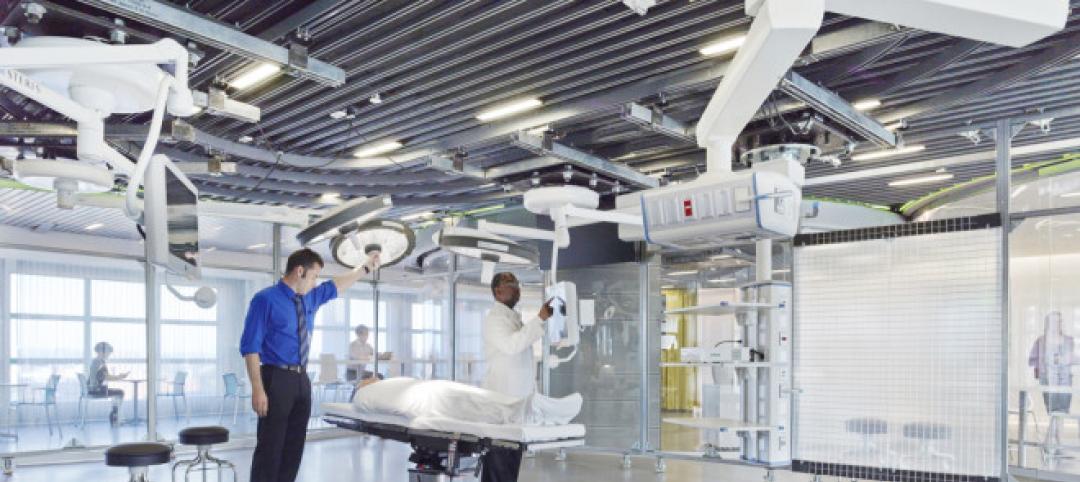
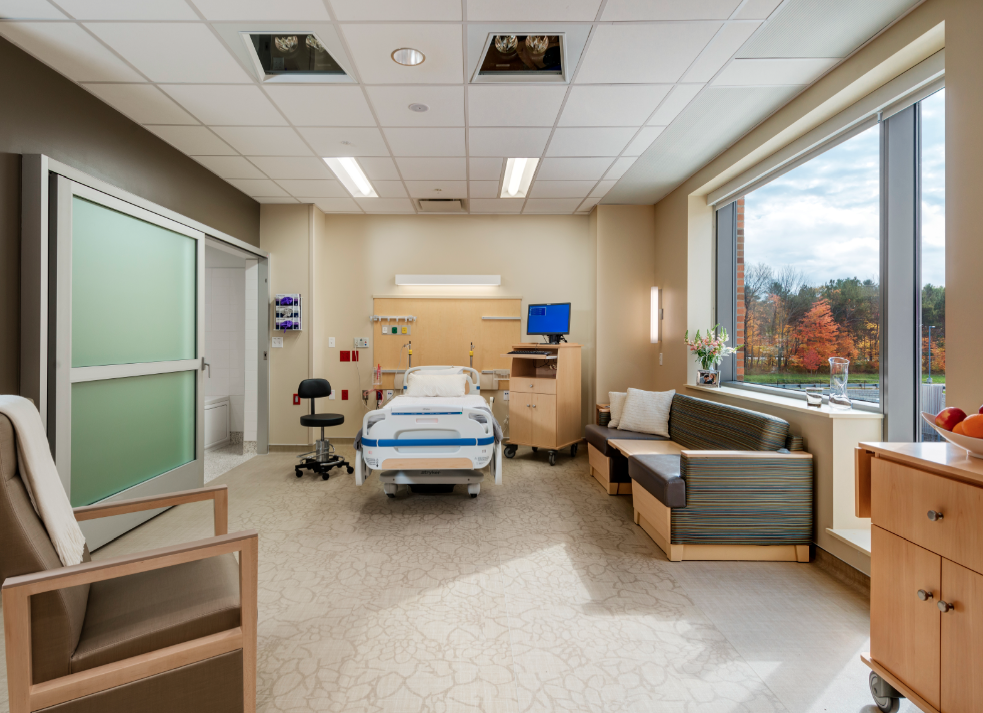
Hospital noise can be an insidious seed planted in a patient’s memory.
