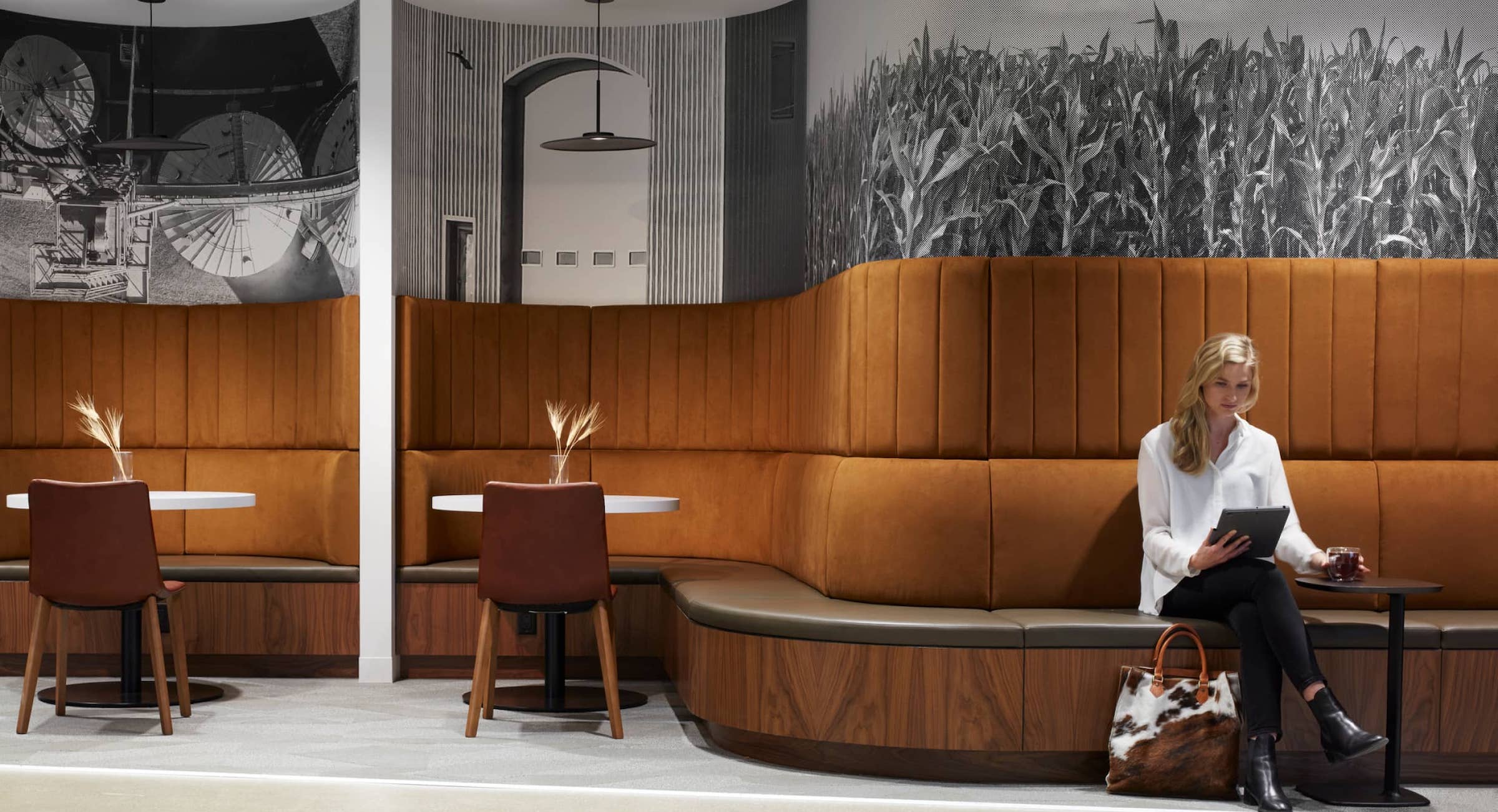
Why brain health? We’ve written before about the need to embrace mental health through the prism of brain health. This emerging and growing concept encompasses neural development, plasticity, functioning, and recovery over the course of our lives.
