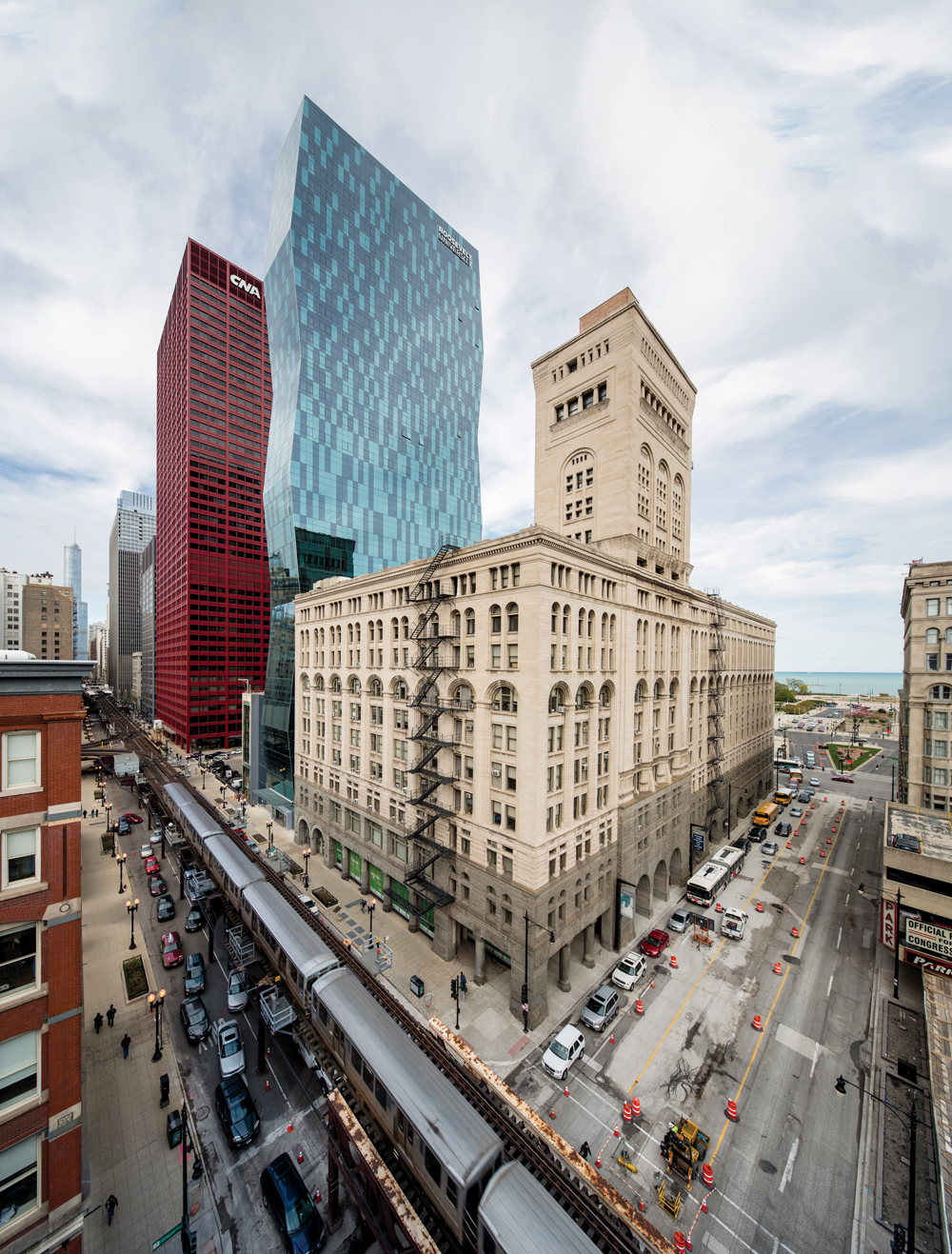
Creating a tall facility on a constrained city site always presents special difficulties for Building Teams. Make the program unusually diverse—in this case, combining residential, classroom, laboratory, office, conference, dining, and recreational functions—and the complexity level increases. Now throw in the need to link the facility to a landmark 1880s structure with different floor-to-floor heights. Finally, have the city of Chicago “orange tag” one of two existing buildings on your site, derailing your plans for a complete demolition.
