When the Boston Watch Company opened its factory in 1854 on the banks of the Charles River in Waltham, Mass., the area was far enough away from the dust, dirt, and grime of Boston to safely assemble delicate watch parts. The factory’s production techniques were very advanced for the time, and business boomed.
In 1907 the company changed its name to the Waltham Watch Company, a name that became synonymous with precision movement and quality timepieces. Several of its watches reside in the Smithsonian Institution’s collection, including Model 1857, Serial No. 67613, a pocket watch gifted to President Abraham Lincoln to commemorate the Gettysburg Address.
As the brand grew in prominence, Waltham became known throughout the world as “Watch City.” Worker housing and supporting businesses sprang up around the factory, transforming the country town into an urban environment. Over the course of a century the factory grew to nearly 500,000 sf, making it one of the world’s largest brick buildings; its frontage along Crescent Street alone was a quarter mile in length.
Despite its massive size, the factory had exceptionally narrow floor plates, less than 25 feet wide from wall to wall in the work areas. The slender design and numerous oversized windows and skylights guaranteed that high levels of natural light flooded the workspaces and provided enough illumination for workers to manipulate tiny watch parts with precision—particularly important in those years before the factory was electrified.
Watchmaking at the factory was discontinued in 1957, but a number of tenants occupied parts of the building over the years, so it was never completely abandoned, nor was its Industrial Revolution architecture ever significantly altered.
That was good news for developer and new owner Berkeley Investments, which saw tremendous potential in the historic building with amazing river views and proximity to the Route 128 tech corridor and downtown Boston. The owner/developer assembled a Building Team that included Bruner/Cott & Associates (architect), Columbia Construction (GC), Epsilon Associates (historic consultant), and Pine & Swallow Associates (environmental consultant) to transform the property into a mixed-use complex with modern office space, retail, restaurants, and residential lofts.
The project was broken up into two phases: a 177,000-sf office component (phase one) and a retail/residential component (phase two, still under construction). The $25 million phase one rehab earned a Gold Award and praise from our judges. “Its reuse is to be celebrated,” said Reconstruction Awards judge Martha Bell, FAIA, LEED AP, principal at Tilton Kelly+Bell, Chicago.
Because the building was in decent shape, the Building Team was able to concentrate on reworking a 19th-century factory into a 21st-century office complex. The major focus: make the imposing structure more approachable and welcoming, create modern, user-friendly interior spaces, and provide a connection between the interior and the outdoors. The main entrances along Crescent Street were reconstructed, and a public exhibit space was installed in the lobby.
Additional access points open the building to the Riverwalk, a pedestrian walking/biking path along the Charles River developed in collaboration with the city’s Department of Conservation and Recreation, and to several courtyards within the complex. The landscaped courtyards serve as rain gardens to cool and clean the stormwater before it’s released into the river. Additional exterior work included brick repair and repointing, repairs to the slate roof, and stabilization of the central smokestack.
The factory’s interior was left largely intact, aside from the installation of the typical modern upgrades: HVAC, electrical, plumbing, telecom, life/safety, ADA compliance. Additional work focused on opening blocked freight passageways to improve interior circulation and views through the building, removing lead paint, and repairing exposed brick walls and timber ceilings. The window sashes, which had been replaced in the 1980s, were fitted with replicas of the originals. The window frames, however, remain original to the building. Thermal calculations and water-pressure testing proved the frames were still viable.