In some ways, brain health is to mental illness what physical fitness is to disease. The current study focuses on employees—while we still have our eye on broader societal concerns, including isolation, anxiety, and various problems that come with balancing technologies in the digital age. In short, we found that brain health strategies work—those who engaged the Brain Health SMARTTM Strategies experienced a marked improvement over the course of our year-long study, as measured by the Center of BrainHealth®’s BrainHealthTM Index.
On a fundamental level, our work shifts the conversation about workplaces. HKS CEO Dan Noble says, “It’s time to change the narrative around how we work and fully leverage our brain capital. And it starts with the actions we take internally, with our own people, to help them emotionally, socially, and cognitively thrive.”
In 2021, HKS partnered with the Center for BrainHealth for a pilot program to investigate the role of place, process/policy, and technology in creating a brain-healthy workplace. The Center for BrainHealth for a pilot program to investigate the role of place, process/policy, and technology in creating a brain-healthy workplace. The Center for BrainHealth is a nonprofit research institute dedicated to advancing the science of brain health,” how the brain best learns, reasons and innovates; actionable ways to protect it from decline; and proactive protocols to repair and generate brain systems.
The organization developed a training program for brain fitness that works just like any physical fitness regime, leveraging 9 Brain Health SMARTTM Strategies that prime the brain to calibrate mental energy, reinforce strategic thinking, and ignite innovation.
The core of our research leveraged a representative sample of HKS employees who participated in the program by completing a brain health assessment, accessing training modules, and translating brain health strategies into their daily lives. Five HKS Living Labs participated during the summer of 2022, as employees returned to the office at a higher frequency as part of their flexible work experience. We captured data and insights through surveys, observations, and interviews. We also convened semi-structured gatherings with colleagues, as well as both virtual and in-person think tanks.
In all, we determined seven key findings from our year-long study. Some corroborate past studies—such as the growing need to address distractions and multitasking. At the same time, others contribute new elements to discussions on mental health. Here are a few key insights from our report (Download the full report):
- The brain can be trained. Our study showed a statistically significant increase in brain health index for individuals who went through the brain health training.1 Those that completed the core cognitive training had a higher average than those that did not.
- Managing distractions is a key challenge for focused work in the office. The office isn’t only for collaboration—workers need spaces deliberately designed for focus work. Acoustics and a lack of environmental control consistently ranked lowest in satisfaction among design elements.
- Multitasking is related to reduced effectiveness and increased burnout. Two out of five of our study’s participants said they frequently multitask—a bad habit related to a host of issues, including burnout. Our workstations are also multitasking alongside us.
- Where we work matters, and using a range of spaces helps. Creating a range of spaces based on task type or working modality may unlock innovation. We found that when participants used a range of spaces, satisfaction with collaborative work effectiveness in the office was higher.
- Digital and physical workplace habits need time to develop. Our satisfaction with individual and collaborative tasks increases with the time we spend in specific locations—we need time to acclimate to our environments for optimum efficiency.
- Being together in-person is related to improved connection to team and increased opportunities for informal knowledge sharing. Over the course of our 10-week study, collaborative behaviors increased and perceived connections to one’s team increased.
- Perceived connections to one’s team are strong, but connection to the community is lagging. After months or years of remote work, we must continuously evaluate how hybrid work arrangements impact interpersonal relationships across the organization.
