Hospitals are energy gluttons. With 24/7/365 operating schedules and stringent requirements for air quality in ORs and other clinical areas, an acute-care hospital will gobble up about twice the energy per square foot of, say, a commercial office building.
It is an achievement worth noting, therefore, when a major hospital achieves LEED Platinum status, especially when that hospital attains 14 of a possible 17 points for Energy & Atmosphere and 11 of 15 for Indoor Environment Quality.
Kudos, therefore, to Dell Children's Medical Center of Central Texas, a 169-bed, 503,000-sf children's hospital and trauma center in Austin, which gained the coveted top spot in green certification (under LEED-NC 2.1) in early 2009, making it the first LEED Platinum hospital in the U.S.
Phil Risner, PE, LEED AP, the owner's project manager and building systems network engineer, said LEED Platinum was the hospital's goal from the outset because “being green” would have “real, positive effects on both the environment and our healthcare delivery capability.”

Wishing is one thing; executing is another. How the Building Team tackled the difficult energy and IEQ problems of such a facility may provide valuable instruction to AEC professionals facing similarly complex situations.
“We had three guiding principles,” recalls Joseph F. Kuspan, AIA, SVP and design director at Karlsberger, the Columbus, Ohio, firm that did the master plan and design for Dell Children's. “One, don't do dumb things to get LEED points. Two, anything less than a 12% return on investment is dumb. And three, we had to know if we were being dumb.” That is, before rejecting any strategy—roof-mounted wind turbines, for example—the team had to weigh it seriously to see whether or not it was truly viable.
A boon from Austin Energy
Dell Children's sits on 32 acres within a 700-acre brownfield redevelopment site that was once home to Austin's municipal airport. To provide power to the new facility, the local utility, Austin Energy, built an $18 million combined cooling/heating power (CCHP) plant. This increased the energy efficiency of the primary fuel conversion for the project from roughly 29% in a conventional power service model, to 75% efficiency.
The CCHP also saved $6.8 million in capital costs that would have gone to boilers, emergency generators, cooling towers, chillers, and the space necessary to house them. The bulk of the savings, $5.8 million, was plowed back into energy-conservation measures and other LEED initiatives.
Equally important to the sustainability of the project was its use of courtyards, which not only opened up the building massing (and played nicely into the project's pace-setting daylighting strategy), but also led to an interesting approach to the hospital's air handling units.

“The owner wanted the AHUs to be in enclosed spaces, not on the roof,” to simplify maintenance and extend their life expectancy, says Kuspan. Instead of doing the usual 10% space gross-up for the mechanical system, the designers put the air handling units in 2,000-sf “rooms” distributed across 15 locations. “We stacked those rooms and put five heat recovery rooms on the roof, because we didn't want to lose that 70° air on a 100° day in Texas,” he says. “That allowed some of the floors below to use that 70° air.”
Each “stack” of AHU rooms was also right-sized to meet the needs of the hospital department it served. One stack might serve a cardio OR, where the room temperature has to be jacked up from 60°F to 90°F in a matter of minutes following surgery, while another stack might serve administrative offices, where the room temperature would be fairly constant.
This innovation produced further benefits and cost savings, says Kuspan. It allowed for shorter duct runs, which enabled the Building Team to overscale the ducts to reduce air velocity and noise. “That kind of background noise can be a stress factor for patients, families, and staff in a hospital setting,” says Kuspan. The designers were also able to reduce the size of fan motors, thereby saving on initial cost as well as operating expenses.
The project's glazing also had to be fine-tuned to achieve a delicate balance between achieving energy savings in the hot Texas sun and not distorting the view to the outdoors. “The grid that was established in the [master] plan was on a 37-degree angle, which was great for some things but tough for sun control,” says Kuspan. Seton Healthcare Network wanted to avoid any hint of a “techy” look on the exterior; therefore, no applied exterior shading devices, no sunshades, no vertical blades, and definitely no motorized systems.
The team solve this problem by using high-efficiency, double-e coated glass high up on the walls and clearer glass, with low-level coatings, in what Kuspan calls “the sweet spot” from three to seven feet above the floor, where greater transparency was called for.
Perhaps the most commendable aspect of Dell Children's, though, is what the Building Team and hospital board didn't do. They stuck to their principles and didn't go overboard to look super-green. Design elements that could have added LEED EA or IEQ points but failed the “don't do anything dumb” rule or fell below 12% ROI didn't make the cut—things like active photovoltaics, roof-mounted wind turbines, vegetative roofs, natural ventilation in the lobby, charging stations for electric vehicles, and a biofuel fueling station for fleet vehicles.
Many other non-energy-related design elements were also scratched, things like denim wall insulation, waterless urinals, an on-site tertiary water treatment plant, pervious pavement and bioswales in the parking lot, a 500,000-gallon rainwater cistern, and recycled gypsum board. All were struck from the program, even though they might have added LEED points.
