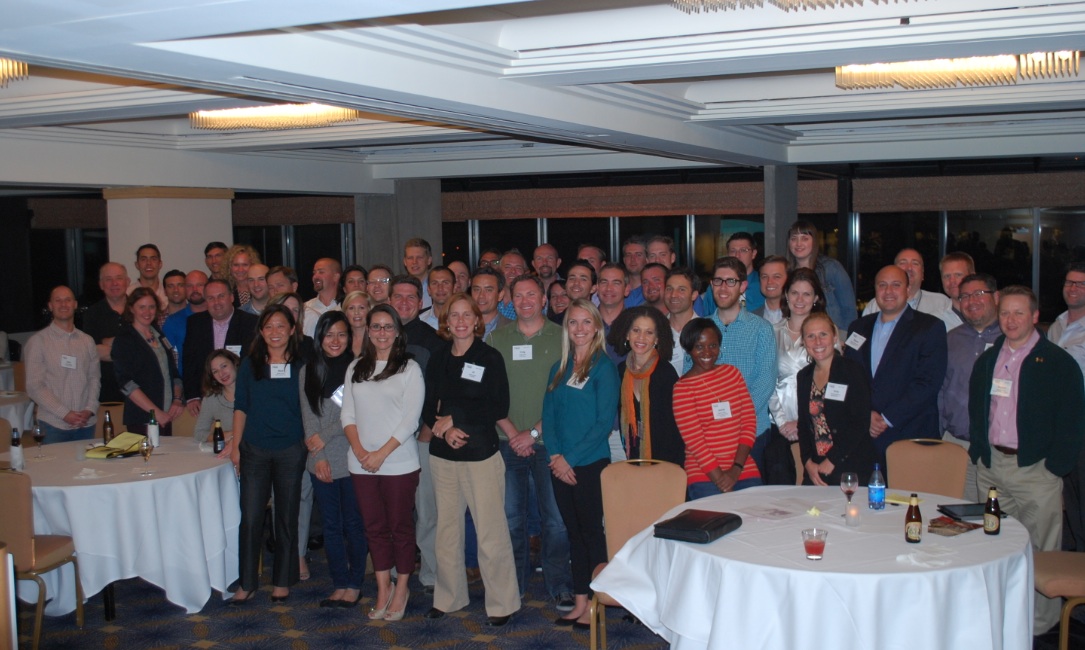
A group of 65 up-and-coming AEC professionals gathered in San Francisco last week for Building Design+Construction's Third Annual Under 40 Leadership Summit. The highlight of the 2.5-day event was the Vision U40 competition, where 15 teams battled for $5,000 in prizes to see who could develop the best solutions for today's pressing social, economic, technical, and cultural problems related to the built environment.
A few of the common themes presented by the groups were mobility (e.g., adapting the food truck concept for special causes, such as health and wellness education) and the use of technology (e.g., tablet and smartphone apps for the built environment).
Each team had just 90 seconds to pitch their concept to the entire group (see videos below), who voted for their top five. The five winning teams—including the $3,000 grand prize team—will be announced later this week.
In the meantime, we want your feedback on the 15 concepts presented at the Under 40 Leadership Summit. Watch the 90-second pitches below and vote for your favorite idea. Click here to vote!
1. Mobile Wellness
Problem: Americans spend 75% of their average day at work, school, or traveling to and from, leaving just six hours for everything else in their lives.
Solution: Bring healthcare and wellness to local communities (especially schools and workplaces) through a comprehensive, incentivized mobile wellness program that adapts the food truck model. Lab services, health checkups, vaccinations, and more, will be administered on the fly, and at the convenience of the consumer.
2. Cultural Food Shift
Problem: The lack of fresh, healthy food in impoverished areas has become an epidemic in the U.S. How can we alter the culture of food in America, where the consumer demands change in the foods offered by local suppliers?
Solution: Inspire healthy eating in areas of low income through easy-to-build-and-maintain personal and community gardens. The gardens will serve not only as a source of food, but also a gathering area where community members can meet to exchange food, goods, and ideas. The program will kick off with private family gardens and eventually expand to include large, public gardens.
3. WellBOX
Problem: During the next 20 years, 970 million people will be added to third-world countries. These areas lack access to critical healthcare services and clean water.
Solution: The WellBOX is a portable health clinic that can be dropped into any region of the world to provide clean drinking water and healthcare services and education. The self-sustaining unit will be powered by solar panels and will tap into a local well to provide water filtration. The modular structure will come equipped with tele-medicine equipment, allowing doctors to diagnos remotely.
4. M.C.R. (Mobile Culture Reinvented)
Problem: Living in and around major cities does not support a healthy lifestyle, due to long commute times and reliability on the car. Americans, on average, spend 600 hours in their car each year, or roughly an hour and 40 minutes per day.
Solution: M.C.R. is a network of workplace solutions that use zoning, technology, telecommuting, and micro-cities to reduce or eliminate lengthy commutes. For example, re-zoning could encourage the creation of micro-cities in the suburbs. Similarly, technology could increase the use of telecommuting.
5. Less = More
Problem: Thirty percent of India's population (1.2 billion people) lives below the poverty line. While the country has a fairly successful food subsidy program, much of the food goes to waste due to a lack of storage space.
Solution: Build "smart" silos that incorporate wireless technology to connect with regional government warehouses that could handle overflows of food.
6. Internext
Problem: The digital information world offers us instantaneous, universal access, but inundates us with data in a constant, overwhelming stream. As a result, our connections to others and our surrounding community are becoming less meaningful. We've lost our sense of place.