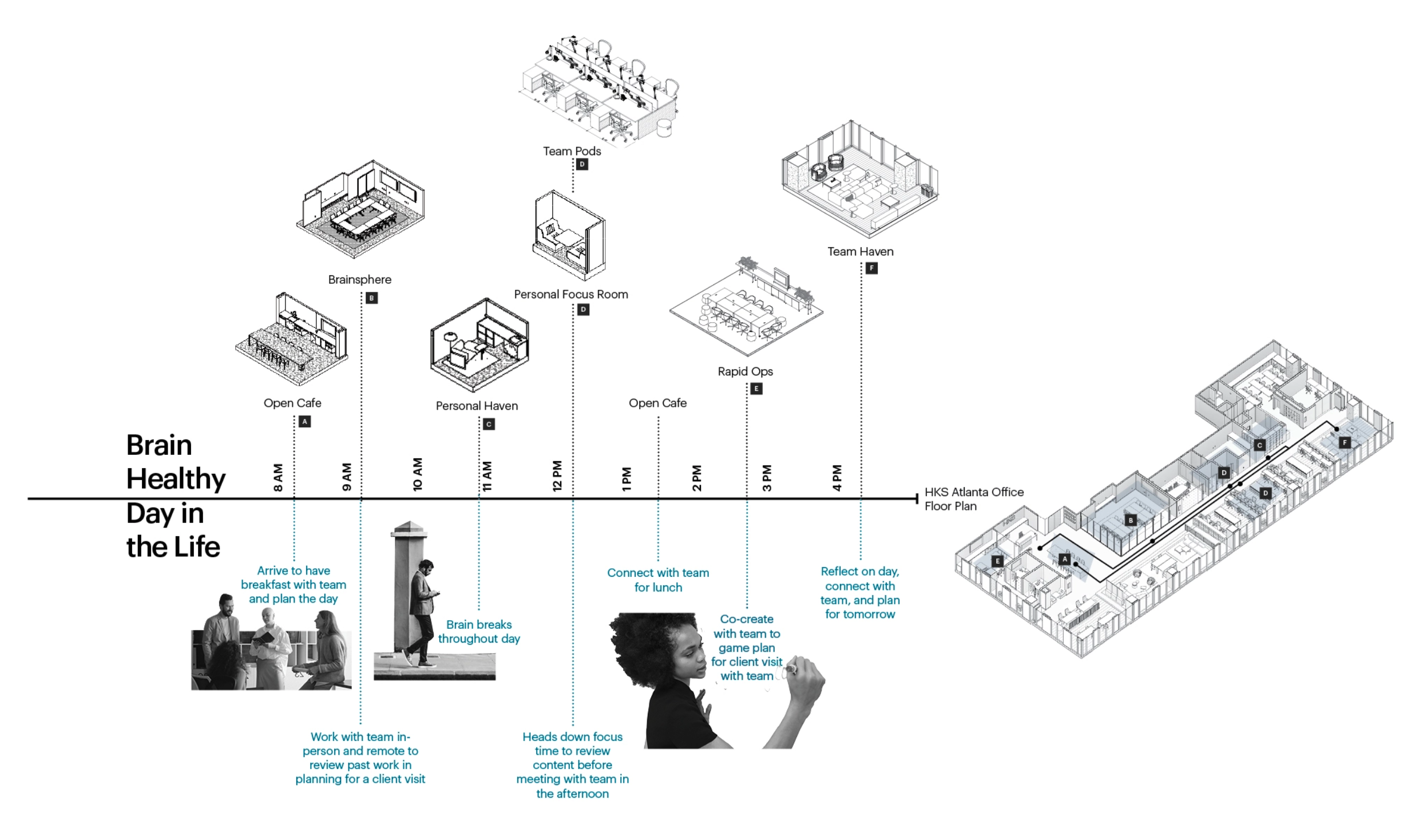
By creating workplace affordances, we translated our key findings into strategies for our work environments. Workplace affordances are how we perceive environments to meet our needs. Based on the research, we proposed five primary affordances: focus, exploration & ideation, collaboration & co-creation, rest & reflection, and social connection. Affordances denote the end goal of how users will engage an environment—but they also begin with a question. Consider—how does the workplace foster social connection and community building? Or, how does our workplace afford us the ability to focus?
We then identified three fundamental habits underpinning a workplace designed for brain health—these are our workplace ABCs. First, the intent of a task must be aligned with the chosen environment. Based on the work an employee must accomplish, they must leverage the unique digital and physical affordances available to them. We also identified that workers need balance throughout the workday. Balanced habits are about variability: working in different modalities and accessing a diversity of spaces. Finally, connection is critical to the workplace for brain health. This means connecting with others to boost a sense of belonging and provide a sense of purpose. Relating to how we align what we do with where we work and finding balance, connection also means equipping workers with the autonomy to choose and the authority to have control over their environment.
What’s next? We’re embracing the experiment: building on what we’ve gathered from our living labs and insights that we’ve gleaned from those who participated in our year-long study. We know that we’re not done yet. Our firm’s Flex Work policy is changing based on our learnings. We’re partnering with the Center for BrainHealth to develop a brain healthy workplace certification to encourage brain health practices and build accountability. We’re also focused on how our brain health explorations support unique business needs, so we’re developing a robust business case and toolkit for brain-healthy workplaces that will extend the work from this insights report into actionable real estate tools and measured impact.