The Building Team for Roosevelt University’s new Wabash Building successfully navigated this minefield, producing a distinctive addition to the South Loop skyline and an appealing new home for the school. Architect VOA Associates, owner’s rep Jones Lang LaSalle, development advisor The John Buck Company, and Power Construction spearheaded a successful functional and aesthetic collaboration that also achieved LEED Gold. The resulting project, at 469 feet in height, is the second-tallest university facility in the U.S. and the sixth-tallest in the world.
From the start, the project was vastly more complex than anything the client had ever attempted. Roosevelt was already occupying the Auditorium Building, a Michigan Avenue icon designed by Adler and Sullivan, as well as a suburban extension campus. To support enrollment growth and program expansion, the university decided to create a tall building that would consolidate many functions while integrating well with the Auditorium.
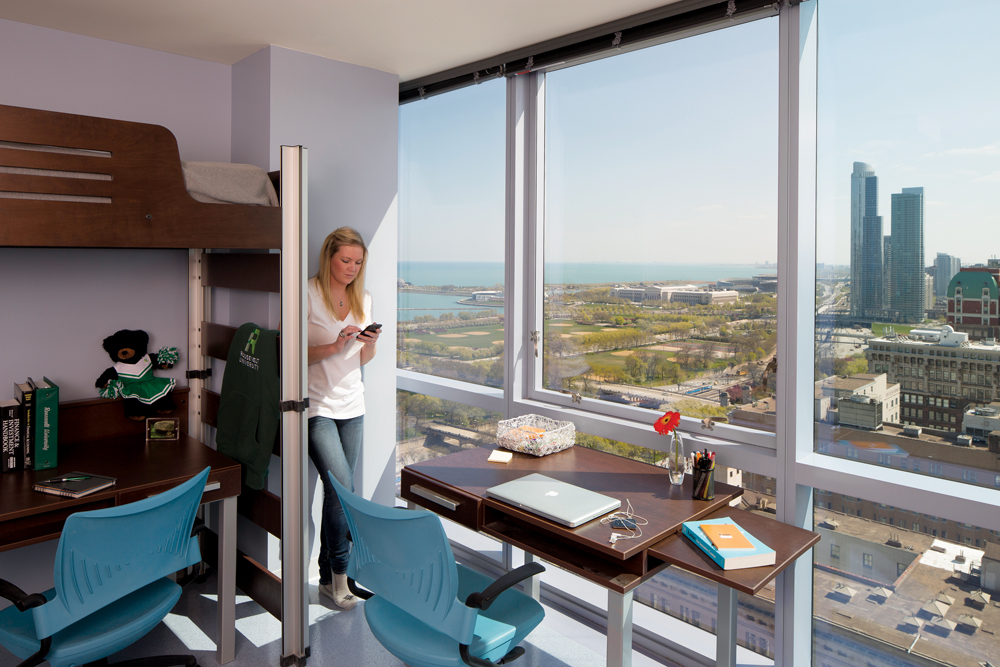
Student residences include 633 beds on 17 floors, mostly in four- and five-person suites consisting of single and double bedrooms sharing a bathroom. Laundry facilities on the 15th floor feature Internet tracking so students can make sure washers and dryers are available before making the trek. Each residential floor has a large study room with breathtaking lake and city views.
With a footprint of only 17,300 sf, the tight site would need to accommodate a program of ~420,000 sf. A nondescript ’70s high-rise Roosevelt had once used for a dorm was demolished. The attractive façade of the adjacent Fine Arts Annex, a slender six-story structure built in the 1920s, was saved to become the front of a student bookstore.
The design solution created a “servant-served” spatial relationship, placing core and support (“servant”) spaces on the north elevation behind a fairly plain precast concrete façade, with unglazed lower floors giving way to a checkerboard window grid higher up. The functional (“served”) spaces are situated on the south side, featuring blue glass and dramatic canted faces inspired by Brancusi’s famed Endless Column sculpture, as well as the faceted façade of the nearby Spertus Institute of Jewish Studies. The servant-served arrangement maximizes spectacular views to the south, east, and west.
