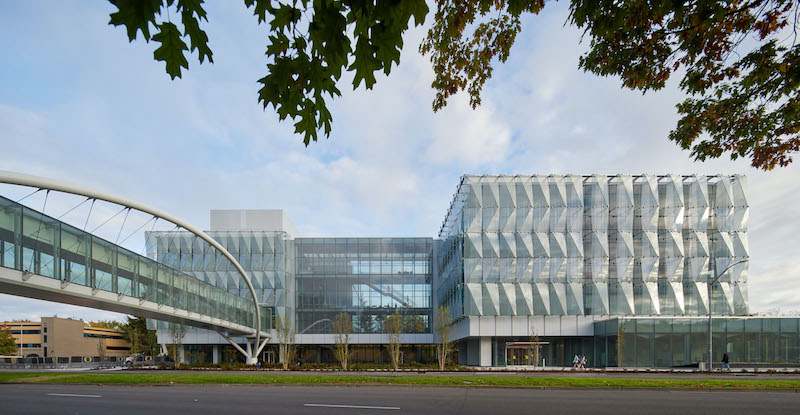
Earlier this month, the University of Oregon in Eugene opened the Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact. The 160,000-sf complex, which consists of two facing L-shaped towers, supports a mission to shorten the timeline between discovery, development, and deployment by bringing together engineering, applied science, business innovations, and culture. Its environment priorities revolve around wellness, human performance, and community. (The Campus’s tagline is “Science Advancing Society.“)
Phil Knight, co-founder and chairman emeritus of Nike, donated $500 million for this project. “Phil was most interested in the mission” of acceleration, Todd Schliemann, FAIA, Design Partner at Ennead Architects, tells BD+C. The Campus’s current focus is bioengineering, and OU partners with Oregon State University to offer a PhD program in that discipline.
Ennead Architects was this project’s design architect, Portland, Ore.-based Bora Architecture & Interiors was its AOR and designed some of the interiors, and Hoffman Construction built the campus.
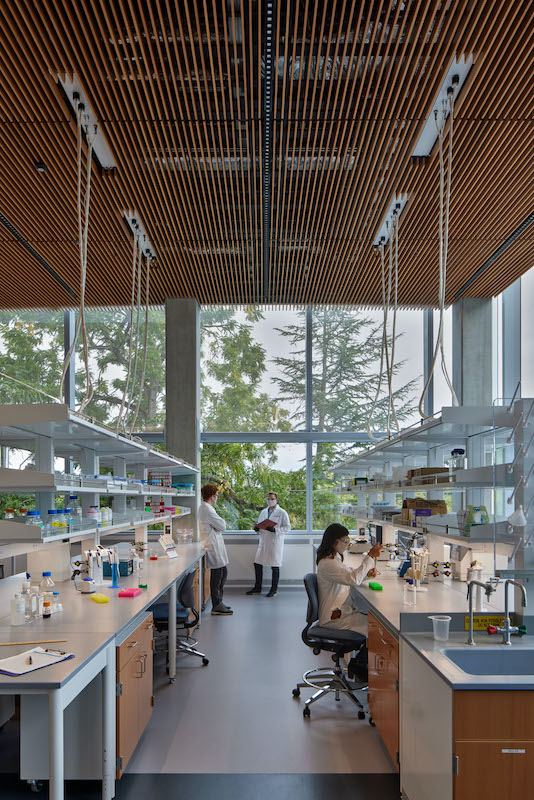

Lab space (above) and work space (below) intersect in the campus's buildings. Mass timber was applied throughout the Campus, including the labs' ceiling.

Built on land where a Domino’s Pizza, a mini-mall and parking lot once stood, the Knight Campus is situated between the University of Oregon’s main campus and parkland straddling the Willamette River. A 190-ft-long, 48-ft-wide enclosed bridge, stretching 35 ft above street traffic, connects Knight Campus to Oregon’s existing campus.
Schliemann says the university is positioning the Knight Campus—which he calls a “humanistic research machine”— as a “gateway building” to a possible future research complex.
During the design process, the university hadn’t decided what disciplines these towers would house. So before designing the Knight Campus, representatives from the design team visited several other universities, including MIT’s Media Lab, Harvard, Stanford, and University of California at San Francisco. What they all have in common, says Schliemann, are collaborative spaces where knowledge can be shared. Stanford’s engineering complex, he adds, is noteworthy for how much natural light it lets inside.
