A few months ago, the world’s first self-described “Marschitect” was working on developing architecture designed specifically to meet the challenges of living on Mars. Now, more and more architects and researchers are taking a shot at developing new and innovative ways for building habitable environments on the surface of the inhospitable planet.
Two of the most recent ideas for potential building materials come from NASA researchers and a team of scientists at Illinois’s Northwestern University.
As Occam’s razor states, the simplest solution is usually the right one, and NASA researchers have taken that idea to heart as they believe the building material that may help solve many of the problems associated with living and building on Mars is regular, everyday ice, csmonitor.com reports.
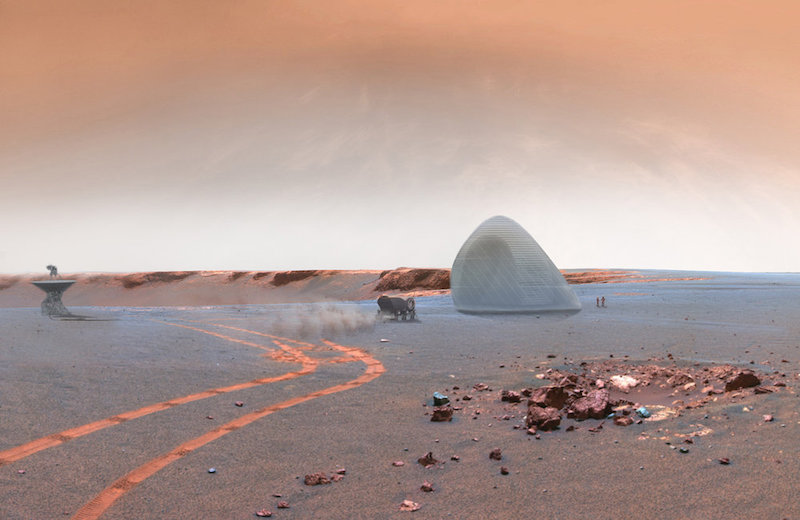
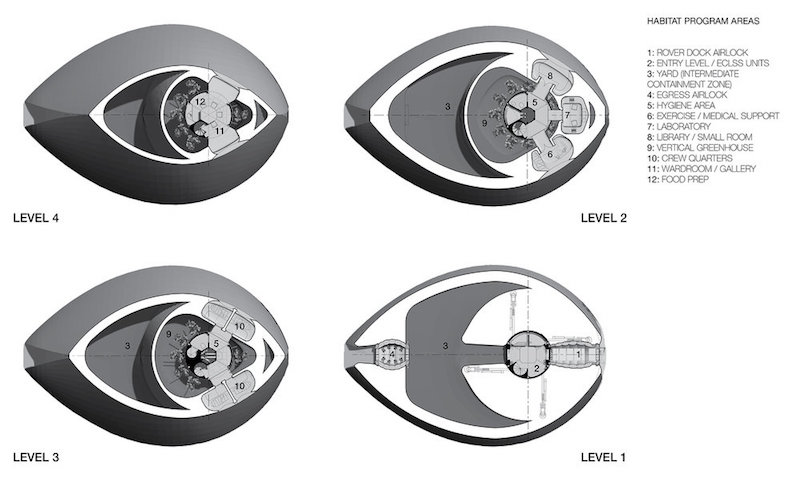
NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently revealed its design concept for the “Mars Ice Home,” which was developed with help from Space Exploration Architecture and the Clouds Architecture Office.
An inflatable inner-tube-like material would provide the actual living quarters for the astronauts while its exterior would be encased in a shell of 3D-printed ice. The ice would protect the structure, and those living within it, from cosmic rays, which are one of the biggest health concerns associated with humans living on Mars. While the ice structure would block the cosmic rays, it would still allow some light to pass through so it would more closely resemble living in a home than a cave or underground and allowing the astronauts to stay connected to natural diurnal cycles.