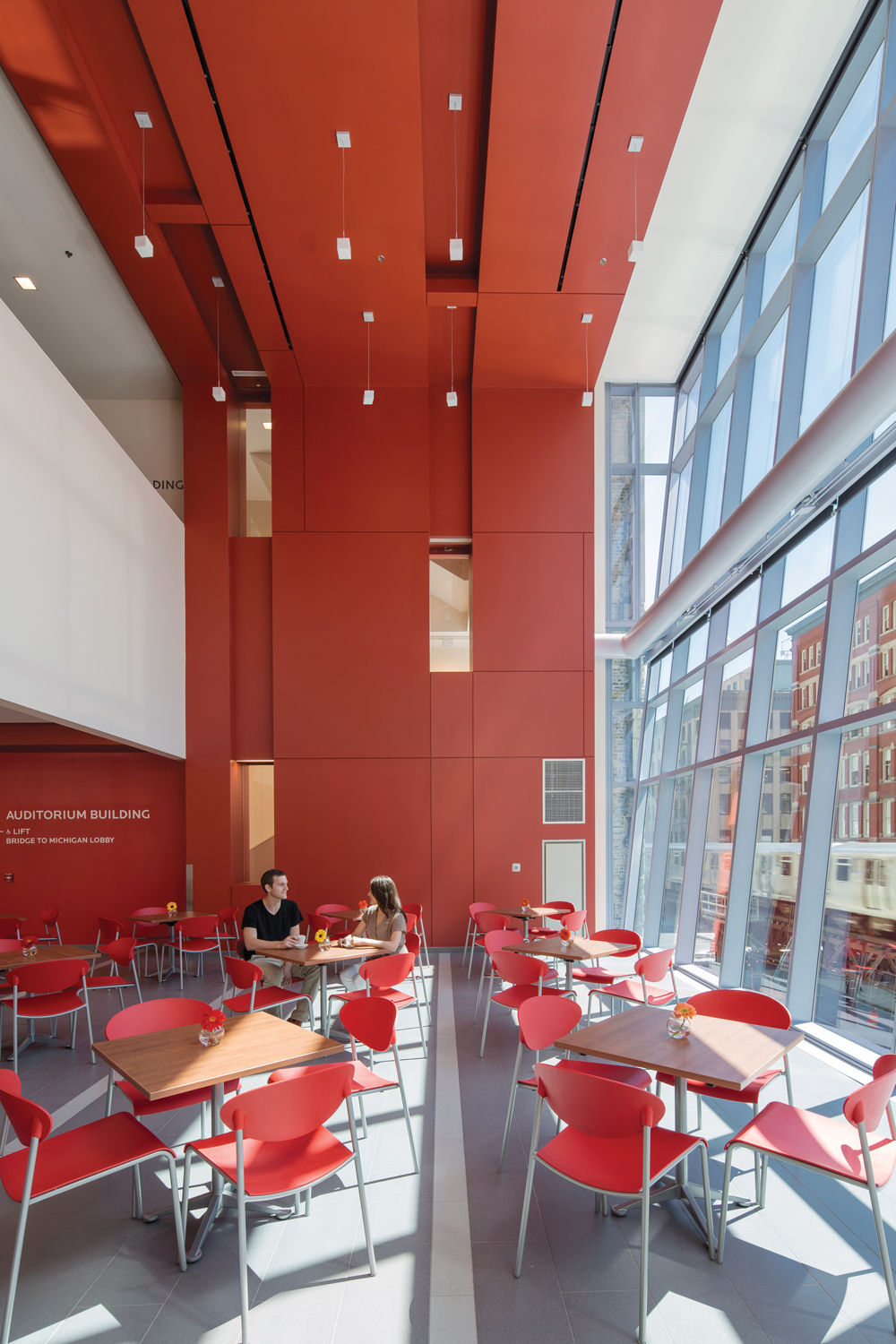
Common areas are clustered in the five lowest floors, including a two-story atrium lobby, student services offices, a student union, a dining hall, and a recreation facility. Classroom and lab spaces and a mechanical floor occupy the midsection, topped by 17 stories of residences.