Click here to download the full report
Citations:
Zientz, J., Spence, J., Chung, S. S. E., Nanda, U., & Chapman, S. B. (in review). Exploring how brain health strategy training informs the future of work. Frontiers in Psychology.
Related Stories
| Oct 13, 2010
Editorial
The AEC industry shares a widespread obsession with the new. New is fresh. New is youthful. New is cool. But “old” or “slightly used” can be financially profitable and professionally rewarding, too.
| Oct 13, 2010
Test run on the HP Z200 SFF Good Value in a Small Package
Contributing Editor Jeff Yoders tests a new small-form factor, workstation-class desktop in Hewlett-Packard’s line that combines performance of its minitower machine with a smaller chassis and a lower price.
| Oct 13, 2010
Prefab Trailblazer
The $137 million, 12-story, 500,000-sf Miami Valley Hospital cardiac center, Dayton, Ohio, is the first major hospital project in the U.S. to have made extensive use of prefabricated components in its design and construction.
| Oct 13, 2010
Thought Leader
Sundra L. Ryce, President and CEO of SLR Contracting & Service Company, Buffalo, N.Y., talks about her firm’s success in new construction, renovation, CM, and design-build projects for the Navy, Air Force, and Buffalo Public Schools.
| Oct 13, 2010
Hospital tower gets modern makeover
The Wellmont Holston Valley Medical Center in Kingsport, Tenn., expanded its D unit, a project that includes a 243,443-sf addition with a 12-room operating suite, a 36-bed intensive care unit, and an enlarged emergency department.
| Oct 13, 2010
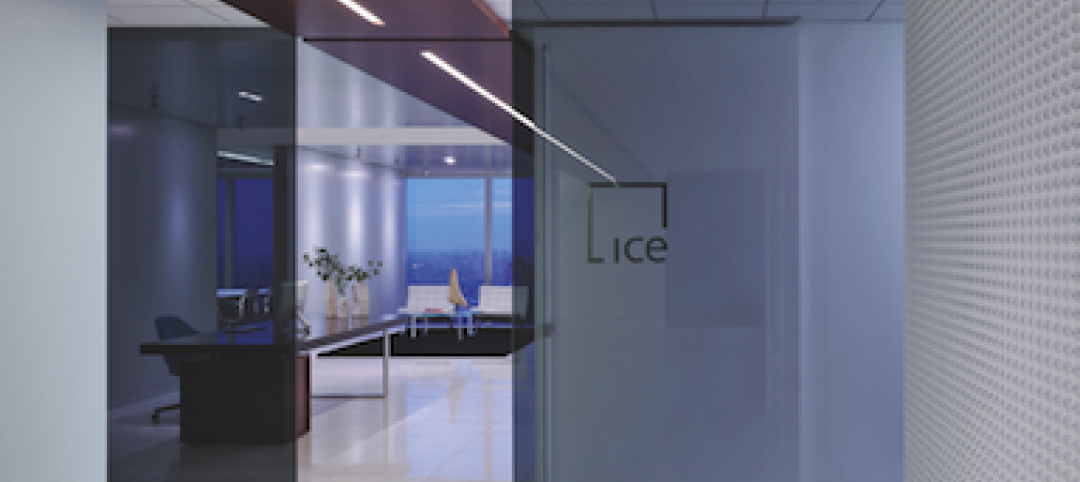
Modern office design accentuates skyline views
Intercontinental|Exchange, a Chicago-based financial firm, hired design/engineering firm Epstein to create a modern, new 31st-floor headquarters.
| Oct 13, 2010
Hospital and clinic join for better patient care
Designed by HGA Architects and Engineers, the two-story Owatonna (Minn.) Hospital, owned by Allina Hospitals and Clinics, connects to a newly expanded clinic owned by Mayo Health System to create a single facility for inpatient and outpatient care.
