Windows not only transform the façade of a building, the natural light that they allow inside is a vital tool in highlighting a building’s interior design elements.
But sunlight is not always needed—or even wanted. At some point in the day, direct sunlight will enter the space, causing glare and heat gain.
Enter the interior shade system.
“The primary purpose of a shade system is to control glare for the user’s visual comfort,” says Kristopher Baker, PE, LEED AP, Senior Associate in the Denver office of Syska Hennessy Group. These systems also help eliminate excess heat caused by direct sunlight.
Designing a shade system is more complex than picking out basic white venetian blinds. The Building Team’s overall design and functional goals should be considered, as well as the end user’s needs. Here are five elements to consider when designing an interior shade system.
1. Make sure the type of shade system meets client needs and program goals.
The type of device should be chosen based on the client’s needs and the overall programmatic goals of the project. Different types of shades have different benefits, according to Baker.
• Honeycomb shades feature two to three layers that trap air inside, acting as insulation and allowing users to reduce heat loss through the windows.
• Venetian blinds are available in various sizes with slats that can be tilted at different angles to control the amount and direction of sunlight that is allowed into a space.
• Roller shades are panels of fabric with varying levels of openness in the weave.
Follow these guidelines to get your shade system right
1. Make sure the type of shade system meets client needs and program goals.
2. Fit the shade system to the specific type
of space you’re working in.
3. Check out the new control mechanisms
that are available.
4. Use shades to help meet your project’s
energy goals.
5. Look into the future of shading technology.
Joseph Parks, national sales manager for commercial window treatments at Lutron, says a shade should be chosen primarily for its function, rather than its form. “A lot of times the fabric is chosen based on the look or the aesthetic or how it matches the interior, rather than how transparent the fabric is with regard to light,” he says.
2. Fit the shade system to the specific type of space you’re working in.
Baker highlights the importance of understanding the space and what it will be used for when designing a shade system. Shades are used to control glare in a specific environment, but not all spaces need shades. For example, an airport terminal is one location where shading devices are not necessarily desirable.
“Having direct sun and having that brightness helps you with your circadian rhythms, and that’s what helps you get over jet lag,” Baker says. “That’s why most of the new airports have a lot of daylight coming into the space.”
However, for an eye clinic, where patients are moving throughout the facility with their pupils dilated, a shade system would be ideal for reducing the amount of direct sunlight penetrating the space.
High-traffic areas such as atriums and lobbies require a more varied approach in shade design, with a number of options for glare control.
The library of Calvert High School in Prince Frederick, Md., is one such location where a shade system was necessary for the productivity and comfort of the occupants. Skylight panels totaling 17,000 sf top the media center, but the possibility of disruptive glare and heat gain posed a challenge. A user-controlled mechanical shade system allows school administrators to control the position of the shades for the comfort of students and staff working below.
3. Check out the new control mechanisms that are available.
The use of automated control systems is on the rise, according to Parks. “There’s certainly a big trend in the solar tracking arena of shades,” he says. “The shades are smart enough to understand where the sun is supposed to be in relation to the building, so they can either manage the daylight or allow more daylight into the space.”
More advanced technology places sensors on the window, allowing for more precise automatic glare control based on the sun’s position.
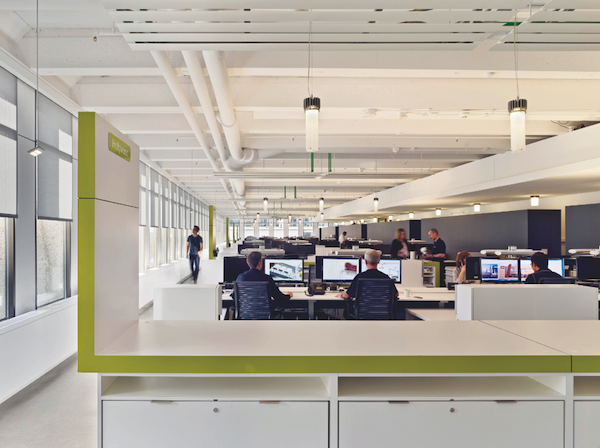
The Portland, Ore., office of engineering firm Glumac features one such automated system. Solar-adaptive roller shades automatically adjust based on the amount of direct sunlight entering the space.
Manual systems have their merits, but Baker warns that building users can override the shading system. “If you walk around an office park, you’ll see that 80 to 85% of the blinds of every office are closed so that people can’t see out,” he says. “People have no problem getting rid of sun when they’re annoyed by it, but when the sun goes away they don’t open them back up.”
If a manual system is specified, user education is vital to ensure building occupants operate the shading system the way the Building Team and owner intended.
4. Use shades to help meet your project’s energy goals.
Shades can lower a building’s HVAC cooling load by about 10% and can increase the daylight harvesting savings by 30–40%, according to Parks. Care must be taken to determine what the building’s overall energy goals will be and how the shade system will fit into that plan.
At the Glumac office, the solar-controlled shades are accompanied by a lighting system with vacancy and daylight sensors that work together to adjust the amount of natural and artificial light in the space, with an ultimate goal of reducing the building’s dependence on electric lighting.
While shade systems are a part of an effective daylighting strategy, Baker stresses that some form of glare control should be implemented in the design of any building, regardless of its daylighting techniques.