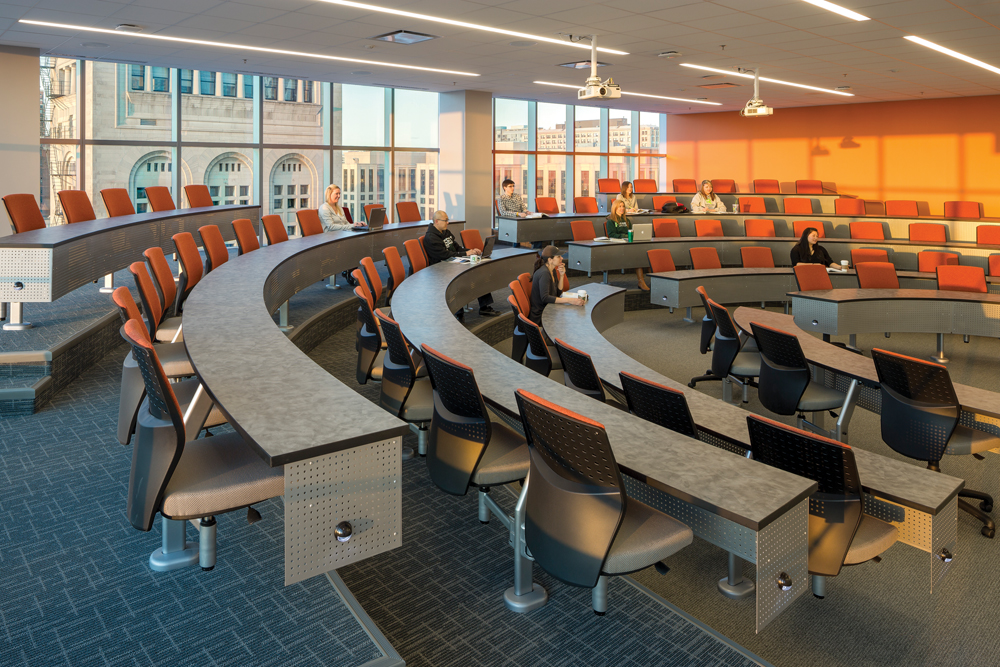
The servant-served organization maximizes clear spans for the large classrooms and labs, including seven classrooms with a capacity of 36 students each, four tiered classrooms seating 60 to 80, and three auditorium classrooms seating 78 to 180. Judiciously placed prefunction spaces serve as interior “quads” for student interaction.
The façade of the slender 1920s building in the foreground was preserved as the front of a new bookstore. The dark, plain north elevation of the new tower, which faces another tall building, delineates the service functions on this side.
Three stories of science labs support instruction and research in biology, chemistry, and physics, as well as office space for science faculty. Roosevelt’s Heller College of Business was also moved to the new skyscraper from a different Loop facility; its students now benefit from a simulated financial trading room and retail store.
Vertical and horizontal circulation within the Roosevelt campus is necessarily complex. Round-the-clock security check-in is required at Floor 14 before students can proceed to the higher levels via dedicated elevators. Hooking the tower onto the Auditorium Building to the south was also tricky but crucial; the older building is still heavily used for classrooms and offices, as well as performances in beautifully restored ArtNouveau theater spaces. Gently sloping hallways now connect the buildings at four points, with generous signage provided to ease wayfinding.
Getting to LEED Gold required an imaginative mix of strategies, from the typical— high-efficiency HVAC, low-flow plumbing, green roofs—to the less common. In the latter category: removable pillow-tops to maximize mattress life cycle, façade patterning intended to deter bird collisions, a food pulper that allows dining hall waste to be hauled off and composted, and a complex network of recycling chutes with an anti-microbial washdown system.
The second-floor dining center seats 300 and offers a mini-mart for snacks and sundries, as well as cold carryout items, hot food, pizza, a deli, a grill station, and a coffee shop.
Structural and logistical issues demanded creative solutions as well, particularly with respect to crane deployment. Many projects on tight urban sites are built around a central crane, resulting in the need to finish the resulting “dead zone” after the crane is dismantled near the end of the job. Engineering-intensive lab spaces in the Wabash Building’s midsection made this scenario particularly unpalatable. Instead, the Building Team devised a method for mounting the crane outside the building footprint, using counterbalance weights and a crane elevator that hugged the façade.
