There are many hurdles to overcome when completing a life cycle cost assessment. LCCAs have been praised by some and criticized or viewed with skepticism by others. Some AEC professionals like to use LCCAs to provide evidence that a certain design with a higher first cost attached to it actually achieves lower total cost of ownership over time.
Such an analysis, however, is only as good as the data that is used to complete it; in the end, you have to be able to justify and defend your results. When completing an LCCA, it is important to remain neutral and to use unbiased data.
Following are some words of advice regarding LCCAs, based on RMF Engineering’s experience on the Berkeley County School District HVAC study.
1. AVOID USING A “SIMPLE PAYBACK” METHODOLOGY. As the name implies, simple payback is a rudimentary methodology, and the results can be unsophisticated and even misleading. This method should not be used as an in-depth LCCA tool.
2. DON’T HIDE YOUR ASSUMPTIONS. The paucity of data on certain costs means that you will have to make assumptions, but these should not be allowed to affect the outcome of the analysis. It is important to thoroughly document all assumptions, costs, and calculations used in the analysis.
3. GET YOUR CONSTRUCTION DATA FROM THE BEST AVAILABLE SOURCES. Not many contractors and sales representatives are willing to divulge their actual cost for equipment, materials, and installation. Usually the best they will give you is the cost in dollars per square foot, which, unfortunately, is not sufficiently detailed to provide a proper analysis.
For HVAC life cycle cost analyses, manufacturers will often provide budget pricing for specific pieces of equipment, which can be useful. Resources such as RSMeans and published pricing guides for piping and other materials are also great resources for calculating cost and should be used instead of general cost.
4. MAKE THE EFFORT TO GET SOLID MAINTENANCE DATA. It is important to have a clear understanding of how an HVAC system will be maintained as well as how much it will cost the owner to maintain. Some owners prefer to do their own maintenance; others contract maintenance out. Some perform maintenance at regularly scheduled intervals; others wait until the equipment breaks down. Maintenance is probably the most poorly documented cost item in most LCCAs, but it can have a major impact on the accuracy and validity of the analysis. Make sure your maintenance data is up to date and specific to your project.
5. NAIL DOWN THE OWNER’S EXPERIENCE WITH EQUIPMENT LIFE. The life cycle of equipment varies by owner and can be drastically different than the manufacturer’s reported data. When comparing different types of systems, it’s important to discuss the owner’s experience with equipment life and how long they plan to use certain products. Any sharp differentiation from the norm could have a significant impact on the outcome of your analysis.
6. ANALYZE THE RESULTS CAREFULLY TO DETERMINE THE LEVEL OF CERTAINTY. For the BCSD project, the difference between the least expensive and next least expensive system was significant (13.1%), so we were comfortable in recommending it. Unfortunately, not every LCCA results in a clear winner. Each analysis will have a different level of uncertainty associated with it due to the assumptions, variables, and the analysis type. The more variables and assumptions there are, the higher the level of uncertainty. There are often intangibles that cannot be associated with a quantifiable cost, and one of these might end up becoming the deciding factor in your analysis.
7. LOOK FOR LCCA FUNDING FROM NON-CLIENT SOURCES. For the Berkeley County SD project the local utility cooperative, which happens to place a great deal of value on customer education, offered to partially fund the study in order to have access to the data. When proposing an LCCA to a client, check around to see who else could benefit from the analysis. There may be funding available to offset the cost to the owner or provide additional funding for a more in-depth study.
8. EXPECT THE UNEXPECTED. For our project, we originally modeled gas boilers for the water-source heat pump system to be similar to the four-pipe system. The energy models showed that there was virtually no requirement for heating of the condenser water loop due to our building type and climate. We suspected this might be the case because a nearby high school had been operating without a boiler and did not have heating problems. It was later decided that an electric boiler would be a better fit for the school district’s HVAC systems because its initial cost and associated annual maintenance costs would be far less than a gas boiler. It’s likely that you will face similar unanticipated results in future projects, so be prepared.
Related Stories
Building Team Awards | Jun 1, 2016
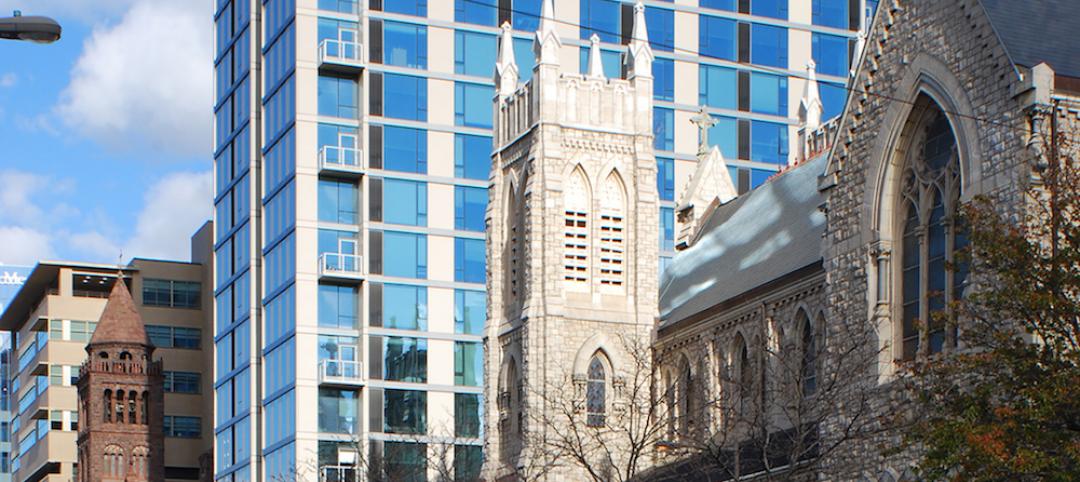
Multifamily tower and office building revitalize Philadelphia cathedral
The Philadelphia Episcopal Cathedral capitalizes on hot property to help fund much needed upgrades and programs.
