Thermal stress is one of many factors that can cause glass to break, even when it is not impacted by a projectile.
Such failures usually are not a testament to the quality of the glass, but rather the result of temperature imbalance within the glass, which can occur when the center of a window or insulating glass unit (IGU) heats and expands while the edges remain cool.
The resulting thermally induced tensile stress on the glass edges can exceed the strength of the glass itself, causing it to break at approximately a 90-degree angle.
Working closely with the IGU fabricator and glass supplier, and conducting a thermal stress analysis at the beginning of the design phase can help architects specify the proper glass for their projects. Here are five thermal stress related rules-of-thumb to consider when specifying glass:
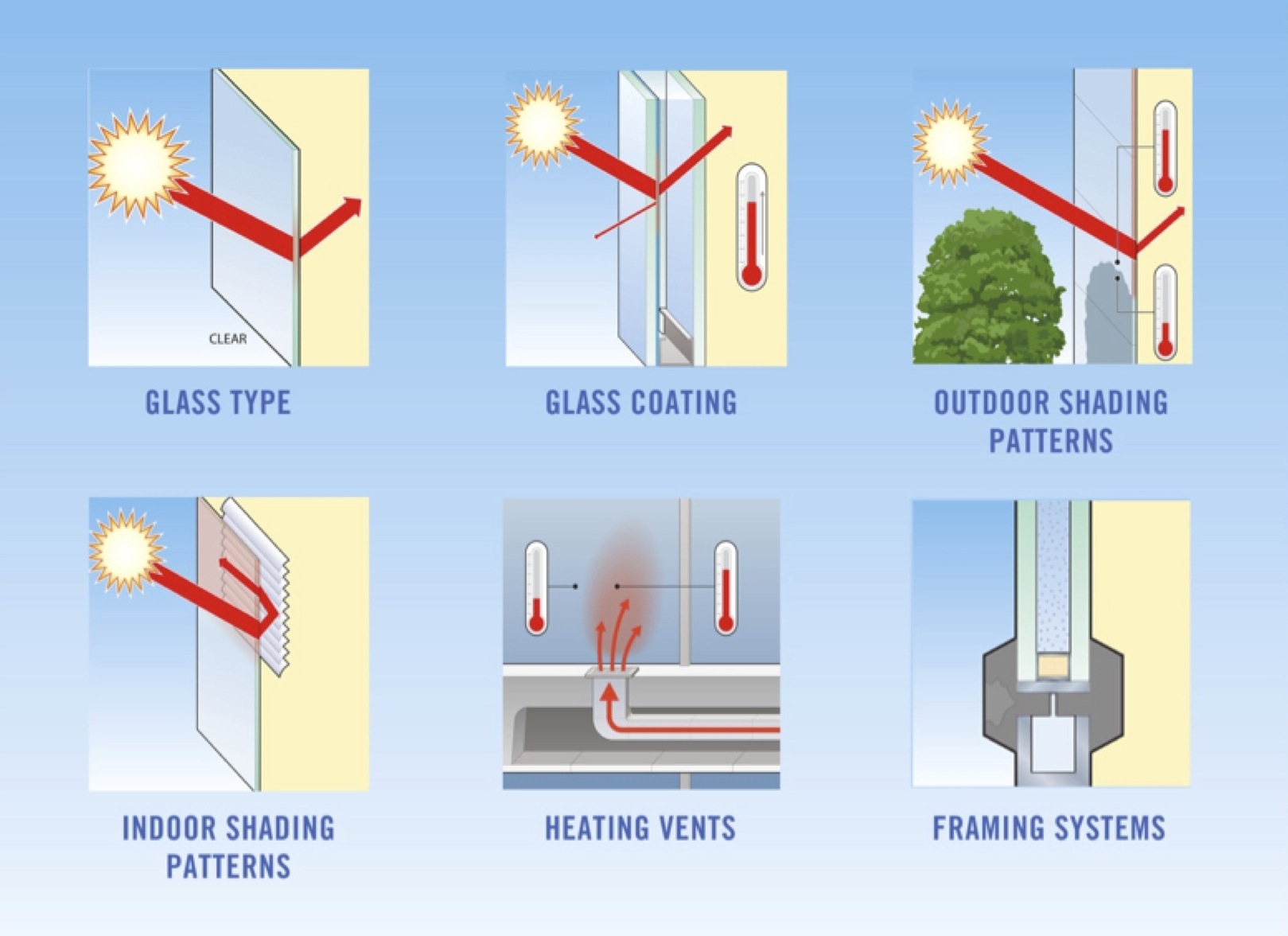
1. Clear or color? Glass can be clear, ultra-clear or tinted in colors such as gray, blue, green and bronze. Tinted glasses absorb solar radiation more than clear glass, which can cause them to collect heat and make them more susceptible to break from thermal stress.
2. Inner or outer surface? Reflective and low-emissivity (low-e) coatings, which improve the solar performance of glass primarily by reflecting solar radiation, can be placed on any one of four surfaces in a dual-pane IGU. While they are usually placed on the inner glass surfaces of the IGU, the coating orientation and the associated risk of thermal stress has to be taken into account.
3. Sunny or shady? Outdoor shading, including overhangs, adjacent buildings, and trees, is one of the most dynamic elements to consider when analyzing thermal stress. Minimizing locations where non-uniform shading of IGUs can occur will help avoid extreme temperature gradients. Interior shading devices, such as blinds or drapes, can increase glass temperature by reflecting solar radiation back through the glass or by reducing the convection and conduction of heat away from the glass. To minimize thermally induced edge stress, the air space around the window glass should be ventilated. There should be a gap of several inches between the glass and shades, blinds or drapes.
