The American Institute of Architects (AIA) announced the release of its first-ever white paper on materials transparency and risk, part of an AIA effort to equip the entire profession with consensus-driven guidance on an issue of critical importance to the profession, its suppliers and clients.
“Whether in politics or in building design, transparency is an increasingly necessary element of modern life,” said AIA CEO Robert Ivy, FAIA. “And when it comes to materials - the very substances of our built environment - it's more important than ever for architects to be able to communicate openly about what they contain.”
The white paper is the product of more than a year of effort by the AIA's Materials Knowledge Working Group (MKWG), pursuant to a position statement approved by the AIA Board of Directors in December 2014. In that statement, the AIA recognized that “building materials impact the environment and human health before, during and after their use,” and it encouraged architects “to promote transparency in materials’ contents and in their environmental and human health impacts.”
“Materials transparency & risk for architects: An introduction to advancing professional ethics while managing professional liability risks,” was created by materials specialists but is aimed at all architects. It provides a backdrop on the necessity for materials transparency and the steps architects should be taking to ensure change, promote openness, and increase collaboration between themselves, their suppliers and their clients.
As an introduction to the white paper, the MKWG compiled five guideposts about which every architect should be aware when it comes to materials transparency. They provide first steps to a deeper understanding of what goes into a building and how it impacts its inhabitants:
- Information is key. Everyone involved in a building project—from initial design to occupancy—should have access to information on the potential health and environmental impacts relating to materials products.
- Materials transparency presents opportunities for architects. These opportunities include competitive advantage, thought leadership, design innovation, and environmental and human health leadership.
- New practices and procedures inherently present potential risks. There is always some risk in advocating for materials transparency and sharing composition information with our clients. This white paper explores those risks in detail.
- Manage potential risks with increased transparency. Although the risks associated with materials transparency are new, architects are familiar with risk management. This white paper offers several strategies for effectively evaluating and mitigating risk.
- The AIA has tools and resources to help architects navigate materials transparency risks and opportunities. Along with this white paper and existing online resources, the AIA will soon publish new model contract language to specifically address materials transparency issues. In addition, the MKWG, made up of expert members, practitioners and partner organizations, is continually developing education and practice tools to help architects optimize their approach to materials transparency.
The AIA has published guidance on how to address materials transparency issues in its contract document B503-2007 Guide for Amendments to AIA Owner-Architect Agreements.
Related Stories
| Mar 21, 2014
Forget wood skyscrapers - Check out these stunning bamboo high-rise concepts [slideshow]
The Singapore Bamboo Skyscraper competition invited design teams to explore the possibilities of using bamboo as the dominant material in a high-rise project for the Singapore skyline.
| Mar 20, 2014
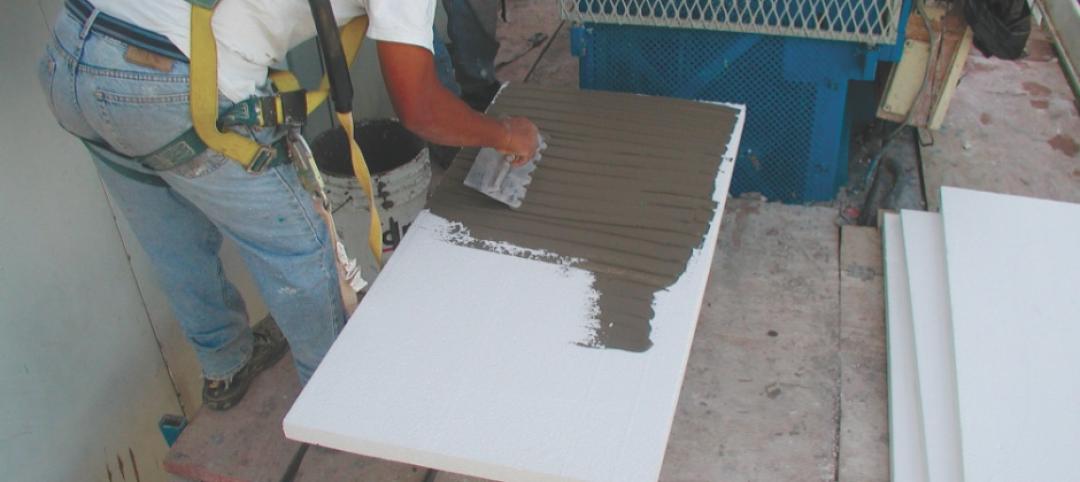
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 20, 2014
13 dazzling wood building designs [slideshow]
From bold structural glulam designs to striking textured wall and ceiling schemes, these award-winning building projects showcase the design possibilities using wood.
| Mar 19, 2014
Federal agency gives thumbs up to tall wood buildings
USDA's support for wood projects includes training for AEC professionals and a wood high-rise design competition, to launch later this year.
| Mar 17, 2014
Rem Koolhaas explains China's plans for its 'ghost cities'
China's goal, according to Koolhaas, is to de-incentivize migration into already overcrowded cities.
