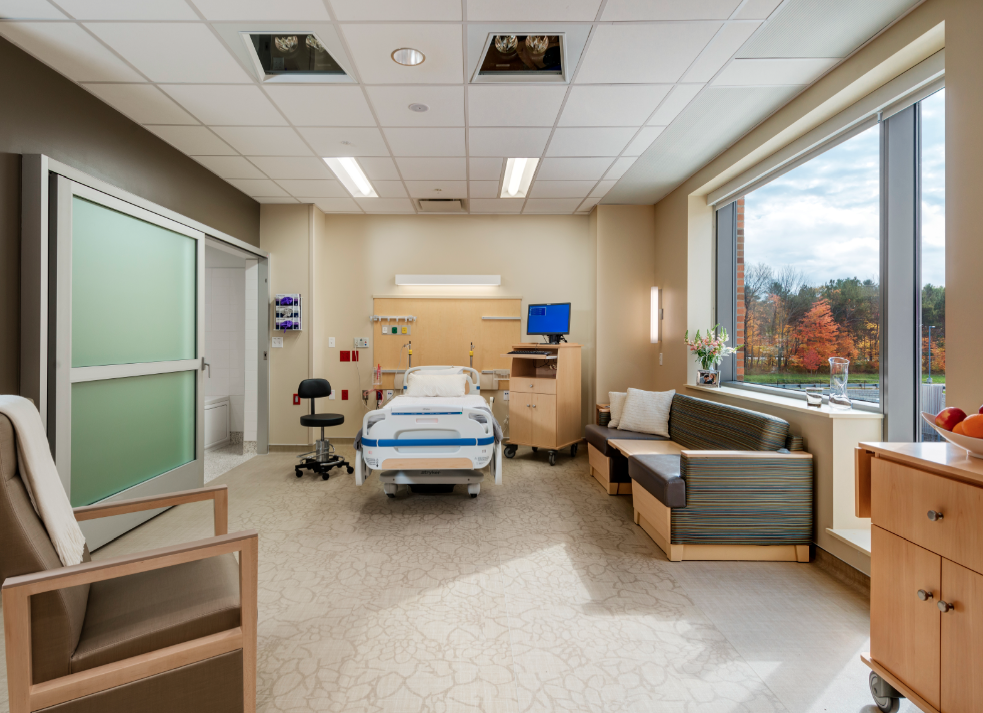
Hospital noise can be an insidious seed planted in a patient’s memory.
“They will recall extraordinary acts of kindness and consideration. However, they will also remember the agony of not being able to sleep, and hearing the nurses and others laughing just beyond their door,” says Chris Kay, ACHE, Managing Principal–National Healthcare & Science Buildings Practice at engineering giant Jacobs.
Some patients are bothered by noise that others shrug off. Volume isn’t necessarily the key factor. That’s the “noise conundrum,” says Kay. Every hospital has its own “culture” of loudness and quiet.
Kay says noise can impact patients through sleep deprivation, greater anxiety, and heightened blood pressure, respiration, and heart rates. It can also affect hospital workers, adding to their stress, lowering their ability to concentrate, and possibly leading to medical and nursing errors.
Kay offers steps to a therapeutic auditory environment:
1. Keep assessing your facility’s noise status. Hospital administrators and clinical staffs can become oblivious to daily noise patterns. They need to stop and listen to determine how loud is loud from the standpoint of patients, families, and visitors.
2. Establish relevant sound standards. EPA noise standards from the 1970s are out of date, says Kay. Any current sound standard needs to reflect the normal functioning of the facility and the needs of patients. That means going beyond decibel measurements and getting personnel involved in monitoring and modeling behavior that results in a healing environment.
3. Set noise impact standards for equipment purchases. For example, if a hospital plans to purchase a portable MRI, it should know beforehand where it’s going to be used, who will actually use it, and its impact on hospital noise.
4. Place nonclinical equipment in appropriate locations. In addition to the beep-beep of clinical and monitoring equipment, patients are bombarded with noise from vacuum cleaners, TVs, ice-making machines, and so on. Decide where and when such devices can be used around patients. “Housekeeping and nursing must bond to care for patients,” Kay notes.
5. Design spaces for sound control. Kay recommends that hospitals retain a noise control engineer to help find and mitigate “erratic” sounds. Spaces should also be retrofitted with acoustic materials that have high sound transmission ratings.
6. Engage and educate staff. Don’t blame the staff for being noisy; instead, make it a matter of patient care and professionalism. Emphasize that excessive noise shows a lack of respect for patients and their families. Whether it’s a door that slams or a cell phone that rings when it shouldn’t, hospitals need to “reclaim the sacred relationship and sacred space for healing,” says Kay.
7. Measure results. Collect data on how such metrics as patients’ complaints, calls for assistance at night, and request for pain medication correlate with noise levels on patient floors.
Related Stories
Game Changers | Feb 5, 2016
Mayo Clinic's breakthrough research lab puts evidence-based design to the test
Mayo teams up with Delos to bring hard science to EBD research.