“You can’t allow the direct sun to come in and splash your desk,” he says. “Fundamentally, the glare control has to be part of a solution, whether there’s daylighting or not.”
5. Look into the future of shading technology.
What is innovative right now might be outdated and less efficient than newer technologies in 10 years. An investment in new technology might prove more efficient and effective than relying on what you’ve always used.
“The technologies are going to continue to get smarter,” says Parks. “We’ve gone pretty far in that we can now sense what is going on right outside the window, but you may see systems that can communicate to building management systems and develop a hierarchy of needs based on temperature and light, rather than just light.”
Baker sees that innovation being taken one step further, with the expansion of dynamic glass technology that may eliminate the need for a shade system altogether.
Electrochromic glass uses an electrical pulse to control the tint of the glass; thermochromic glass changes the tint based on the surface’s temperature.
“If the sun is on that glass, then it goes dark; if the sun is not on that glass, it stays clear,” Baker says. “It’s expensive technology right now, but if they get a hold in the marketplace, you will not need interior blinds.”
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
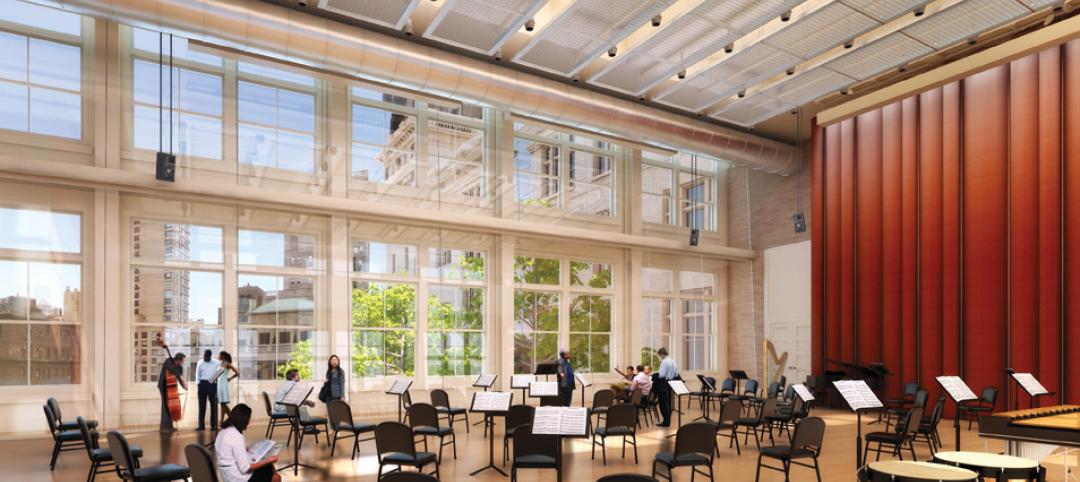
Carnegie Hall vaults into the 21st century with a $200 million renovation
Historic Carnegie Hall in New York City is in the midst of a major $200 million renovation that will bring the building up to contemporary standards, increase educational and backstage space, and target LEED Silver.
| May 17, 2011
Redesigning, redefining the grocery shopping experience
The traditional 40,000- to 60,000-sf grocery store is disappearing and much of the change is happening in the city. Urban infill sites and mixed-use projects offer grocers a rare opportunity to repackage themselves into smaller, more efficient, and more convenient retail outlets. And the AEC community will have a hand in developing how these facilities will look and operate.
| May 17, 2011
Architecture billings index fell in April, hurt by tight financing for projects
The architecture billings index, a leading indicator of U.S. construction activity, fell in April, hurt by tight financing for projects. The architecture billings index fell 2.9 points last month to 47.6, a level that indicates declining demand for architecture services, according to the American Institute of Architects.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 17, 2011
Gilbane partners with Steel Orca on ultra-green data center
Gilbane, along with Crabtree, Rohrbaugh & Associates, has been selected to partner with Steel Orca to design and build a 300,000-sf data center in Bucks County, Pa., that will be powered entirely through renewable energy sources--gas, solar, fuel cells, wind and geo-thermal. Completion is scheduled for 2013.
| May 17, 2011
Should Washington, D.C., allow taller buildings?
Suggestions are being made that Washington revise its restrictions on building heights. Architect Roger Lewis, who raised the topic in the Washington Post a few weeks ago, argues for a modest relaxation of the height limits, and thinks that concerns about ruining the city’s aesthetics are unfounded.
| May 17, 2011
The New Orleans master plan
At an afternoon panel during last week's AIA National Conference in New Orleans, Goody Clancy Principal David Dixon and Manning Principal W. Raymond Manning shared their experiences creating the New Orleans Master Plan, a document that sets a new course for the city, from land use and transportation planning to environmental protection.
| May 17, 2011
Do these buildings look like buffalo to you?
It’s hard to contemplate winter now that we’re mid-spring, but when the seasons change, ice skaters in Winnipeg will be able to keep warm in plywood shelters designed by Patkau Architects. The designers created temporary shelters inspired by animal behavior—specifically, buffalo bracing against the wind. Check them out.
| May 16, 2011
USGBC and AIA unveil report for greening K-12 schools
The U.S. Green Building Council and the American Institute of Architects unveiled "Local Leaders in Sustainability: A Special Report from Sundance," which outlines a five-point national action plan that mayors and local leaders can use as a framework to develop and implement green schools initiatives.