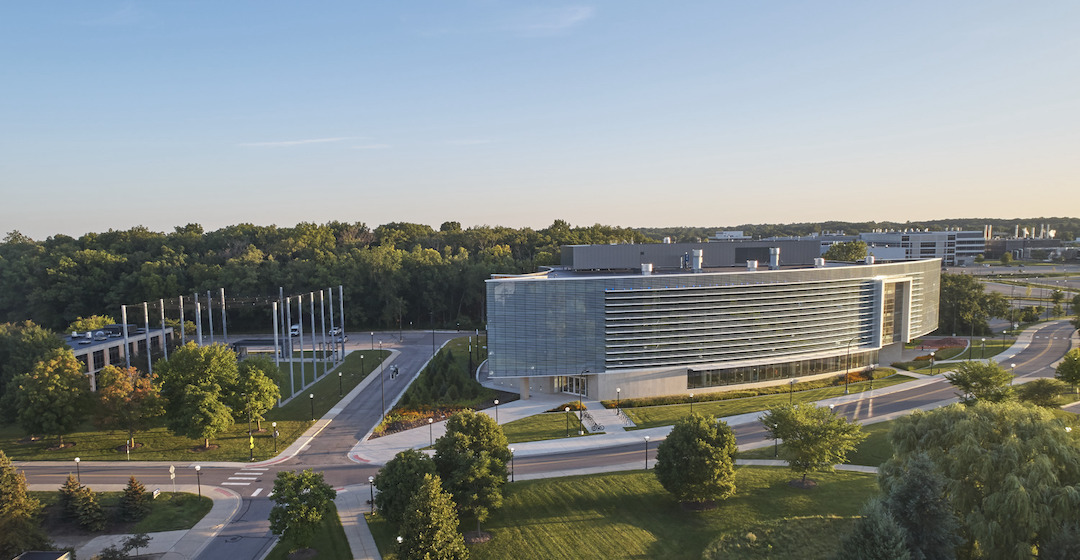
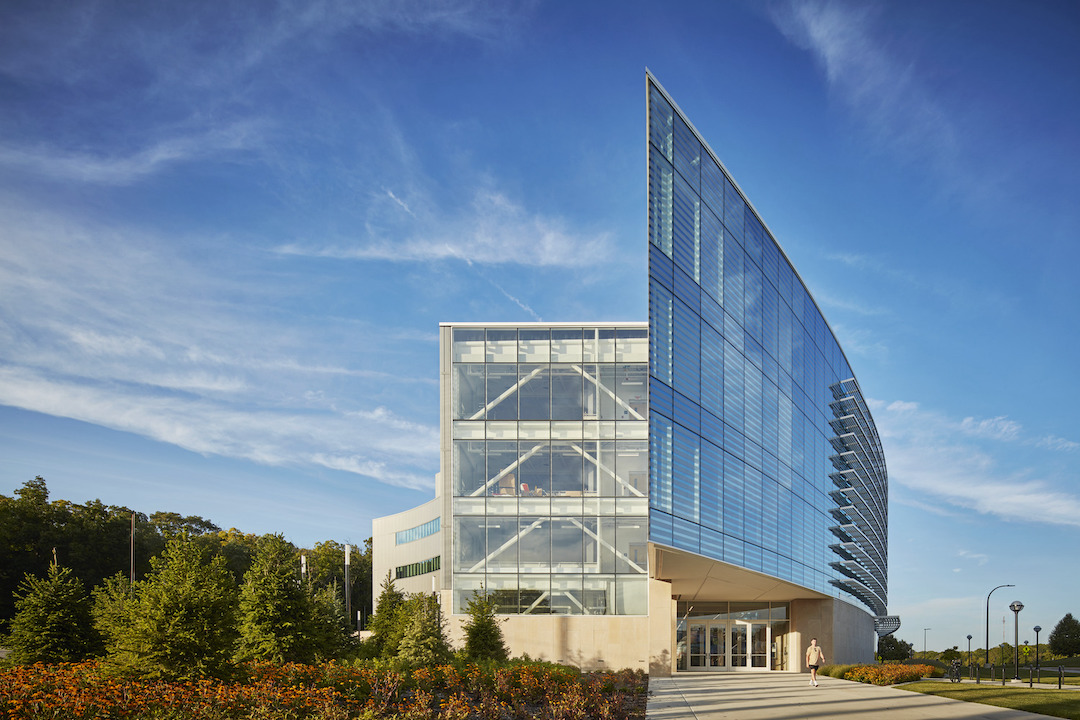
The Ford Robotics Building has completed and opened on the University of Michigan (U-M) campus. The $75 million project represents a singular new home for the university’s relationship with Ford and acts as a showcase for robotics research, cross disciplinary collaboration, and innovative industry/education collaboration.