Today, the Wabash Building is a lively, 24/7 community that brings the school’s social justice mission to life, hosting students from 34 states and more than a dozen countries. Chicago Tribune architecture critic Blair Kamin is among the admirers of Roosevelt’s bold experiment: “It achieves a genuine, artful dialogue between past and present … a building of considerable promise.”
This tiered classroom is one of several large, general instructional spaces provided in the building’s middle floors. Thoughtfully planned daylighting is a hallmark of the project.
Project summary
GOLD AWARD
Roosevelt University Wabash Building
Chicago
BUILDING TEAM
Submitting firms: VOA Associates (architect) and Jones Lang Lasalle (owner’s rep)
Development advisor: The John Buck Company
Associate architect: Johnson & Lee Ltd.
Structural: Magnusson Klemencic Associates
MEP: WMA Consulting Engineers
Contractor: Power Construction
GENERAL INFORMATION
Project size: 420,000 sf
Construction cost: $123 million
Construction time: November 2009 (demolition) to March 2012 (completion)
Delivery method: Design/bid/build
Related Stories
Multifamily Housing | Jun 28, 2023
Sutton Tower, an 80-story multifamily development, completes construction in Manhattan’s Midtown East
In Manhattan’s Midtown East, the construction of Sutton Tower, an 80-story residential building, has been completed. Located in the Sutton Place neighborhood, the tower offers 120 for-sale residences, with the first move-ins scheduled for this summer. The project was designed by Thomas Juul-Hansen and developed by Gamma Real Estate and JVP Management. Lendlease, the general contractor, started construction in 2018.
Architects | Jun 27, 2023
Why architects need to think like developers, with JZA Architecture's Jeff Zbikowski
Jeff Zbikowski, Principal and Founder of Los Angeles-based JZA Architecture, discusses the benefits of having a developer’s mindset when working with clients, and why architecture firms lose out when they don’t have a thorough understanding of real estate regulations and challenges.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Average U.S. apartment rent reached all-time high in May, at $1,716
Multifamily rents continued to increase through the first half of 2023, despite challenges for the sector and continuing economic uncertainty. But job growth has remained robust and new households keep forming, creating apartment demand and ongoing rent growth. The average U.S. apartment rent reached an all-time high of $1,716 in May.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Dallas high-rise multifamily tower is first in state to receive WELL Gold certification
HALL Arts Residences, 28-story luxury residential high-rise in the Dallas Arts District, recently became the first high-rise multifamily tower in Texas to receive WELL Gold Certification, a designation issued by the International WELL Building Institute. The HKS-designed condominium tower was designed with numerous wellness details.
University Buildings | Jun 26, 2023
Addition by subtraction: The value of open space on higher education campuses
Creating a meaningful academic and student life experience on university and college campuses does not always mean adding a new building. A new or resurrected campus quad, recreational fields, gardens, and other greenspaces can tie a campus together, writes Sean Rosebrugh, AIA, LEED AP, HMC Architects' Higher Education Practice Leader.
Standards | Jun 26, 2023
New Wi-Fi standard boosts indoor navigation, tracking accuracy in buildings
The recently released Wi-Fi standard, IEEE 802.11az enables more refined and accurate indoor location capabilities. As technology manufacturers incorporate the new standard in various devices, it will enable buildings, including malls, arenas, and stadiums, to provide new wayfinding and tracking features.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
Office Buildings | Jun 26, 2023
Electric vehicle chargers are top priority for corporate office renters
Businesses that rent office space view electric vehicle (EV) charging stations as a top priority. More than 40% of companies in the Americas and EMEA (Europe, the Middle East and Africa) are looking to include EV charging stations in future leases, according to JLL’s 2023 Responsible Real Estate study.