Almost three-quarters of the office space is leased, once again bringing jobs and activity to the South Side of Waltham. “They recreated the nerve center of the community,” said Reconstruction Awards judge David Callan, PE, SVP at Environmental Systems Design, Chicago. “The neighborhood surrounding it is there because of this factory, and bringing it back reenergizes the community.” BD+C
PROJECT SUMMARY
Building Team
Submitting firm: Bruner/Cott & Associates (architect)
Owner/developer: Berkeley Investments
Structural engineer: DM Berg Consultants
MEP engineer: Avid Engineers
GC: Columbia Construction
Historical consultant: Epsilon Associates
Environmental consultant: Pine and Swallow Associates
Landscape design: Richard Burch Associates
General Information
Size: 177,000 gsf
Construction cost: $25 million
Construction period: February 2008 to July 2009
Delivery method: Design-bid-build
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
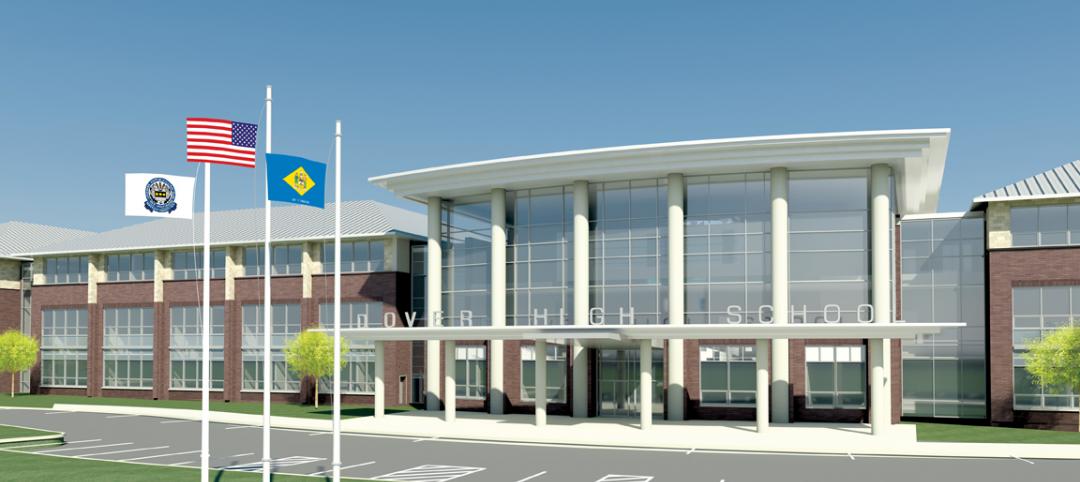
One of Delaware’s largest high schools seeks LEED for Schools designation
The $82 million, 280,000-sf Dover (Del.) High School will have capacity for 1,800 students and feature a 900-seat theater, a 2,500-seat gymnasium, and a 5,000-seat football stadium.
| May 18, 2011
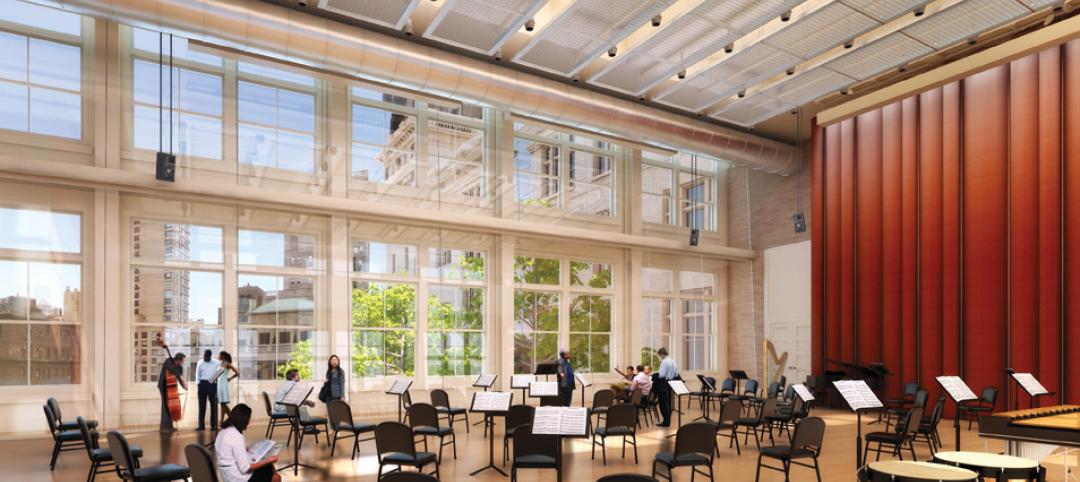
Carnegie Hall vaults into the 21st century with a $200 million renovation
Historic Carnegie Hall in New York City is in the midst of a major $200 million renovation that will bring the building up to contemporary standards, increase educational and backstage space, and target LEED Silver.