Building Team Awards | Jun 1, 2016
Central utility power plant takes center stage at UC San Diego Jacobs Medical Center
An undulating roof, floor-to-ceiling glass, and façade scheme give visual appeal to a plant that serves the 10-story medical center.
Architects | May 31, 2016
JLG Architects acquires Minneapolis-based Studio Five Architects
Led by Linda McCracken-Hunt, SFA is one of Minnesota’s oldest woman-owned architecture firms.
Building Team Awards | May 31, 2016
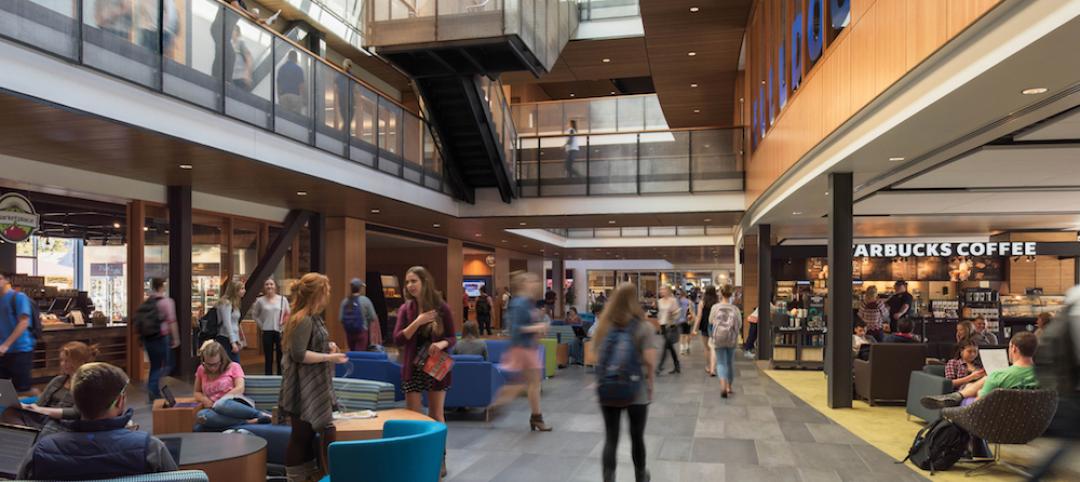
Gonzaga's new student center is a bustling social hub
Retail mall features, comfortable furniture, and floor-to-ceiling glass add vibrancy to the new John J. Hemmingson Center.
Building Team Awards | May 27, 2016
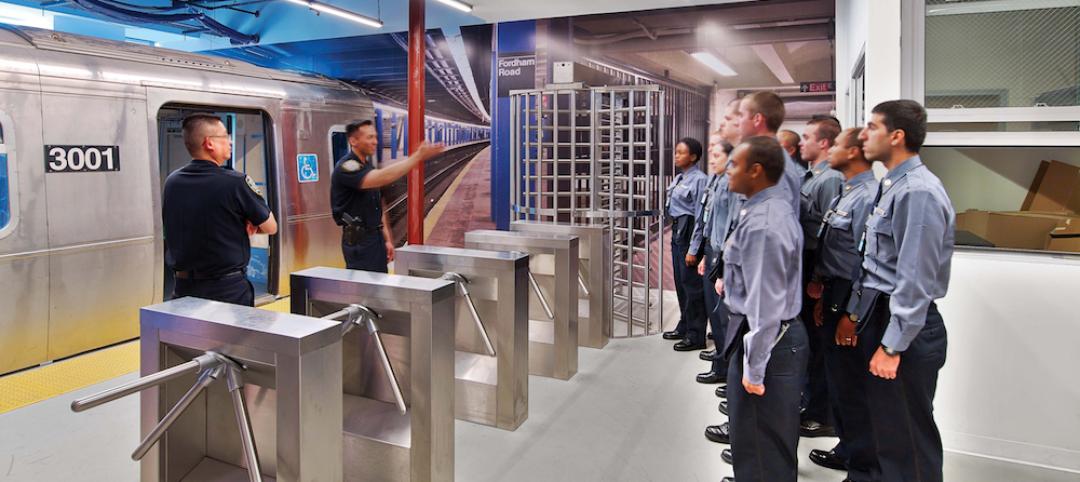
Big police academy trains thousands of New York's finest
The Police Training Academy in Queens, N.Y., consists of a 480,000-sf academic/administration building and a 240,000-sf physical training facility, linked by an aerial pedestrian bridge.
