There are many hurdles to overcome when completing a life cycle cost assessment. LCCAs have been praised by some and criticized or viewed with skepticism by others. Some AEC professionals like to use LCCAs to provide evidence that a certain design with a higher first cost attached to it actually achieves lower total cost of ownership over time.
Such an analysis, however, is only as good as the data that is used to complete it; in the end, you have to be able to justify and defend your results. When completing an LCCA, it is important to remain neutral and to use unbiased data.
Following are some words of advice regarding LCCAs, based on RMF Engineering’s experience on the Berkeley County School District HVAC study.
1. AVOID USING A “SIMPLE PAYBACK” METHODOLOGY. As the name implies, simple payback is a rudimentary methodology, and the results can be unsophisticated and even misleading. This method should not be used as an in-depth LCCA tool.
2. DON’T HIDE YOUR ASSUMPTIONS. The paucity of data on certain costs means that you will have to make assumptions, but these should not be allowed to affect the outcome of the analysis. It is important to thoroughly document all assumptions, costs, and calculations used in the analysis.
3. GET YOUR CONSTRUCTION DATA FROM THE BEST AVAILABLE SOURCES. Not many contractors and sales representatives are willing to divulge their actual cost for equipment, materials, and installation. Usually the best they will give you is the cost in dollars per square foot, which, unfortunately, is not sufficiently detailed to provide a proper analysis.
For HVAC life cycle cost analyses, manufacturers will often provide budget pricing for specific pieces of equipment, which can be useful. Resources such as RSMeans and published pricing guides for piping and other materials are also great resources for calculating cost and should be used instead of general cost.
4. MAKE THE EFFORT TO GET SOLID MAINTENANCE DATA. It is important to have a clear understanding of how an HVAC system will be maintained as well as how much it will cost the owner to maintain. Some owners prefer to do their own maintenance; others contract maintenance out. Some perform maintenance at regularly scheduled intervals; others wait until the equipment breaks down. Maintenance is probably the most poorly documented cost item in most LCCAs, but it can have a major impact on the accuracy and validity of the analysis. Make sure your maintenance data is up to date and specific to your project.
5. NAIL DOWN THE OWNER’S EXPERIENCE WITH EQUIPMENT LIFE. The life cycle of equipment varies by owner and can be drastically different than the manufacturer’s reported data. When comparing different types of systems, it’s important to discuss the owner’s experience with equipment life and how long they plan to use certain products. Any sharp differentiation from the norm could have a significant impact on the outcome of your analysis.
6. ANALYZE THE RESULTS CAREFULLY TO DETERMINE THE LEVEL OF CERTAINTY. For the BCSD project, the difference between the least expensive and next least expensive system was significant (13.1%), so we were comfortable in recommending it. Unfortunately, not every LCCA results in a clear winner. Each analysis will have a different level of uncertainty associated with it due to the assumptions, variables, and the analysis type. The more variables and assumptions there are, the higher the level of uncertainty. There are often intangibles that cannot be associated with a quantifiable cost, and one of these might end up becoming the deciding factor in your analysis.
7. LOOK FOR LCCA FUNDING FROM NON-CLIENT SOURCES. For the Berkeley County SD project the local utility cooperative, which happens to place a great deal of value on customer education, offered to partially fund the study in order to have access to the data. When proposing an LCCA to a client, check around to see who else could benefit from the analysis. There may be funding available to offset the cost to the owner or provide additional funding for a more in-depth study.
8. EXPECT THE UNEXPECTED. For our project, we originally modeled gas boilers for the water-source heat pump system to be similar to the four-pipe system. The energy models showed that there was virtually no requirement for heating of the condenser water loop due to our building type and climate. We suspected this might be the case because a nearby high school had been operating without a boiler and did not have heating problems. It was later decided that an electric boiler would be a better fit for the school district’s HVAC systems because its initial cost and associated annual maintenance costs would be far less than a gas boiler. It’s likely that you will face similar unanticipated results in future projects, so be prepared.
Related Stories
Architects | Feb 28, 2022
JLL continues expansion in Southwest with acquisition of San Diego’s Gilliland Construction Management
JLL announced that it has completed the acquisition of Gilliland Construction Management, a leader in project and construction management services for life sciences, lab, retail, hospitality, industrial, multifamily, and office properties.
Codes and Standards | Feb 24, 2022
Most owners adapting digital workflows on projects
Owners are more deeply engaged with digital workflows than other project team members, according to a new report released by Trimble and Dodge Data & Analytics.