In some cases, otherwise popular sustainable design elements were ruled out by the owner. For example, interior light shelves were vetoed by the hospital because they were seen as dust collectors and a potential infection control threat. Even without light shelves, however, the Building Team was able to use the open spaces in the courtyards to daylight more than 80% of occupied administrative and nonclinical spaces. Perhaps more remarkable was their ability to get daylight into 35% of diagnostic and treatment areas. By using the LEED “alternative compliance path,” the project was able to earn the first LEED point for daylighting by a hospital.
Of course, not everything worked as planned. Motion sensors were used extensively to control lighting use, but this went a bit too far when the motion sensors in the on-call room kept turning the lights on every time the residents rolled over in their sleep. These motion sensors were quickly removed. Seton Healthcare's Risner and his staff also had to do a lot of fine-tuning to optimize all the mechanical systems.
By sticking to their guiding principles, however, the owner and the Building Team were able to produce a BMW project at a KIA price. “A lot of people think we must have had an $800 per square foot budget, that's just not true,” says Kuspan. The construction cost was somewhere between $280/sf and $305/sf, depending on whether the $18 million for the cogeneration plant is included in the calculation.
“That's not an exorbitant cost per square foot for a project like this,” says Kuspan. Not when you get the kinds of bragging rights Dell Children's Medical Center has earned.
Related Stories
Building Technology | May 4, 2023
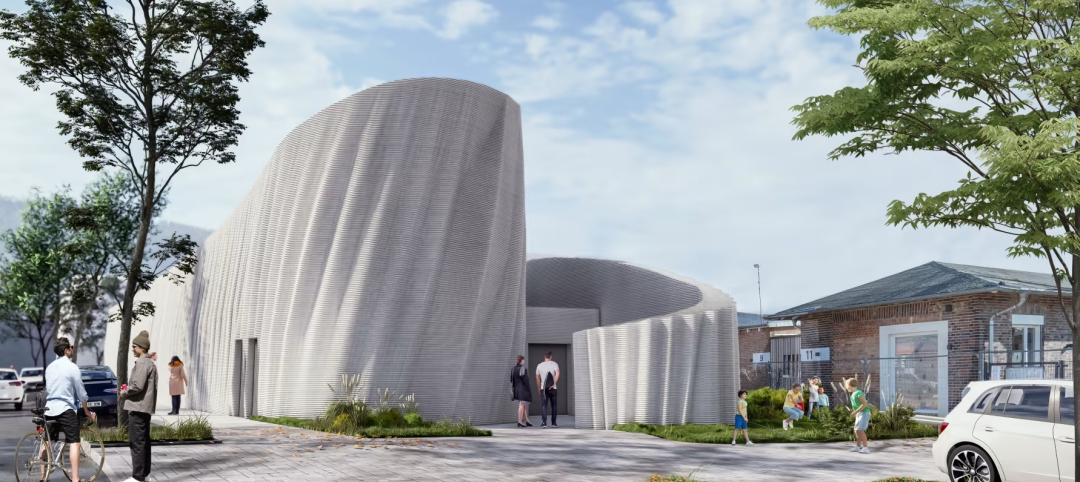
3D printing for construction advances in Germany
The largest 3D-printed building in Europe will have a much lower carbon footprint.
Mass Timber | May 3, 2023
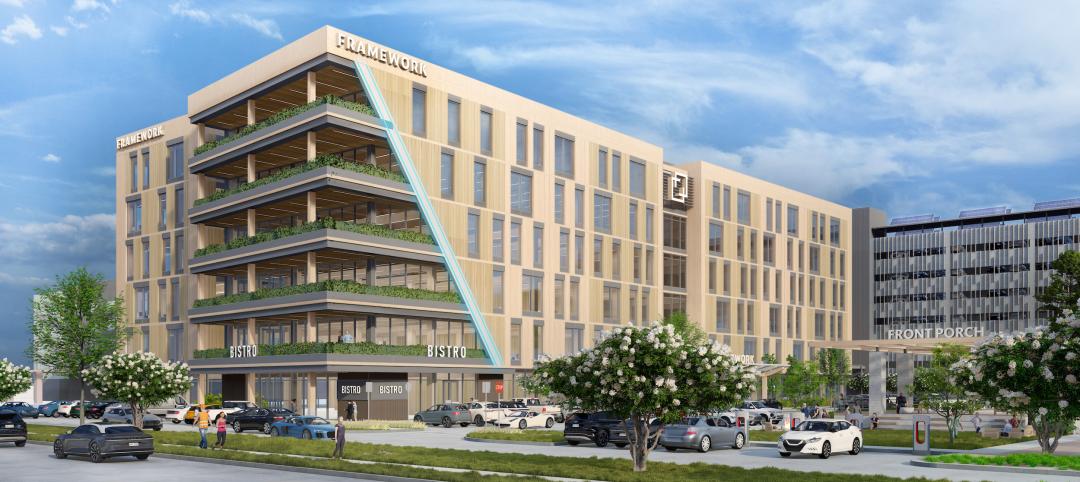
Gensler-designed mid-rise will be Houston’s first mass timber commercial office building
A Houston project plans to achieve two firsts: the city’s first mass timber commercial office project, and the state of Texas’s first commercial office building targeting net zero energy operational carbon upon completion next year. Framework @ Block 10 is owned and managed by Hicks Ventures, a Houston-based development company.
