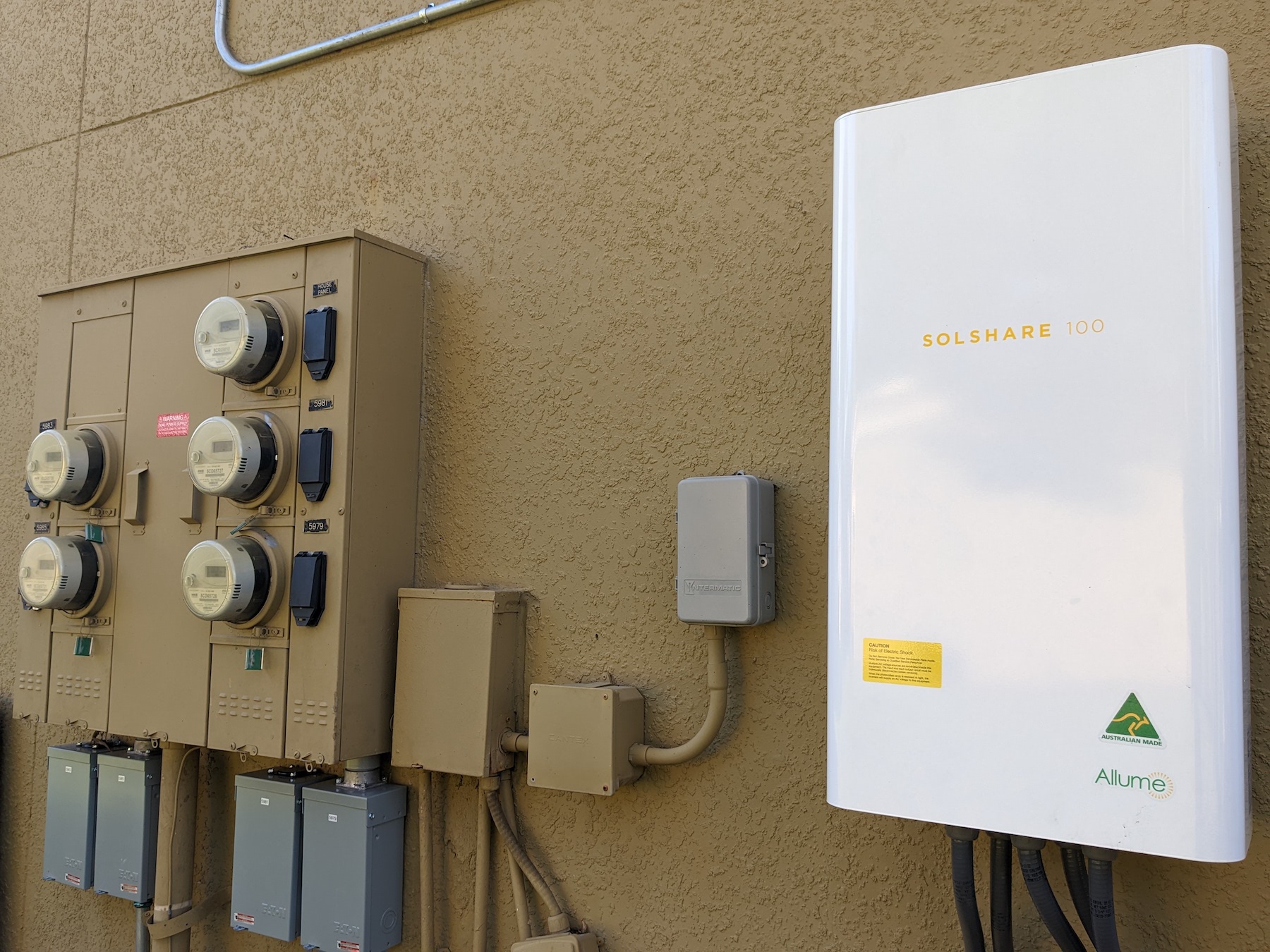
Allume Energy is looking to change that. The Australia-based company, with offices in Los Angeles, recently completed its first successful U.S. deployment of SolShare, the company’s shared solar energy technology. Its pilot in the U.S. is a complex in Orlando, Fla., where Allume has connected 65 apartments. Another smaller project in Jackson, Miss., has nine apartment connections. In Jackson, the local utility lowered the application cost because the building caters to lower-income tenants.