‘NEIGHBORHOODS’ BRING RESEARCHERS TOGETHER
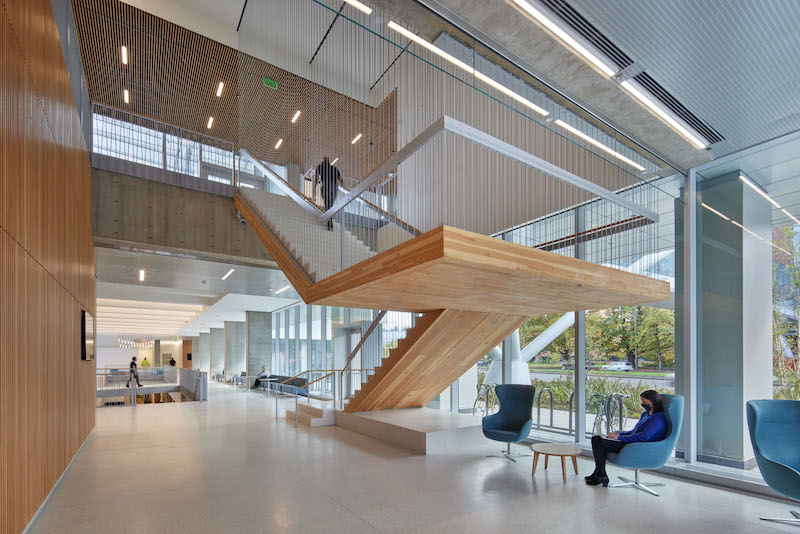

Staircases made from cross-laminated timber connect the floors.
The Knight Campus has several distinguishing characteristics:
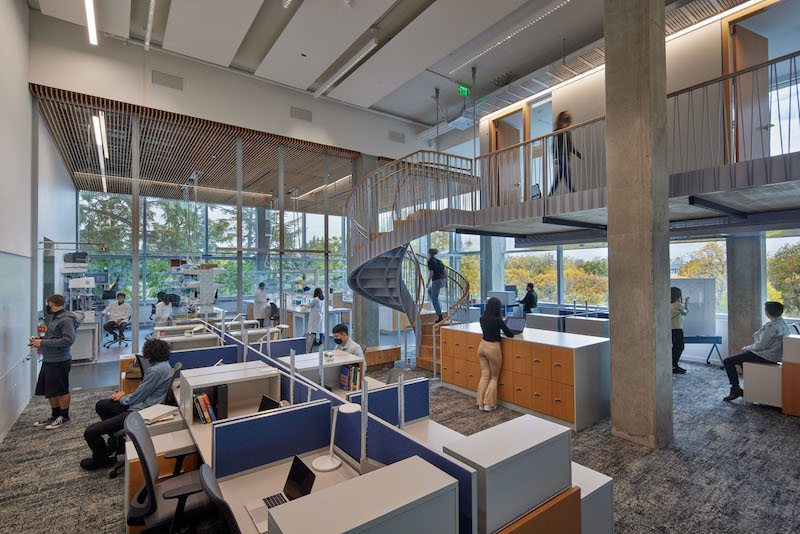
•Its two upper floors include four research “neighborhoods” that each has a wet bench area, computational space, and offices where Principal Investigators work. Schliemann contends that this is one of the first lab buildings in the U.S. where PIs are this visible to other research teammates.
•The Campus’s double-skinned façade showcases an outer wall consisting of 650 glass panels and designed to resemble water flowing over rocks. This cascading wall is stabilized by an inner curtainwall made up of 900 glass panels. Schliemann says that this design and materials were chosen to let more natural light and panoramic exterior views into the building (which, he contends, improves working conditions), and for passive energy performance (the inner wall of the façade never gets exceedingly warm).