| Oct 13, 2010
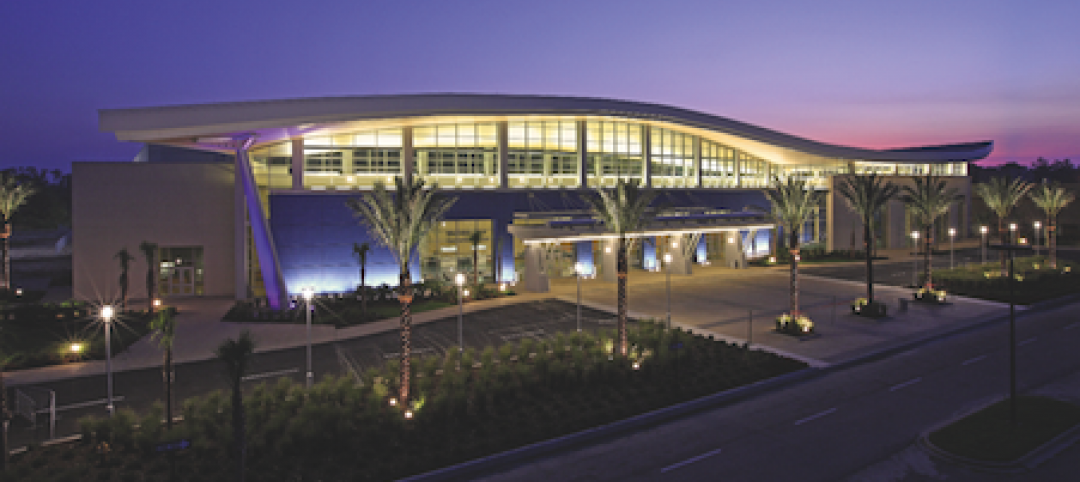
Biloxi’s convention center bigger, better after Katrina
The Mississippi Coast Coliseum and Convention Center in Biloxi is once again open for business following a renovation and expansion necessitated by Hurricane Katrina.
| Oct 13, 2010
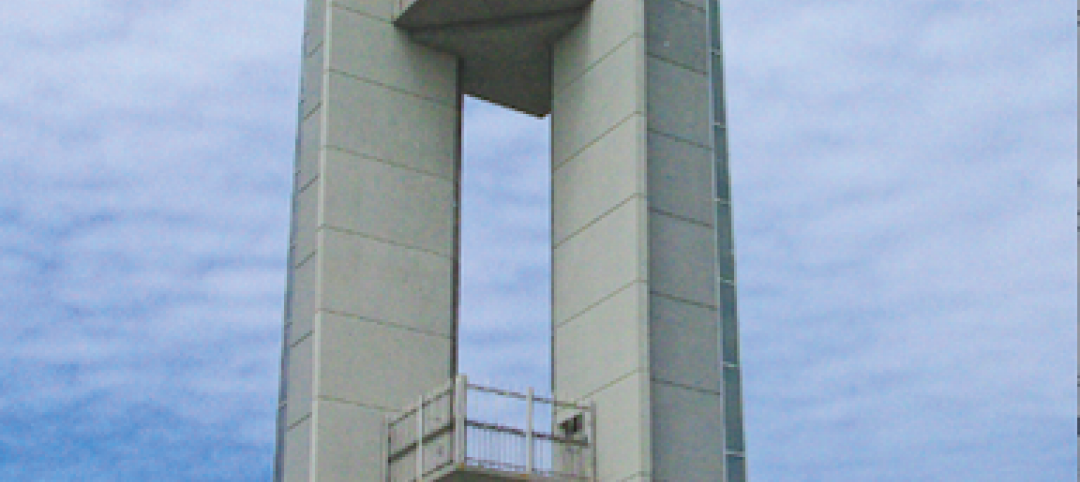
Tower commemorates Lewis & Clark’s historic expedition
The $4.8 million Lewis and Clark Confluence Tower in Hartford, Ill., commemorates explorers Meriwether Lewis and William Clark at the point where their trek to the Pacific Ocean began—the confluence of the Mississippi and Missouri Rivers.
| Oct 13, 2010
Maryland replacement hospital expands care, changes name
The new $120 million Meritus Regional Medical Center in Hagerstown, Md., has 267 beds, 17 operating rooms with high-resolution video screens, a special care level II nursery, and an emergency room with 53 treatment rooms, two trauma rooms, and two cardiac rooms.
