Game Changers | Feb 4, 2016
GAME CHANGERS: 6 projects that rewrite the rules of commercial design and construction
BD+C’s inaugural Game Changers report highlights today’s pacesetting projects, from a prefab high-rise in China to a breakthrough research lab in the Midwest.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 27, 2016
CBRE: Here's what healthcare owners need to know when selecting a real estate developer
Understanding equity sources, balancing costs, and involving legal departments early in the process can help health systems maintain leverage during the RFP process, writes CBRE Healthcare’s Chris Bodnar.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 27, 2016
South Carolina governor’s push to repeal health facility construction rules gets boost from Feds
Legislature may move to strike certificate of need requirements.
Metals | Jan 19, 2016
6 ways to use metal screens and mesh for best effect
From airy façades to wire mesh ceilings to screening walls, these projects show off the design possibilities with metal.
Great Solutions | Jan 19, 2016
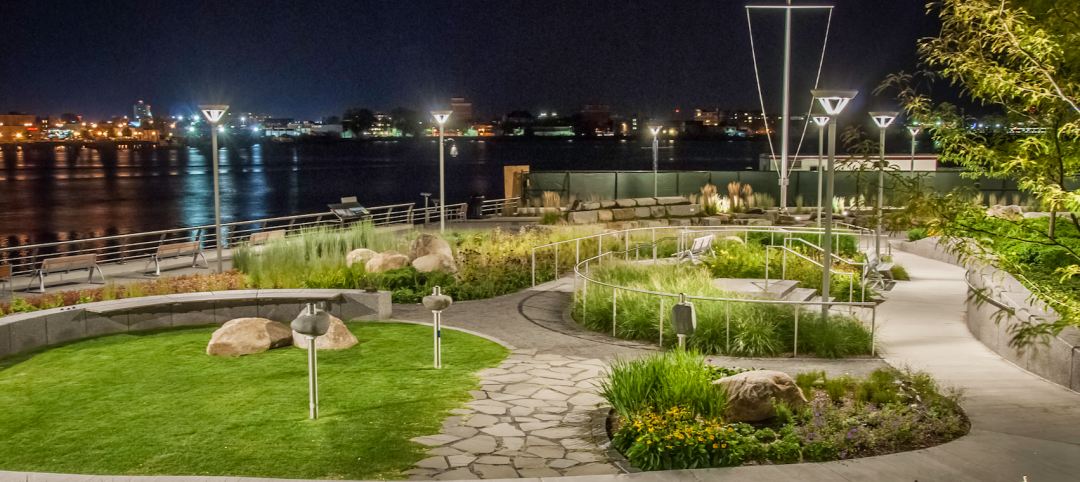
Healing garden doubles as therapy trails
A Boston-area hospital takes the healing garden to the next level.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 15, 2016
Mount Sinai Health System signs first healthcare IPD IFOA contract in New York City
Francis Cauffman, Syska Hennessy, Turner Construction are the primary parties in agreement.
| Jan 14, 2016
How to succeed with EIFS: exterior insulation and finish systems
This AIA CES Discovery course discusses the six elements of an EIFS wall assembly; common EIFS failures and how to prevent them; and EIFS and sustainability.
Great Solutions | Jan 6, 2016
Shepley Bulfinch develops elegant design solution to address behavioral issues in emergency departments
ED scheme allows staff to isolate unruly patients and visitors in a secure area.
Great Solutions | Jan 4, 2016
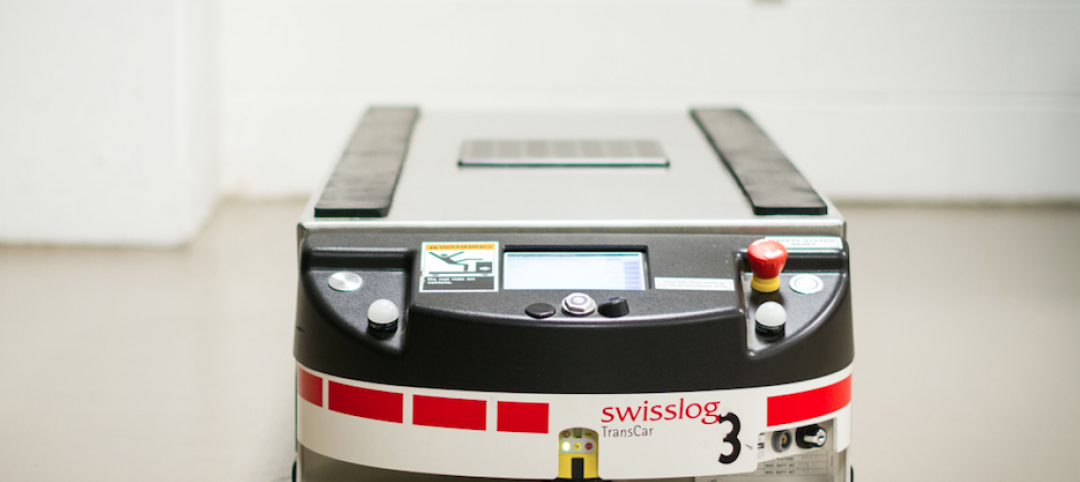
Toronto’s newest hospital employs 10 robots for moving food, supplies, and equipment
The 1.8 million-sf Humber River Hospital is loaded with high-tech gadgets. Its coolest innovation is the use of automated guided vehicles.