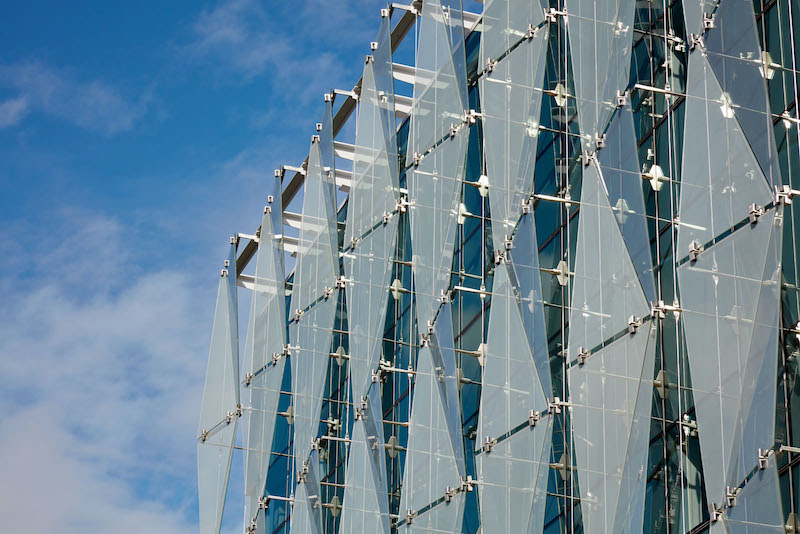

The Campus's double-skinned facade lets more natural light into the buildings and keeps heat from penetrating the inner curtainwall.
The wall structure was light enough to be hung from the roof component.
•Mass timber is prevalent throughout the Knight Campus, whose construction used 20,500 sf of cross-laminated timber that includes 180 CLT panels and 4,000 lbs of wood for each of the building’s staircases. The 21-foot floor-to-floor height allows for suspended mezzanine structures of mass timber containing offices for faculty, creating a new level of connectivity to their labs and graduate students.
Mass timber “is one of the most sustainable ways to construct a building” says Schliemann. (The Knight Campus is targeting LEED Gold certification.) Using mass timber also supports Oregon’s local economy. While vibration prevents a lab space from being made entirely with mass timber, “we could use it for offices, stairs, ceilings and bridges. Plus, we didn’t have to sheetrock the ceilings, as fire codes have finally caught up with mass timber” as a fireproofing agent.
Also see: Researchers use U. of Arkansas buildings as testbed for CLT panels.
SPACES FOR FORMAL OR RELAXED INNOVATION AND INTERACTION
Among the Knight Campus’s amenities are a 6,000-sf Innovation Center and 1,000-sf Wellness Center. While the Innovation Center might seem small when compared to other university research facilities, Schliemann counters that its scale is deceptive. “It gets innovators out into the real world.” He adds that all Knight Campus labs are leasable and tenant-adaptable.
The Wellness Center started out as a locker room with showers. Then spaces for yoga and other exercise regimens were included. Schliemann says the campus has a program where students can take bike rides with researchers.
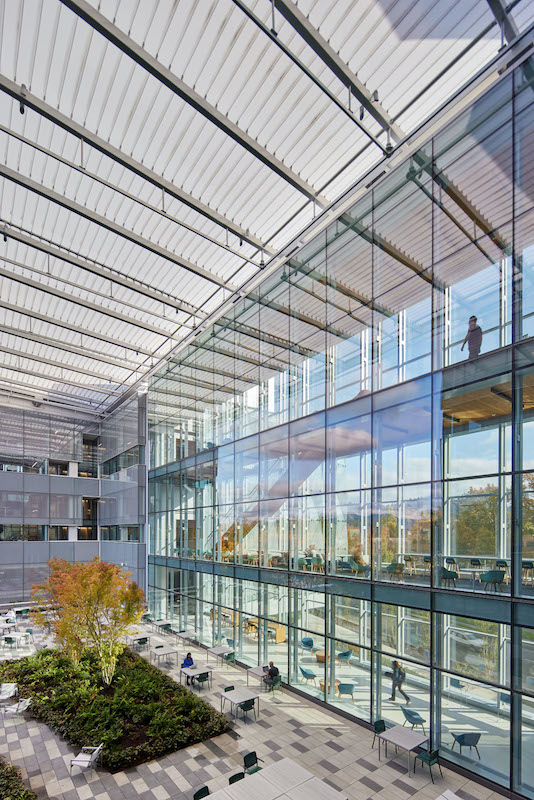

An elevated terrace and courtyard between the Campus's two buildings is covered with a canopy made from ETFE.