Controlling the energy flow
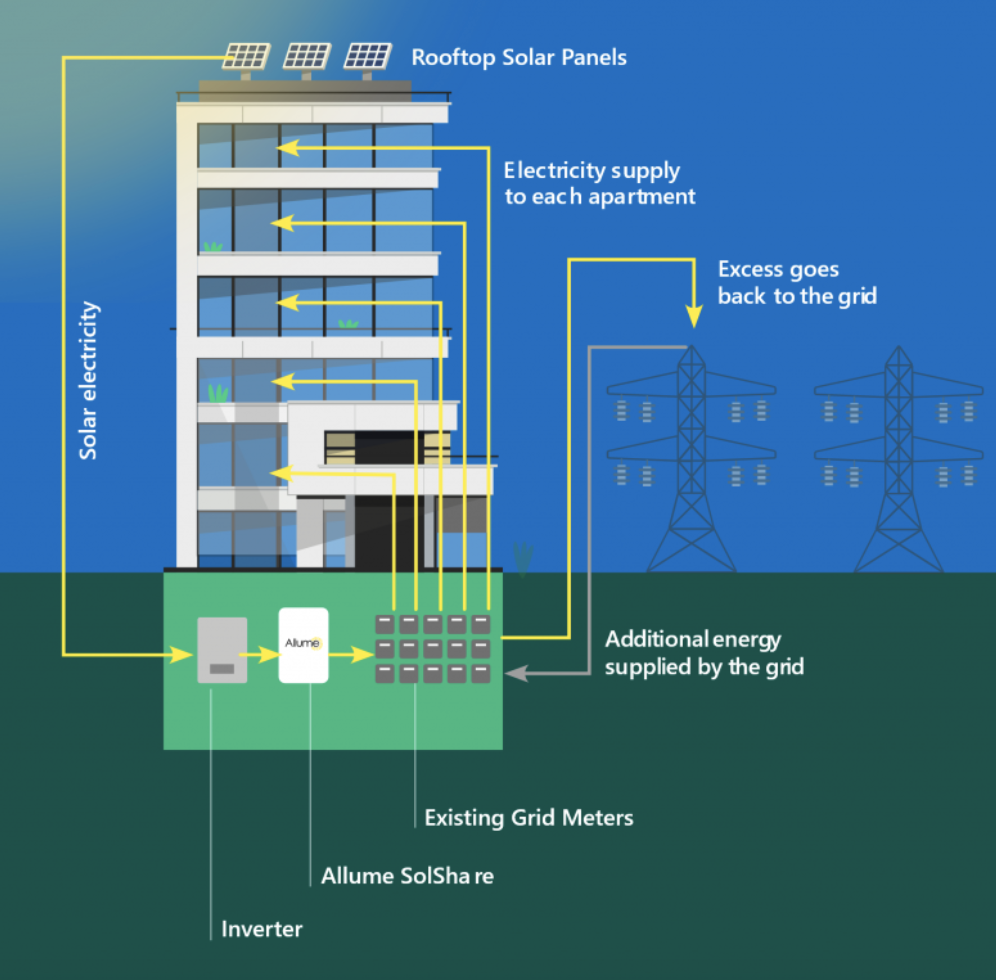
Here’s how SolShare works: Energy from a rooftop solar array flows into the building’s inverter that changes the energy to AC electricity. The inverter sends the electrical current through the SolShare unit to grid meters that are hooked up to apartments. (One SolShare unit can feed up to 10 grid meters.) The electrical distribution moves among the grid boxes several times per second, so when one meter is configured with limits for a particular tenant, the incoming energy gets allocated to the other meters. Any overflow can be sold back to the local energy grid.
Melissa Bergsneider, an executive account manager for Allume Energy, explains that prior to the introduction of the SolShare solution, most landlords were distributing solar energy only to their buildings’ common areas, like a lobby or gym. Those that have been delivering solar energy to apartments were faced with the challenge of how to divide the energy if, for example, a tenant goes on vacation, or an apartment unit is vacant.