Laboratories | Jun 23, 2023
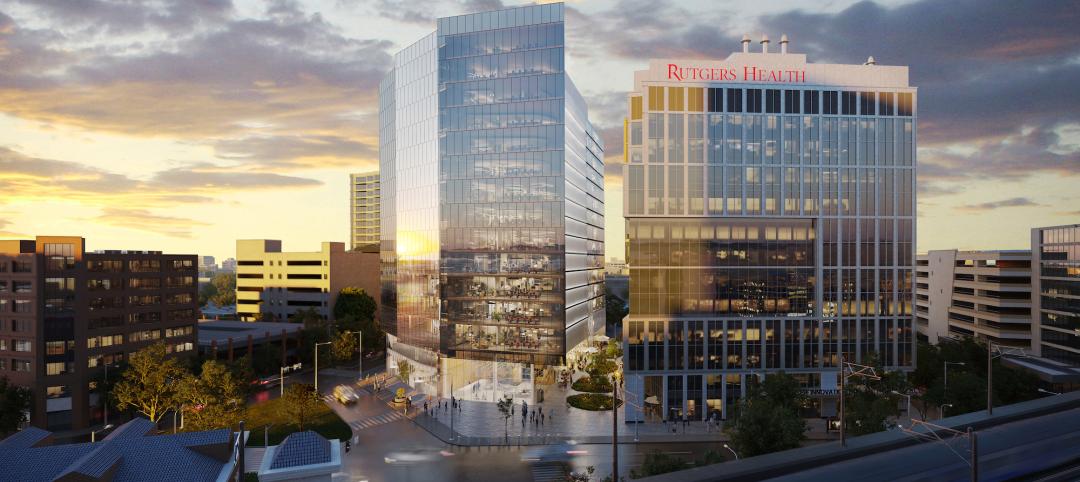
A New Jersey development represents the state’s largest-ever investment in life sciences and medical education
In New Brunswick, N.J., a life sciences development that’s now underway aims to bring together academics and researchers to work, learn, and experiment under one roof. HELIX Health + Life Science Exchange is an innovation district under development on a four-acre downtown site. At $731 million, HELIX, which will be built in three phases, represents New Jersey’s largest-ever investment in life sciences and medical education, according to a press statement.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Jun 22, 2023
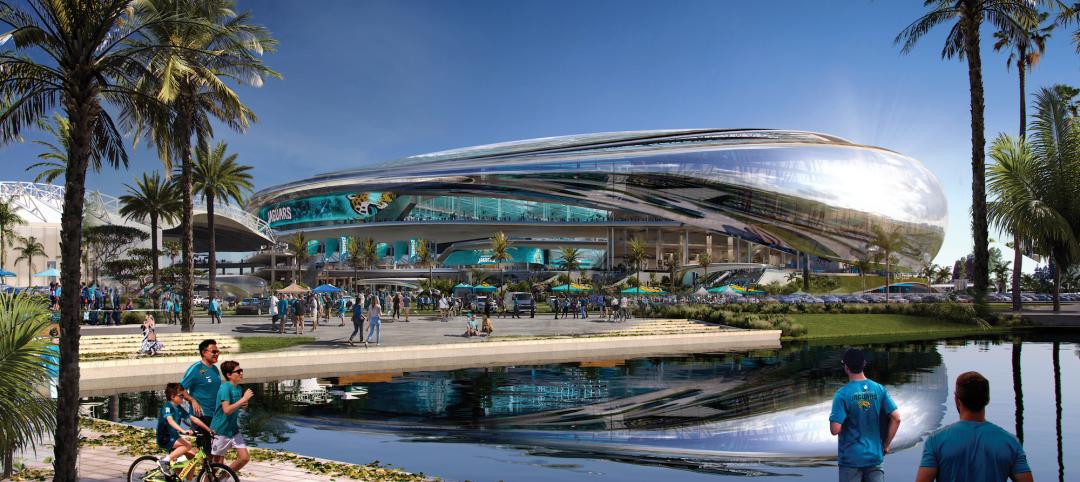
NFL's Jacksonville Jaguars release conceptual designs for ‘stadium of the future’
Designed by HOK, the Stadium of the Future intends to meet the evolving needs of all stadium stakeholders—which include the Jaguars, the annual Florida-Georgia college football game, the TaxSlayer.com Gator Bowl, international sporting events, music festivals and tours, and the thousands of fans and guests who attend each event.