Located on the University of Michigan North Campus, the building anchors the west end of a Michigan Avenue mobility testbed that begins in Detroits Corktown neighborhood and runs through Dearborn to Ann Arbor. The four-story, 134,000-sf project is an interdisciplinary center for mathematics, engineering, and computer programming faculty and researchers. The facility will be home to researchers that were previously spread across 23 separate buildings and is also the first robotics facility to co-locate an industry team (Ford’s mobility research center) with a university’s robotics leadership.

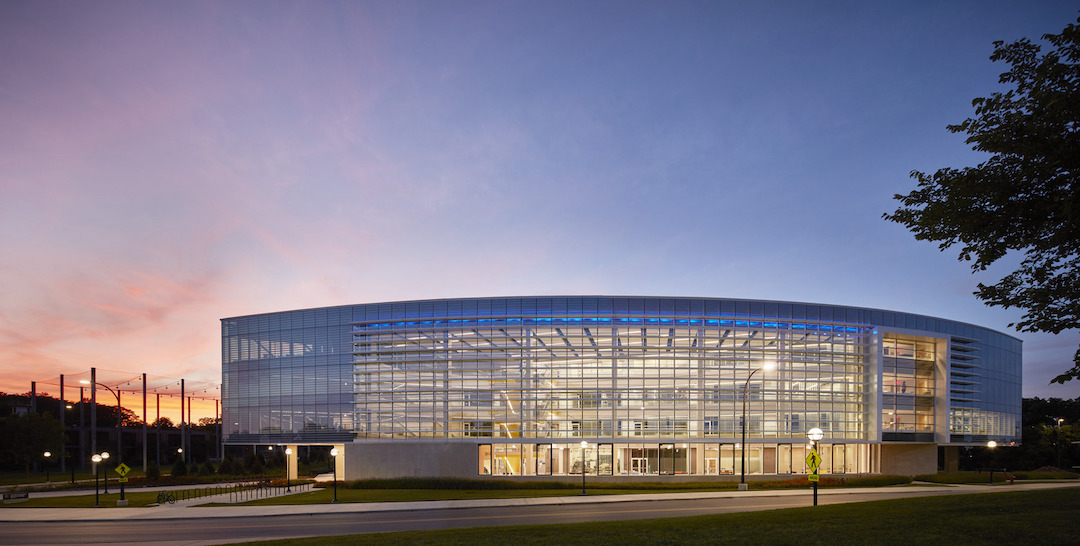
HED, in an effort to reflect a robotics program incorporates both theory and making, designed the building to appear both extroverted and enclosed simultaneously. From the outside, the most striking feature is the glass-clad facade that curves along Hayward Street. Composed of large bands of fritted glass with 30-inch-deep sunshades spaced 42 inches apart, the south-oriented glass wall allows diffused daylight deep into the building interior. The facade also allows visitors to see the activities occurring within.