SolShare, on the other hand, is “behind the meter,” and its software lets tenants monitor the energy usage. Landlords can still set the rules for how solar energy is allocated throughout the building. One of the advantages of this system, she says, is that it can connect as many apartments as needed. And unlike other so-called “social” solar systems, SolShare provides solar energy at the point of generation rather than exporting it back to the grid.
Allume Energy, which has been in business since 2015, has found that SolShare is reducing tenants’ energy bill, on average, by 30-35%. Bergsneider says that some landlords have been offering Solar as a Service, and are charging tenants a monthly fee for access.
Tax credit boosts demand
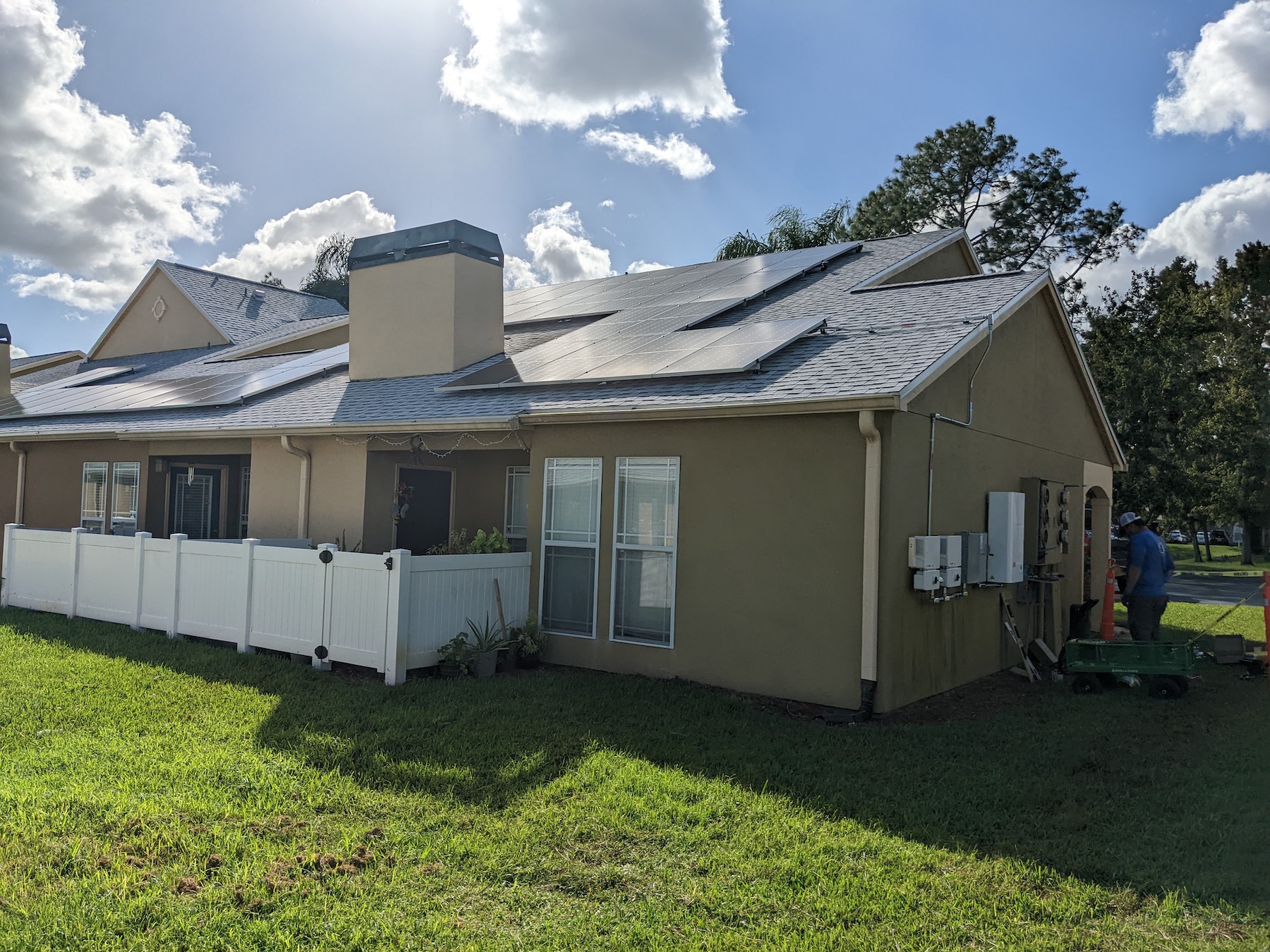

Bergsneider declined to disclose SolShare’s cost. She does note, though, that on past projects, SolShare accounted for between 6% and 8% of the total system installation.