| May 17, 2011
Redesigning, redefining the grocery shopping experience
The traditional 40,000- to 60,000-sf grocery store is disappearing and much of the change is happening in the city. Urban infill sites and mixed-use projects offer grocers a rare opportunity to repackage themselves into smaller, more efficient, and more convenient retail outlets. And the AEC community will have a hand in developing how these facilities will look and operate.
| May 17, 2011
Architecture billings index fell in April, hurt by tight financing for projects
The architecture billings index, a leading indicator of U.S. construction activity, fell in April, hurt by tight financing for projects. The architecture billings index fell 2.9 points last month to 47.6, a level that indicates declining demand for architecture services, according to the American Institute of Architects.
| May 17, 2011
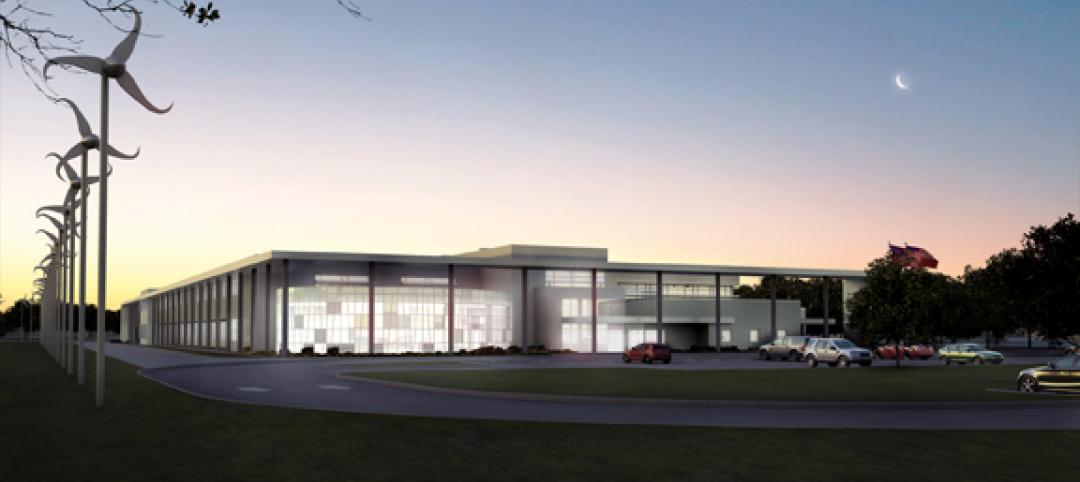
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 17, 2011
Gilbane partners with Steel Orca on ultra-green data center
Gilbane, along with Crabtree, Rohrbaugh & Associates, has been selected to partner with Steel Orca to design and build a 300,000-sf data center in Bucks County, Pa., that will be powered entirely through renewable energy sources--gas, solar, fuel cells, wind and geo-thermal. Completion is scheduled for 2013.
| May 17, 2011
Should Washington, D.C., allow taller buildings?
Suggestions are being made that Washington revise its restrictions on building heights. Architect Roger Lewis, who raised the topic in the Washington Post a few weeks ago, argues for a modest relaxation of the height limits, and thinks that concerns about ruining the city’s aesthetics are unfounded.
| May 17, 2011
The New Orleans master plan
At an afternoon panel during last week's AIA National Conference in New Orleans, Goody Clancy Principal David Dixon and Manning Principal W. Raymond Manning shared their experiences creating the New Orleans Master Plan, a document that sets a new course for the city, from land use and transportation planning to environmental protection.
| May 17, 2011
Do these buildings look like buffalo to you?
It’s hard to contemplate winter now that we’re mid-spring, but when the seasons change, ice skaters in Winnipeg will be able to keep warm in plywood shelters designed by Patkau Architects. The designers created temporary shelters inspired by animal behavior—specifically, buffalo bracing against the wind. Check them out.