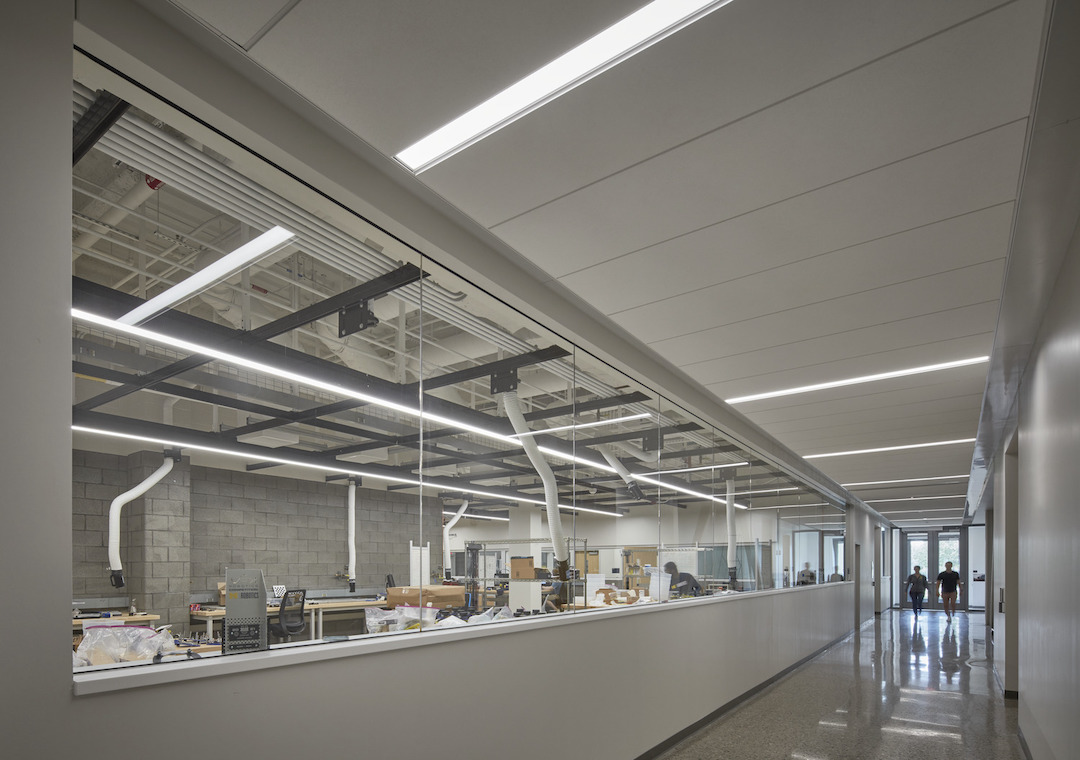
Upon entry, visitors arrive within a four-story atrium defined on one side by the curved smooth-facing glass wall and balconies for the top three floors. The atrium is designed for a wide variety of uses and special events with a cafe, large-scale video screen, and a sophisticated sound system. The atrium is heated through displacement ventilation. Researchers all enter the labs via a shared team collaboration space, ensuring chance encounters, interaction, and collaboration between them.
HED designed the Ford Robotics Building to promote proximity and spontaneous interaction between students, faculty, researchers, and visiting industry professionals. The building includes the new hub of the U-M Robotics Institute on the first three floors and Ford’s robotic and mobility research lab on the fourth floor.