Allume Energy’s primary target is low-rise attached rental houses, although it has installed SolShare in mixed-use buildings with commercial tenants. Most of SolShare’s demand is for retrofitting existing buildings, and Allume has been working with solar installation partners; the company has a training program, and a team member is on site for each installation.
Bergsneider attributes demand to the Solar Investment Tax Credit, which offers a 30% credit for individuals installing solar systems on residential properties. This tax credit was extended as part of the August 2022 passage of the Inflation Reduction Act. Bergsneider says there’s a 20% “adder” credit for properties with lower-income residents.
SolShare also helps developers and landlords decarbonize their buildings as part of their Environmental, Social, and Governance goals.
Currently, Allume Energy is focusing its expansion on the Southeast in the U.S. It has also been getting interest for SolShare from building owners in the Northeast and West Coast. Internationally, Allume Energy is targeting Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom.
Related Stories
Smart Buildings | Jan 7, 2015
Best practices for urban infill development: Embrace the region's character, master the pedestrian experience
If an urban building isn’t grounded in the local region’s character, it will end up feeling generic and out-of-place. To do urban infill the right way, it’s essential to slow down and pay proper attention to the context of an urban environment, writes GS&P's Joe Bucher.
| Jan 6, 2015
Construction permits exceeded $2 billion in Minneapolis in 2014
Two major projects—a new stadium for the Minnesota Vikings NFL team and the city’s Downtown East redevelopment—accounted for about half of the total worth of the permits issued.
| Jan 2, 2015
Construction put in place enjoyed healthy gains in 2014
Construction consultant FMI foresees—with some caveats—continuing growth in the office, lodging, and manufacturing sectors. But funding uncertainties raise red flags in education and healthcare.
Sponsored | | Dec 30, 2014
Case studies: Engineered wood brings cost savings, design flexibility across commercial project types
For commercial architects facing increasing pressure to design innovative structures while simultaneously cutting costs and accommodating tight deadlines, engineered wood systems are providing a welcome solution.
| Dec 28, 2014
Robots, drones, and printed buildings: The promise of automated construction
Building Teams across the globe are employing advanced robotics to simplify what is inherently a complex, messy process—construction.
| Dec 28, 2014
AIA course: Enhancing interior comfort while improving overall building efficacy
Providing more comfortable conditions to building occupants has become a top priority in today’s interior designs. This course is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.
| Dec 28, 2014
6 trends steering today's college residence halls
University students want more in a residence hall than just a place to sleep. They want a space that reflects their style of living and learning.
| Dec 22, 2014
Studio Gang to design Chicago’s third-tallest skyscraper
The first U.S. real-estate investment by The Wanda Group, owned by China’s richest man, will be an 88-story, 1,148-ft-tall mixed-use tower designed by Jeanne Gang.
| Dec 17, 2014
ULI report looks at growing appeal of micro unit apartments
New research from the Urban Land Institute suggests that micro units have staying power as a housing type that appeals to urban dwellers in high-cost markets who are willing to trade space for improved affordability and proximity to downtown neighborhoods.
| Dec 15, 2014
SHoP Architects plans to turn NY's Seaport District into pedestrianized, mixed-use area
The scheme includes a proposed 500-foot luxury residential tower that would jut out into the harbor, extending the Manhattan grid out into the waterfront.
