Between the Campus’s two buildings is an elevated terrace and courtyard, protected by a transparent plastic canopy, where students and faculty can relax, socialize, and connect with nature, as the terrace overlooks landscaping and the tree-covered Coburg Hills.
Related Stories
University Buildings | Jun 29, 2015
Ensuring today’s medical education facilities fit tomorrow’s healthcare
Through thought-leading design, medical schools have the unique opportunity to meet the needs of today’s medical students and more fully prepare them for their future healthcare careers. Perkins+Will’s Heidi Costello offers five key design factors to improve and influence medical education.
University Buildings | May 30, 2015
Texas senate approves $3 billion in bonds for university construction
For the first time in nearly a decade, Texas universities could soon have some state money for construction.
University Buildings | May 19, 2015
Special Report: How your firm can help struggling colleges and universities meet their building project goals
Building Teams that want to succeed in the higher education market have to help their clients find new funding sources, control costs, and provide the maximum value for every dollar.
University Buildings | May 19, 2015
Renovate or build new: How to resolve the eternal question
With capital budgets strained, renovation may be an increasingly attractive money-saving option for many college and universities.
University Buildings | May 19, 2015
KU Jayhawks take a gander at a P3 development
The P3 concept is getting a tryout at the University of Kansas, where state funding for construction has fallen from 20% of project costs to about 11% over the last 10 years.
University Buildings | May 5, 2015
Where the university students are (or will be)
SmithGroupJJR's Alexa Bush discusses changing demographics and the search for out-of-state students at public universities.
BIM and Information Technology | Apr 9, 2015
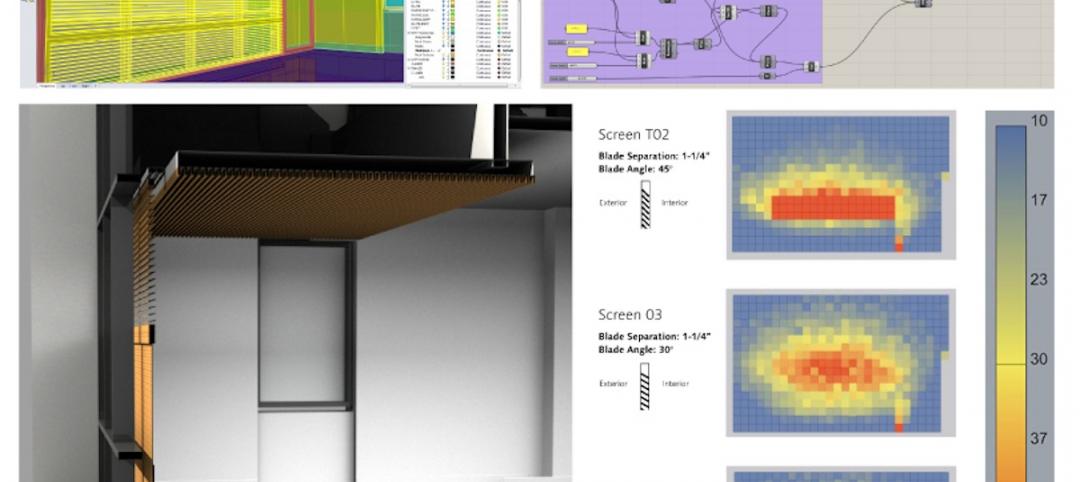
How one team solved a tricky daylighting problem with BIM/VDC tools, iterative design
SRG Partnership's Scott Mooney describes how Grasshopper, Diva, Rhino, and 3D printing were utilized to optimize a daylighting scheme at Oregon State University's new academic building.
Sponsored | University Buildings | Apr 8, 2015
Student Housing: The fight against mold starts in the bathroom
University Buildings | Apr 8, 2015
The competitive advantage of urban higher-ed institutions
In the coming years, urban colleges and universities will outperform their non-urban peers, bolstered by the 77 million Millennials who prefer to live in dense, diverse, and socially rich environments, writes SmithGroupJJR's Michael Johnson.
University Buildings | Mar 18, 2015
Academic incubators: Garage innovation meets higher education
Gensler's Jill Goebel and Christine Durman discuss the role of design in academic incubators, and why many universities are building them to foster student growth.