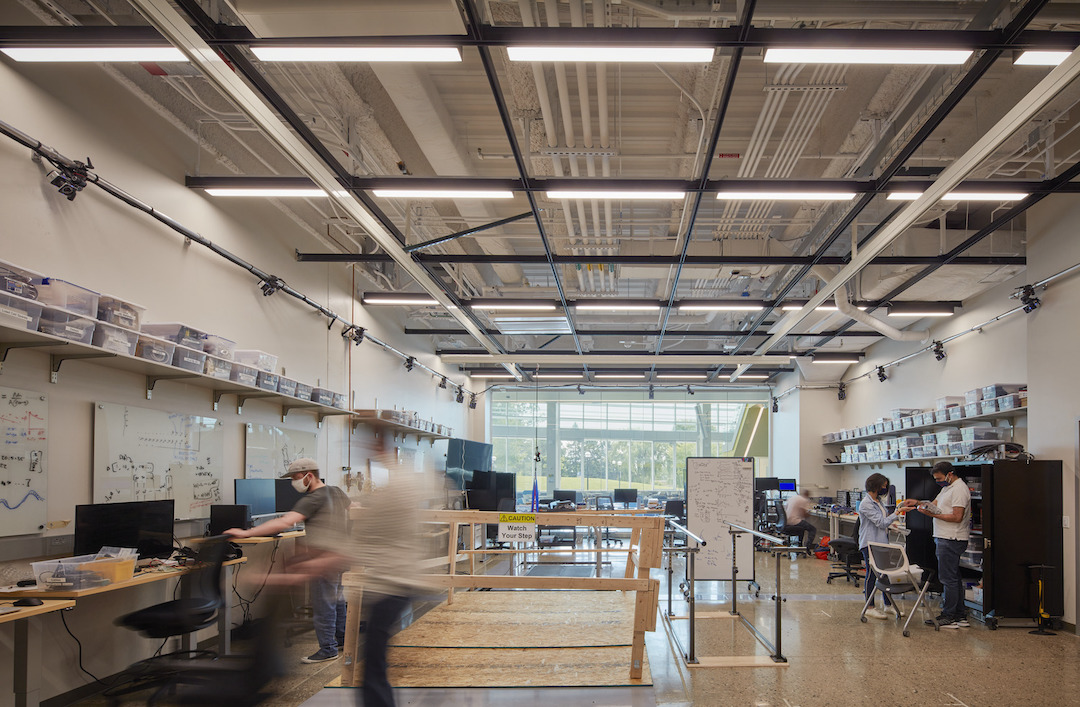
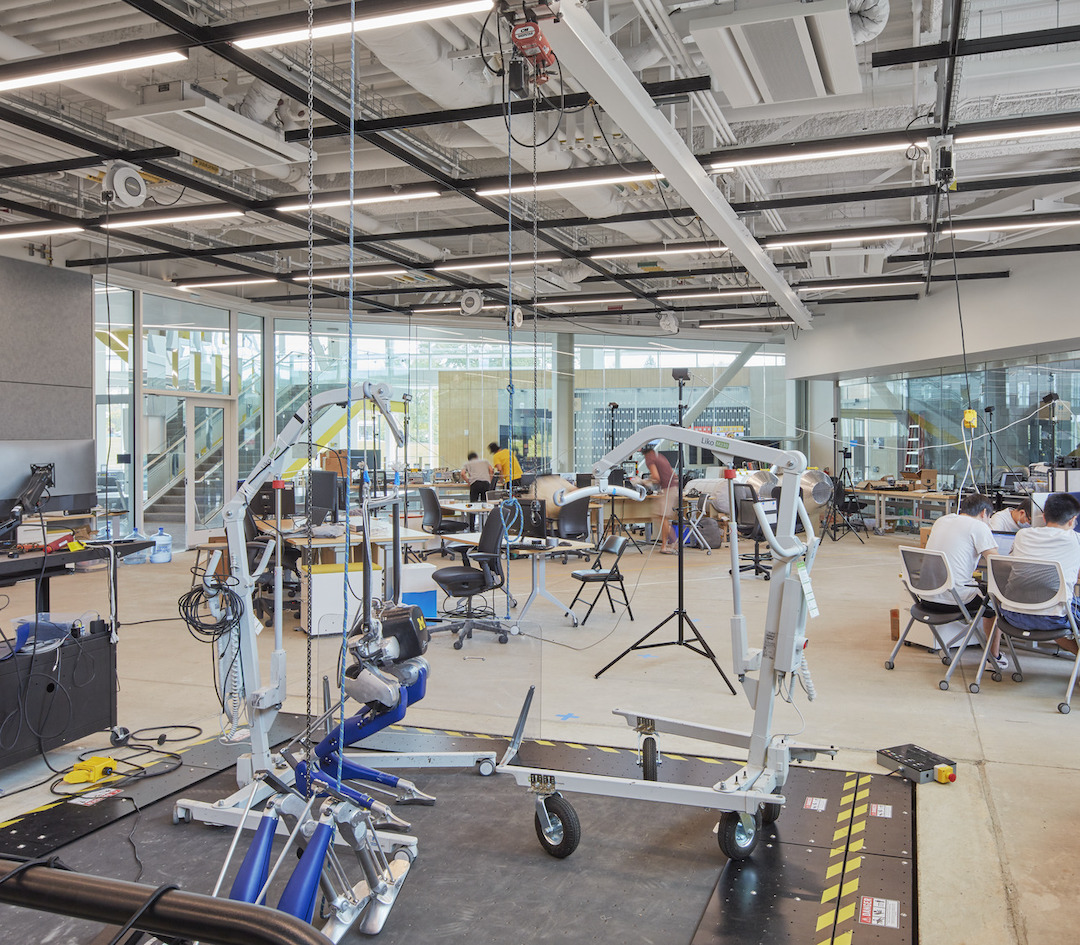
The custom U-M research labs are designed for robots that fly, walk, roll, and augment the human body. Multiple labs are incorporated within the building, including the Ronald D. And Regina C. McNeil Walking Robotics Laboratory for developing and testing legged robots. This specific lab has an in-ground treadmill that can hit 31 mph and a 20% grade, as well as carry obstacles to test walking robots that could aid in disaster relief and lead to better prosthetics and exoskeletons. A rehabilitation lab is designed for advanced prosthetics and robotic controls with a movable “earthquake platform” that can tilt in any direction while force-feedback plates measure ground contact.