Solution: Internext filters when and where you receive specific digital information based on rules you set, helping you prioritize your life following preferences that reflect your values. Want to spend more time with your family? Set a rule that holds all email after 6 p.m. on workdays. Want to connect with fans of your favorite team while on vacation? Let Internext find the popular hangouts.
7. Healthotron
Problem: Childhood obesity has doubled over the past 30 years. In 2010, more than one-third of the children in the U.S. were overweight or obese.
Solution: Apply the food truck model to health and wellness education. The Healthotron integrates playscapes, interactive video games, and large-screen TVs for teaching kids and parents about nutrition and exercise. A smartphone/tablet app alerts kids when the truck is nearby, encouraging groups of children to get out and play.
8. Design Pulse
Problem: The AEC industry has a good understanding of how design impacts economic and environmental factors, but what about human and social capital issues? How could design decisions holistically improve the human spirit?
Solution: Design Pulse is a sortable, searchable database offering architects and designers a wealth of real-time information about a given environment. The goal: arm design professionals with metrics needed to make design choices that will have a positive effect on the human spirit. The database will aggregate data from a number of sources: geospatial apps, Wikipedia, social media, and wearable computers like Fitbits and Nike FuelBand.
9. The Kids Are Alright
Problem: The younger generation prefers to stay inside, whether in the classroom or on the couch. Additionally, parents are missing out on sharing the same learning opportunities their children have.
Solution: Create a Foursquare-type mobile app that, instead of pulling up nearby restaurants, provides educational information based on your current location—from details on the oak tree in your backyard to the history of the landmark building in the center of town. The app encourages kids and their parents to interact with and learn about their surrounding environment.
10. F.A.B.R.I.C.
Problem: "Unsocial" media has unraveled the fabric of our neighborhoods. How do we encourage people to get outside and interact and connect with their neighbors and communities?
Solution: This digitized sidewalk encourages people to get outside and weave back into their communities. F.A.B.R.I.C. (short for "future, active, bio-optic, responsive, inter-community" sidewalk) features virtual, interactive games, energy generation, social spaces, and an associated mobile app that, for instance, will alert users when a friend is nearby.
11. A Seed That Inspires
Problem: Most communities are strongly focused on the growth of its children, with large investments in schools and other programs. But most working adults end up separated from the educational process. How can we reintegrate the adult population with the educational process, and, more importantly, the educational process with the adult population?
Solution: What if we gave the children in our communities the right to lead us? For one day a week, they select the initiatives and the next steps for the community, and they are empowered to direct us. As adults, we take a step back from the work world and learn from the imagination, skills, and inspiration of our children.
12. Shyft
Problem: There are many issues with urban mobility today, including congested roads that lead to lengthy commutes and large, fixed, costly transit systems that offer limited coverage.
Solution: Shyft combines multiple emerging technologies with existing municipal mass transit solutions to bring innovative commuting to the masses. The system partners existing vehicle commuters with people in need of a ride, based on the commute route. All users are pre-screened, and drivers can earn money for picking up Shyft members.
13. Destination Food
Problem: More than 23 million Americans live without access to affordable, nutritious food. Making things worse, 40% of the food in the U.S. goes to waste.
Solution: Destination Food is an open-source technology platform that connects food supply with demand in a simple, convenient, and affordable way. The app includes a database of profiles and ratings for growers, GPS mapping for connecting consumers to the closest food suppliers, and a scheduling tool for setting up deliveries.
14. ENVIROpedia
Problem: The issues of global warming, climate change, and the environment are extremely complex. What can we do about them as individuals?
Solution: ENVIROpedia is an open-source, crowd-sourced information exchange platform that relies on the power of many to answer tough questions about local environments and economies. Want to know where your concrete mix came from? Or the environmental impact of a copper roof? Simply ask the group. Chances are someone will know the answer.
15. URB-RAL
Problem: The growing urbanization movement will continue to widen the gap between urban and suburban environments. The two have quite a bit to offer one another.
Solution: URB-RAL will establish physical and virtual hubs to encourage and facilitate trade between urban and rural communities. The program will partner urban neighborhoods with sister rural communities and use vehicles to exchange goods and services (e.g., medical services for rural communities and fresh food for urban areas).
Related Stories
| Mar 14, 2012
Hyatt joins Thornton Tomasetti as VP in Chicago
A forensic specialist, Hyatt has more than 10 years of experience performing investigations of structural failures throughout the U.S.
| Mar 14, 2012
Tsoi/Kobus and Centerbrook to design Jackson Laboratory facility in Farmington, Conn.
Building will house research into personalized, gene-based cancer screening and treatment.
| Mar 13, 2012
China's high-speed building boom
A 30-story hotel in Changsha went up in two weeks. Some question the safety in that, but the builder defends its methods.
| Mar 13, 2012
Commercial glazer Harmon expanding into Texas
Company expanding into the Texas market with a new office in Dallas and a satellite facility in Austin.
| Mar 13, 2012
Worker office space to drop below 100-sf in five years
The average for all companies for square feet per worker in 2017 will be 151 sf, compared to 176 sf, and 225 sf in 2010.
| Mar 12, 2012
Improving the performance of existing commercial buildings: the chemistry of sustainable construction
Retrofitting our existing commercial buildings is one of the key steps to overcoming the economic and environmental challenges we face.
| Mar 7, 2012
Firestone iPad app offers touch technology
Free app provides a preview of Firestone’s Roots to Rooftop Building Envelope Solution with an overview of all the products from ground and stormwater management solutions, to complete wall panel and commercial roofing system applications.
| Mar 7, 2012
LEO A DALY opens new office in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Jay N. Kline, Regional Manager – Saudi Arabia, to lead new office.