4. Where to place a vent? If heating vents, registers and grilles point directly at glass units, warm air will cause the glass to heat up and, under certain conditions, break. Make sure vents are carefully placed to reduce thermal stress risk and avoid placing them between the glass and interior shading devices.
5. How to frame it? Glass framing systems that have low heat capacity also can minimize the chance of a thermal stress break. Structural gaskets and narrow metal framing are favorable because they have less effect on the glass temperature around the edges. Conversely, massive framing – whether metal, masonry or even wood – can have more of an effect, resulting in thermal imbalance and risk of glass breakage.
To learn more about avoiding thermal breakage of insulated glass units and other glass-related topics, visit the PPG Glass Education Center at www.educationcenter.ppg.com.
Related Stories
Architects | May 2, 2024
Emerging considerations in inclusive design
Design elements that consider a diverse population of users make lives better. When it comes to wayfinding, some factors will remain consistent—including accessibility and legibility.
K-12 Schools | Apr 30, 2024
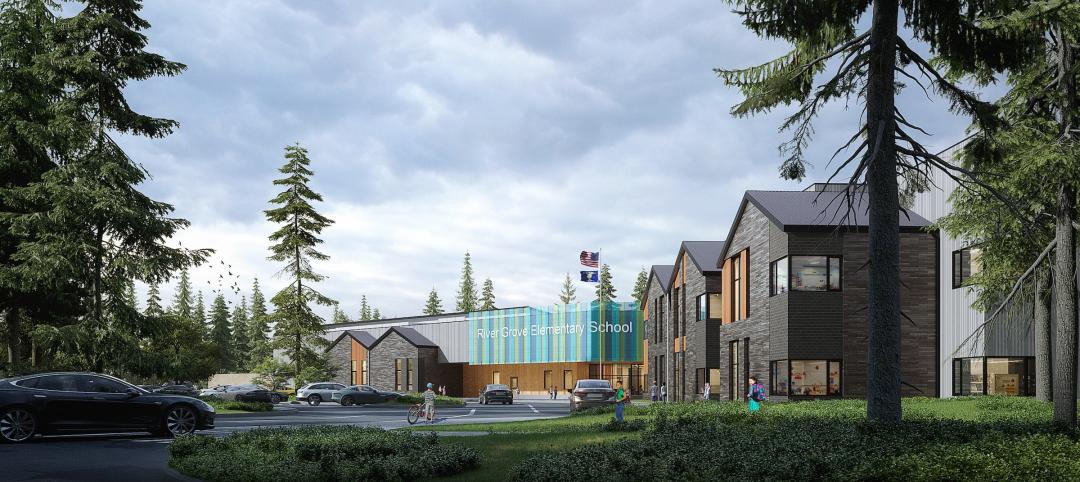
Fully electric Oregon elementary school aims for resilience with microgrid design
The River Grove Elementary School in Oregon was designed for net-zero carbon and resiliency to seismic events, storms, and wildfire. The roughly 82,000-sf school in a Portland suburb will feature a microgrid—a small-scale power grid that operates independently from the area’s electric grid.
AEC Tech | Apr 30, 2024
Lack of organizational readiness is biggest hurdle to artificial intelligence adoption
Managers of companies in the industrial sector, including construction, have bought the hype of artificial intelligence (AI) as a transformative technology, but their organizations are not ready to realize its promise, according to research from IFS, a global cloud enterprise software company. An IFS survey of 1,700 senior decision-makers found that 84% of executives anticipate massive organizational benefits from AI.
Codes and Standards | Apr 30, 2024
Updated document details methods of testing fenestration for exterior walls
The Fenestration and Glazing Industry Alliance (FGIA) updated a document serving a recommended practice for determining test methodology for laboratory and field testing of exterior wall systems. The document pertains to products covered by an AAMA standard such as curtain walls, storefronts, window walls, and sloped glazing. AAMA 501-24, Methods of Test for Exterior Walls was last updated in 2015.
MFPRO+ News | Apr 29, 2024
World’s largest 3D printer could create entire neighborhoods
The University of Maine recently unveiled the world’s largest 3D printer said to be able to create entire neighborhoods. The machine is four times larger than a preceding model that was first tested in 2019. The older model was used to create a 600 sf single-family home made of recyclable wood fiber and bio-resin materials.
K-12 Schools | Apr 29, 2024
Tomorrow's classrooms: Designing schools for the digital age
In a world where technology’s rapid pace has reshaped how we live, work, and communicate, it should be no surprise that it’s also changing the PreK-12 education landscape.
Adaptive Reuse | Apr 29, 2024
6 characteristics of a successful adaptive reuse conversion
In the continuous battle against housing shortages and the surplus of vacant buildings, developers are turning their attention to the viability of adaptive reuse for their properties.
AEC Innovators | Apr 26, 2024
National Institute of Building Sciences announces Building Innovation 2024 schedule
The National Institute of Building Sciences is hosting its annual Building Innovation conference, May 22-24 at the Capital Hilton in Washington, D.C. BI2024 brings together everyone who impacts the built environment: government agencies, contractors, the private sector, architects, scientists, and more.
Mass Timber | Apr 25, 2024
Bjarke Ingels Group designs a mass timber cube structure for the University of Kansas
Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG) and executive architect BNIM have unveiled their design for a new mass timber cube structure called the Makers’ KUbe for the University of Kansas School of Architecture & Design. A six-story, 50,000-sf building for learning and collaboration, the light-filled KUbe will house studio and teaching space, 3D-printing and robotic labs, and a ground-level cafe, all organized around a central core.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Apr 25, 2024
How pools can positively affect communities
Clark Nexsen senior architects Jennifer Heintz and Dorothea Schulz discuss how pools can create jobs, break down barriers, and create opportunities within communities.