A three-story fly zone allows for the testing of drones and other autonomous aerial vehicles indoors. An outdoor Mars yard was designed with input from planetary scientists at U-M and NASA to enable researchers and student teams to test rover and lander concepts on a landscape that mimics the Martian surface. An AI-designed “robot playground” outdoor obstacle course is designed for testing robots on stairs, rocks, and water surrounded by motion capture cameras. A high-bar garage space for self-driving cars allows for teams to test connected and automated vehicles in urban and suburban environments. Ford roboticists occupy the building’s fourth floor research lab and offices.
The Ford Robotics Building is expected to achieve LEED Gold certification. HED provided architecture, landscape architecture, interior design, and structural, mechanical, and electrical engineering services on the project.

Related Stories
| Jun 12, 2014
Tod Williams Billie Tsien Architects' design selected for new UCSC facility
The planned site is a natural landscape among redwood trees with views over Monterey Bay, a site that the architects have called “one of the most beautiful they have ever worked on.”
| Jun 12, 2014
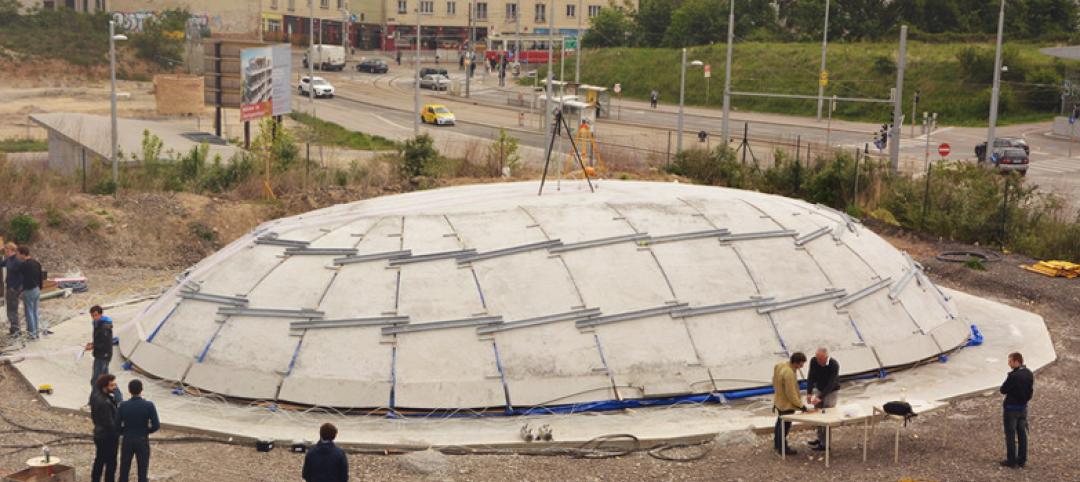
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 11, 2014
5 ways Herman Miller's new office concept rethinks the traditional workplace
Today's technologies allow us to work anywhere. So why come to an office at all? Herman Miller has an answer.
| Jun 9, 2014
6 design strategies for integrating living and learning on campus
Higher education is rapidly evolving. As we use planning and design to help our clients navigate major shifts in culture, technology, and funding, it is essential to focus on strategies that help foster an education that is relevant after graduation. One way to promote relevance is to strengthen the bond between academic disciplines and the campus residential life experience.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
Sponsored | | May 27, 2014
Grim Hall opens the door to fire safety with fire-rated ceramic glass
For the renovation of Lincoln University’s Grim Hall life sciences building into a state-of-the-art computer facility, Tevebaugh Associates worked to provide students and faculty with improved life safety protection. Updating the 1925-era facility's fire-rated doors was an important component of the project.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.