“They will recall extraordinary acts of kindness and consideration. However, they will also remember the agony of not being able to sleep, and hearing the nurses and others laughing just beyond their door,” says Chris Kay, ACHE, Managing Principal–National Healthcare & Science Buildings Practice at engineering giant Jacobs.
Some patients are bothered by noise that others shrug off. Volume isn’t necessarily the key factor. That’s the “noise conundrum,” says Kay. Every hospital has its own “culture” of loudness and quiet.
Kay says noise can impact patients through sleep deprivation, greater anxiety, and heightened blood pressure, respiration, and heart rates. It can also affect hospital workers, adding to their stress, lowering their ability to concentrate, and possibly leading to medical and nursing errors.
Kay offers steps to a therapeutic auditory environment:
1. Keep assessing your facility’s noise status. Hospital administrators and clinical staffs can become oblivious to daily noise patterns. They need to stop and listen to determine how loud is loud from the standpoint of patients, families, and visitors.
2. Establish relevant sound standards. EPA noise standards from the 1970s are out of date, says Kay. Any current sound standard needs to reflect the normal functioning of the facility and the needs of patients. That means going beyond decibel measurements and getting personnel involved in monitoring and modeling behavior that results in a healing environment.
3. Set noise impact standards for equipment purchases. For example, if a hospital plans to purchase a portable MRI, it should know beforehand where it’s going to be used, who will actually use it, and its impact on hospital noise.
4. Place nonclinical equipment in appropriate locations. In addition to the beep-beep of clinical and monitoring equipment, patients are bombarded with noise from vacuum cleaners, TVs, ice-making machines, and so on. Decide where and when such devices can be used around patients. “Housekeeping and nursing must bond to care for patients,” Kay notes.
5. Design spaces for sound control. Kay recommends that hospitals retain a noise control engineer to help find and mitigate “erratic” sounds. Spaces should also be retrofitted with acoustic materials that have high sound transmission ratings.
6. Engage and educate staff. Don’t blame the staff for being noisy; instead, make it a matter of patient care and professionalism. Emphasize that excessive noise shows a lack of respect for patients and their families. Whether it’s a door that slams or a cell phone that rings when it shouldn’t, hospitals need to “reclaim the sacred relationship and sacred space for healing,” says Kay.
7. Measure results. Collect data on how such metrics as patients’ complaints, calls for assistance at night, and request for pain medication correlate with noise levels on patient floors.
Related Stories
| Sep 29, 2014
10 common deficiencies in aging healthcare facilities
VOA's Douglas King pinpoints the top issues that arise during healthcare facilities assessments, including missing fire/smoke dampers, out-of-place fire alarms, and poorly constructed doorways.
| Sep 25, 2014
Look to history warily when gauging where the construction industry may be headed
Precedents and patterns may not tell you all that much about future spending or demand.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 23, 2014
Cedars-Sinai looks to streamline trauma care with first-of-its-kind OR360 simulation space
The breakthrough simulation center features moveable walls and a modular ceiling grid that allow doctors and military personnel to easily reconfigure the shape and size of the space.
| Sep 22, 2014
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 20, 2014
Healthcare conversion projects: 5 hard-earned lessons from our experts
Repurposing existing retail and office space is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for hospital systems to expand their reach from the mother ship. Our experts show how to avoid the common mistakes that can sabotage outpatient adaptive-reuse projects.
| Sep 19, 2014
8 hot healthcare projects win interior design awards
Winners of IIDA's 2014 Healthcare Interior Design Competition include Perkins+Will, AECOM, Buffalo Design, and SmithGroupJJR, for projects from Cincinnati to Toronto.
| Sep 15, 2014
Ranked: Top international AEC firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Parsons Brinckerhoff, Gensler, and Jacobs top BD+C's rankings of U.S.-based design and construction firms with the most revenue from international projects, as reported in the 2014 Giants 300 Report.
| Sep 15, 2014
Perkins+Will unveils design for Ghana's largest hospital
The new hospital will be home to numerous hospital services including public health, accident and emergency, imaging, obstetrics, gynecology, dental, surgical, intensive care and administration.