AEC Tech | May 1, 2023
Utilizing computer vision, AI technology for visual jobsite tasks
Burns & McDonnell breaks down three ways computer vision can effectively assist workers on the job site, from project progress to safety measures.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Building Technology | Apr 24, 2023
Let’s chat about AI: How design and construction firms are using ChatGPT
Tech-savvy AEC firms that already use artificial intelligence to enhance their work view the startling evolution of ChatGPT mostly in a positive light as a potential tool for sharing information and training employees and trade partners. However, the efficacy of ChatGPT is likely to rest on the construction industry’s aggregation of quality data that, until recently, has been underwhelming for getting the greatest bang from AI and machine learning.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
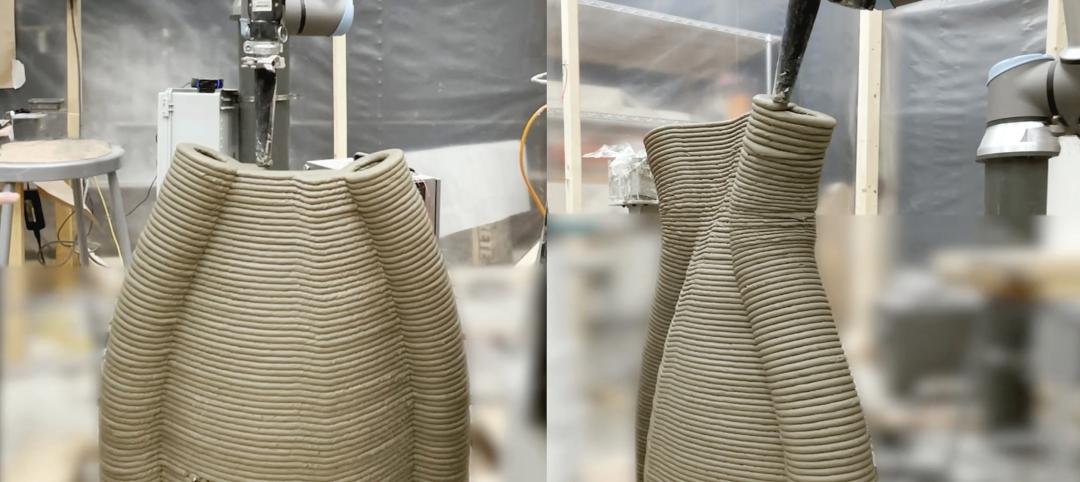
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Apr 5, 2023
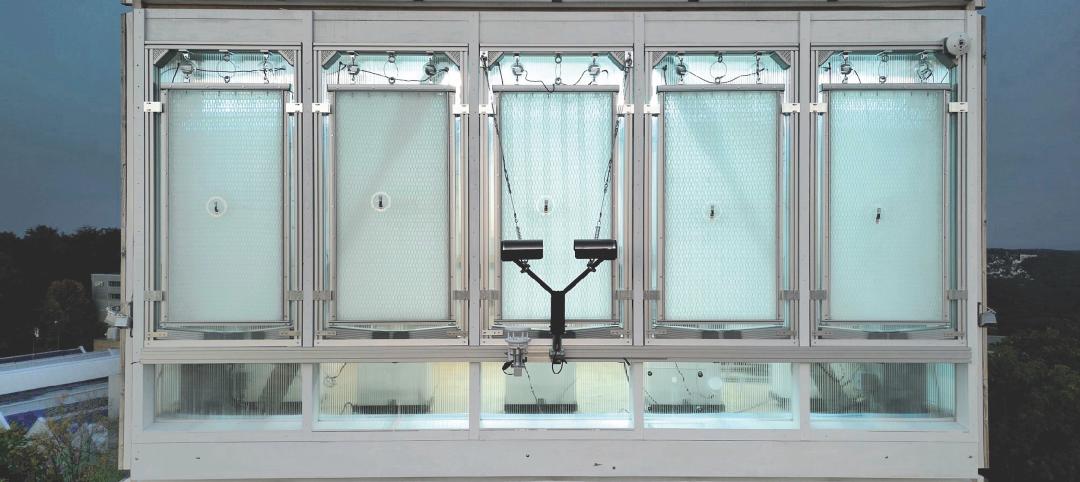
Façade innovation: University of Stuttgart tests a ‘saturated building skin’ for lessening heat islands
HydroSKIN is a façade made with textiles that stores rainwater and uses it later to cool hot building exteriors. The façade innovation consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator.