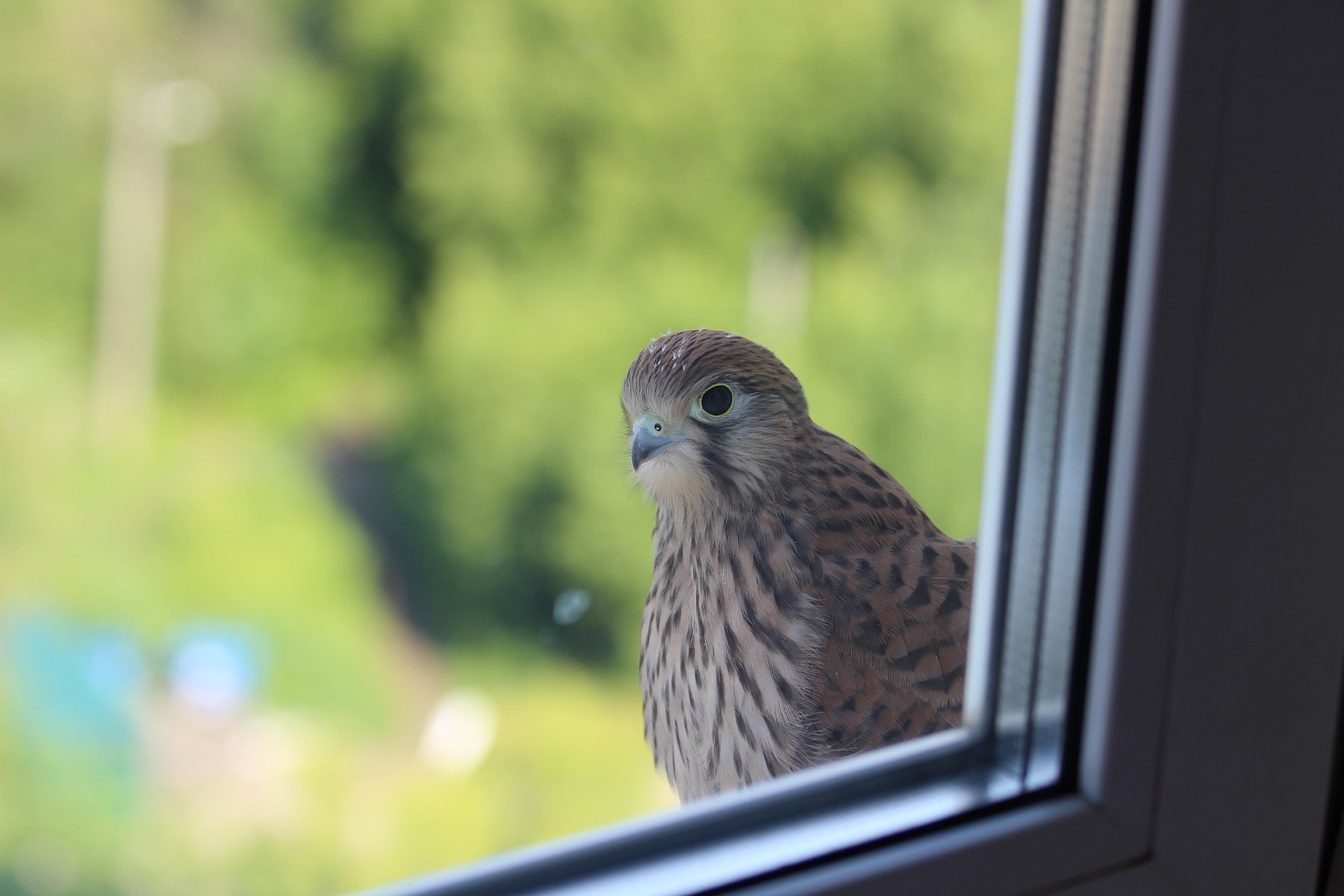
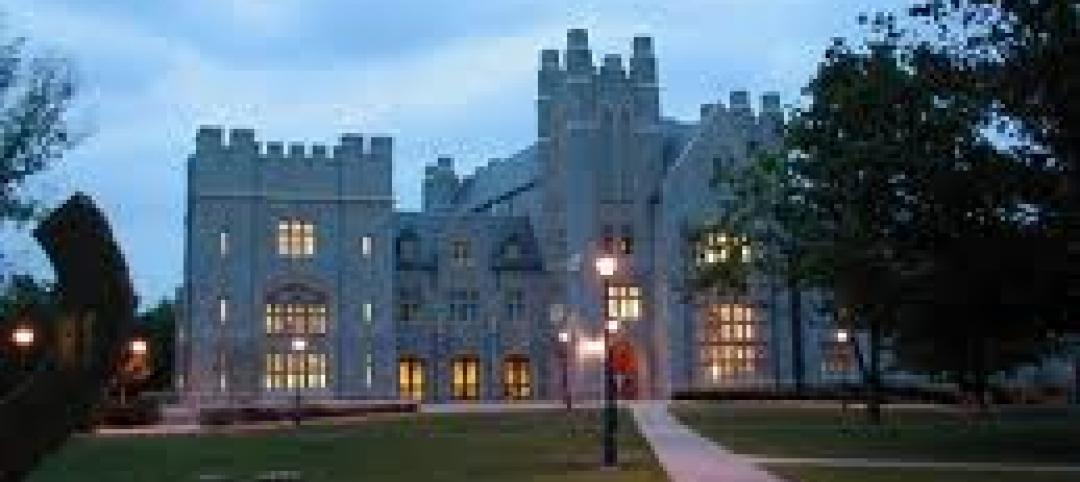
American Bird Conservancy (ABC), working with Washington College in Maryland, says it has doubled its capacity to test and rate glass and other materials for their ability to deter bird collisions. “The move will help ABC meet high demand for testing from glass manufacturers—a vital component of the organization’s work to reduce the threat of window collisions for birds,” according to a news release.
A glass testing tunnel at Washington College’s Foreman’s Branch Bird Observatory in Chestertown, Maryland began operations last fall. The new tunnel is one of just two facilities in North America that can test glass and issue a “bird-friendly” rating, called a Material Threat Factor.
This rating system makes it easier for governments to enact bird-friendly policies and for architects to design buildings that are safer for birds. Windows are among the deadliest threats that migratory birds meet on their journeys, killing up to a billion in the U.S. each year.
Glass can be made safer for birds by adding visible markers that birds can see. “The challenge is finding a balance between human aesthetic preferences and birds’ need for a visual hint that glass is solid—a challenge made more difficult because humans’ forward vision is superior to that of most birds,” ABC says. “The good news is that most bird-friendly patterns are barely noticeable to people.”
Related Stories
| Feb 9, 2012
Initiative to sell off under-used federal property gaining momentum
The bill is similar to a White House planto cut $8 billion worth of building costs by the end of the 2012 fiscal year, and to establish a panel to identify other sites worth selling or donating to nonprofits or state and local governments.
| Feb 9, 2012
Computer tool helps engineers design roof cladding using Canada's building code
Easier to design roof cladding that can withstand winds in a given area.
| Feb 9, 2012
Rapid growth of zero energy buildings expected
Much of that growth will be in the European Union, where near-zero energy buildings are mandated by 2019 for public buildings, and by 2021 for all construction.
| Feb 9, 2012
Stiffer OSHA fines put strain on Kansas contractors
A fine for a violation that once cost between $750 and $1,200 now runs $7,000 or more per incident, according to a state industry association official.
| Feb 8, 2012
California likely to eliminate redevelopment agencies
Leaders of California cities had been trying to fashion a compromise with lawmakers after the state Supreme Court ruled the state had the authority to eliminate the agencies and use their property tax money for local services.
| Feb 8, 2012
Project aimed at economical seismic retrofits on historic Memphis structures
The group will develop a low-cost seismic retrofit model that would benefit aging brick-and-mortar structures. It involves bolting steel brackets to existing wooden floor and ceiling joists.
| Jan 26, 2012
Tampa moves to streamlined online permitting system
The system will replace an inefficient patchwork of old software and is designed to provide businesses, homeowners, and contractors with online access to permitting and licensing information.
| Jan 26, 2012
Industry challenges Connecticut's suit over defective construction work
The dispute arose over multimillion-dollar leaks at the University of Connecticut's law library.
| Jan 5, 2012
Some ADA accessibility rules change in 2012
Some changes to the Americans with Disabilities Act go into effect beginning March 15, 2012.
| Jan 5, 2012
Ontario's stringent energy code has builders concerned over indoor air quality
Some Ontario builders are worried that new building code requirements with stricter energy efficiency measures could lead to poor indoor air quality.