Multifamily Housing | Feb 24, 2022
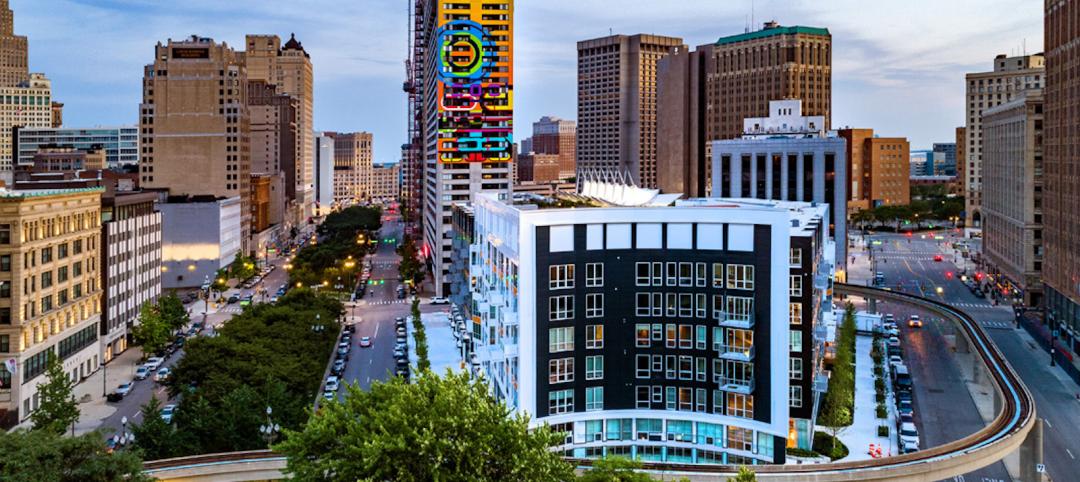
First new, mixed-use high-rise in Detroit’s central business district in nearly 30 years opens
City Club Apartments completed two multifamily projects in 2021 in downtown Detroit including the first new, mixed-use high-rise in Detroit’s central business district in nearly 30 years.
| Feb 24, 2022
Signs of ‘Antiwork’ appear in the architecture industry
Reddit's r/Antiwork forum highlights the mounting pressures everyday workers face in a purely capitalistic society. AEC industry professionals are not immune to these pressures.
Office Buildings | Feb 23, 2022
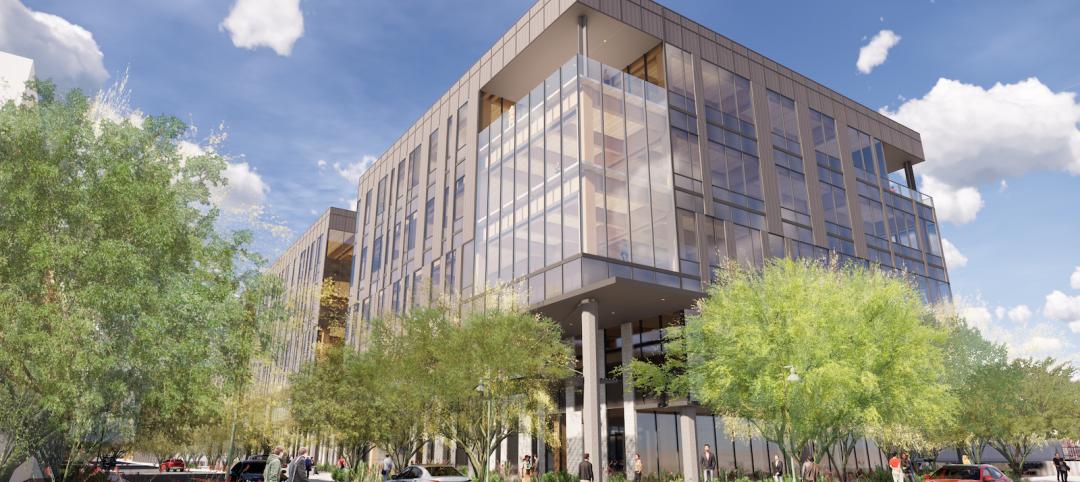
The Beam on Farmer, Arizona’s first mass timber, multi-story office building tops out
The Beam on Farmer, Arizona’s first mass timber, multi-story office building, topped out on Feb. 10, 2022.
Codes and Standards | Feb 21, 2022
More bad news on sea level rise for U.S. coastal areas
A new government report predicts sea levels in the U.S. of 10 to 12 inches higher by 2050, with some major cities on the East and Gulf coasts experiencing damaging floods even on sunny days.
Wood | Feb 18, 2022
$2 million mass timber design competition: Building to Net-Zero Carbon (entries due March 30!)
To promote construction of tall mass timber buildings in the U.S., the Softwood Lumber Board (SLB) and USDA Forest Service (USDA) have joined forces on a competition to showcase mass timber’s application, commercial viability, and role as a natural climate solution.
University Buildings | Feb 18, 2022
On-campus performing arts centers and museums can be talent magnets for universities
Cultural facilities are changing the way prospective students and parents view higher education campuses.
University Buildings | Feb 17, 2022
A vacated school in St. Louis is turned into a center where suppliers exchange ideas
In 1871, The Carondelet School, designed by Frederick William Raeder, opened to educate more than 400 children of laborers and manufacturers in St. Louis. The building is getting a second lease on life, as it has undergone a $2 million renovation by goBRANDgo!, a marketing firm for the manufacturing and industrial sectors.
Data Centers | Feb 15, 2022
Data center boom: How two AEC firms plan to meet unprecedented demand for data center facilities
Ramboll's Jim Fox and EYP Mission Critical Facilities' Rick Einhorn discuss the recent joining of their companies at a time of unprecedented data center demand. BD+C's John Caulfield leads the discussion with Fox, Ramboll's Managing Director for the Americas, and Einhorn, EYP Mission Critical Facilities' Managing Director.