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
| Mar 10, 2014
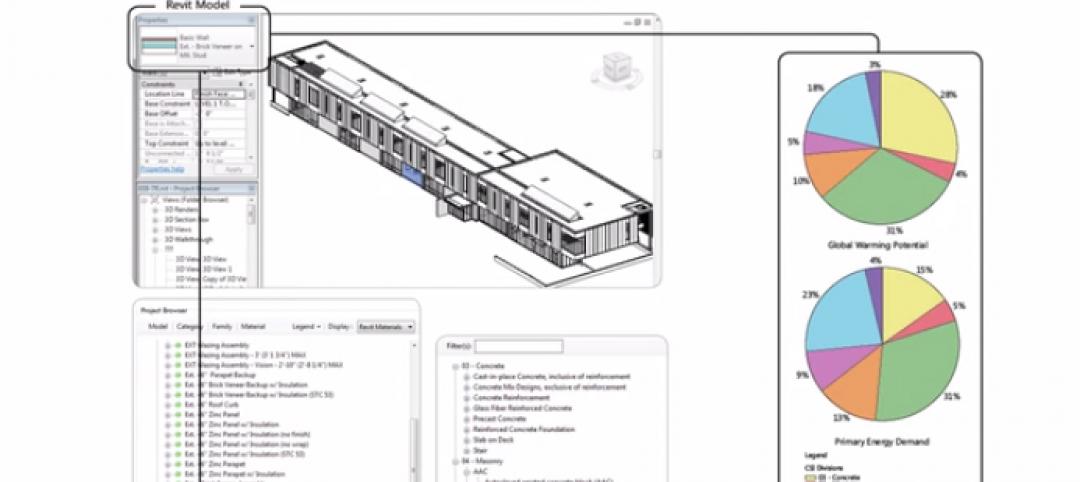
Meet Tally – the Revit app that calculates the environmental impact of building materials
Tally provides AEC professionals with insight into how materials-related decisions made during design influence a building’s overall ecological footprint.
| Mar 5, 2014
5 tile design trends for 2014
Beveled, geometric, and high-tech patterns are among the hot ceramic tile trends, say tile design experts.
| Mar 4, 2014
How EIFS came to America
Design experts from Hoffmann Architects offer a brief history of exterior insulation and finish systems in the U.S.
| Feb 27, 2014
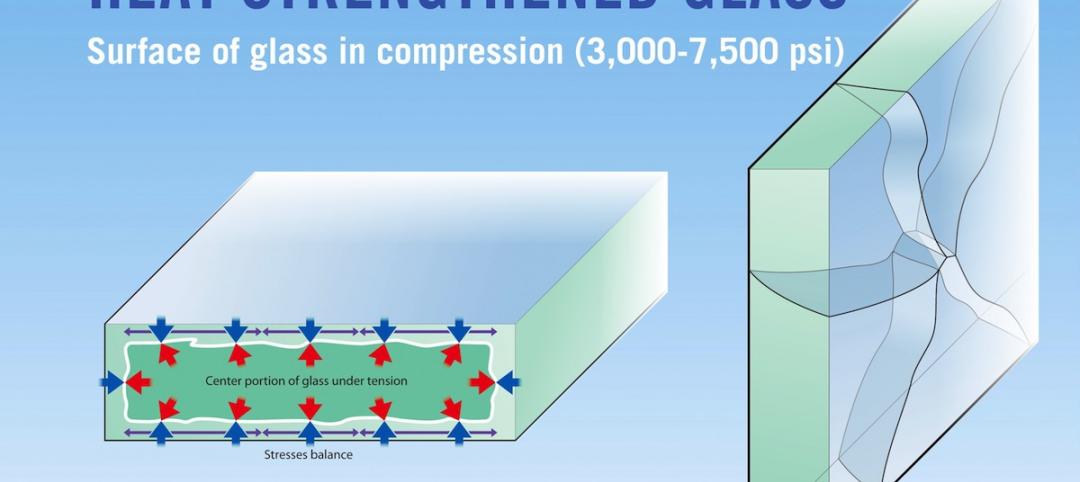
12 facts about heat-treated glass: Why stronger isn’t always better
Glass is heat-treated for two reasons: the first is to increase its strength to resist external stresses such as wind and snow loads, or thermal loads caused by the sun’s energy. The second is to temper glass so that it meets safety glazing requirements defined by applicable codes or federal standards.