Building Team Awards | May 26, 2016
Cimpress office complex built during historically brutal Massachusetts winter
Lean construction techniques were used to build 275 Wyman Street during a winter that brought more than 100 inches of snow to suburban Boston.
Building Team Awards | May 25, 2016
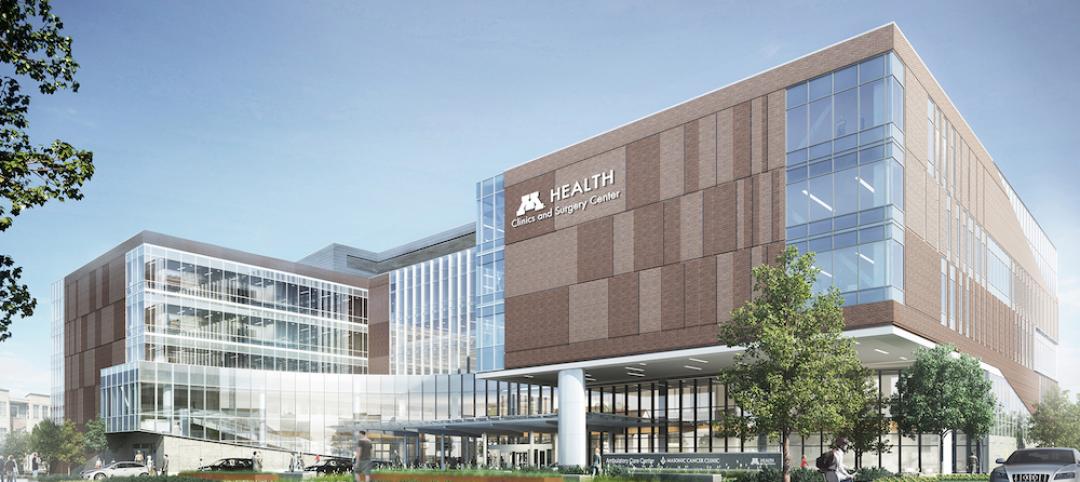
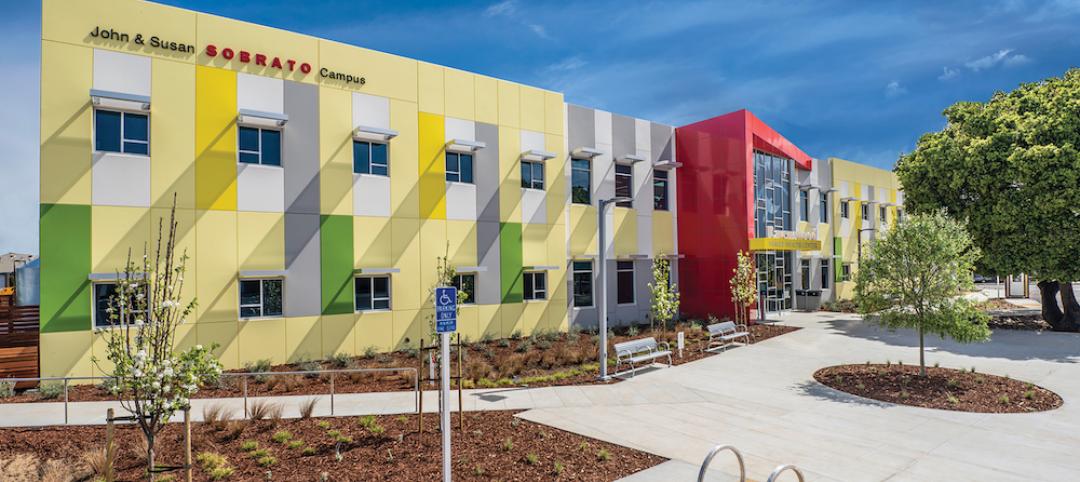
New health center campus provides affordable care for thousands of Northern Californians
The 38,000-sf, two-level John & Susan Sobrato Campus in Palo Alto is expected to serve 25,000 patients a year by the end of the decade.
Architects | May 24, 2016
Lissoni Architettura’s NYC Aquatrium takes first place in New York City Waterfront Design competition
NYC Aquatrium was selected from among 178 proposals from 40 countries as the winner of Arch Out Loud’s NYC Aquarium & Public Waterfront design competition
Building Team Awards | May 24, 2016
Los Angeles bus depot squeezes the most from a tight site
The Building Team for the MTA Division 13 Bus Operations and Maintenance Facility fit 12 acres’ worth of programming in a multi-level structure on a 4.8-acre site.
Building Team Awards | May 23, 2016
'Greenest ballpark' proves a winner for St. Paul Saints
Solar arrays, a public art courtyard, and a picnic-friendly “park within a park" make the 7,210-seat CHS Field the first ballpark to meet Minnesota sustainable building standards.