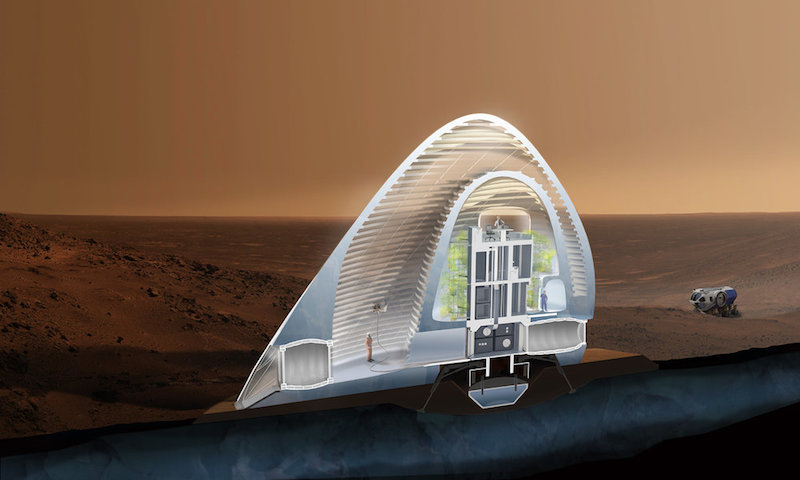 Cross section of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
Cross section of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
The ice shell would be five centimeters thick and is envisioned as a series of nested domes enclosed by a transparent ETFE (Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) membrane. The outer shell creates a “front yard” that astronauts can occupy without the use of an EVA suit. The inner shell will provide a vertical hydroponic greenhouse that surrounds the inhabitants.
The Mars Ice House would be constructed without the need of a crew being present. The module would descend to the planet’s surface and land. Then the construction process would begin: the foundation is sintered, the ETFE membrane is inflated, the airlocks are deployed, the ice for the outer and inner shells is printed, and the plant-growing process beings. Only after all of this occurs does the crew arrive.
Since one of the biggest hurdles to building on Mars revolves around transporting any possible building materials to the planet, the lightness of the inflatable structure and the availability of ice on Mars make the Mars Ice Home a very intriguing possibility.
 Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
Another proposal for building on Mars uses the planets limited resources, as well, but instead of ice, a team of scientists from Northwestern University developed a form of “Martin concrete” that can be created using soil from the Red Planet, Dezeen reports.
The concrete is created by mixing the soil with molten sulfur and, according to the scientists, could be used to build entire villages on Mars. Most importantly, the concrete doesn’t require any water to make. The building material can endure low temperatures, is resistant to acid and salt, and can be melted down and recycled to build a different structure.
The idea of using the soil found on Mars to create a building material is not a new one. Foster + Partners created a concept for a 3D-printed habitat built by robots that uses regolith, loose soil, and rocks as the building materials, but according to Dezeen, this is the first time a report has detailed how this could actually be feasible.
After a series of trial and error experiments, the team, consisting of Lin Wan, Roman Wendner, and Gianluca Cusatis, determined an even mix of sulfur and aggregate would produce a material with a strength of 50 megapascals. When the difference of gravity on the surface of Mars is factored in, the material will be three times stronger, making it suitable for building on Mars.
The time it takes to travel to Mars makes the necessity of building a habitat for the astronauts on its surface unavoidable. While the development of Martian architecture may seem like nothing more than an exercise in creativity, it is actually an integral part of one day setting foot on Mars.
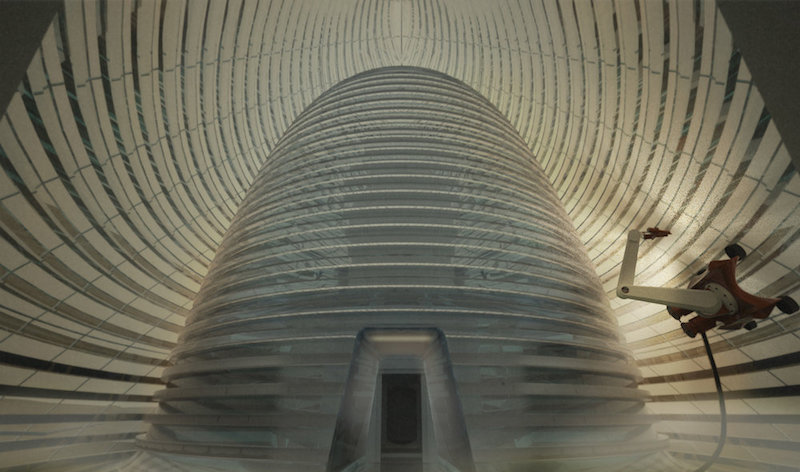 The "front yard" of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
The "front yard" of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
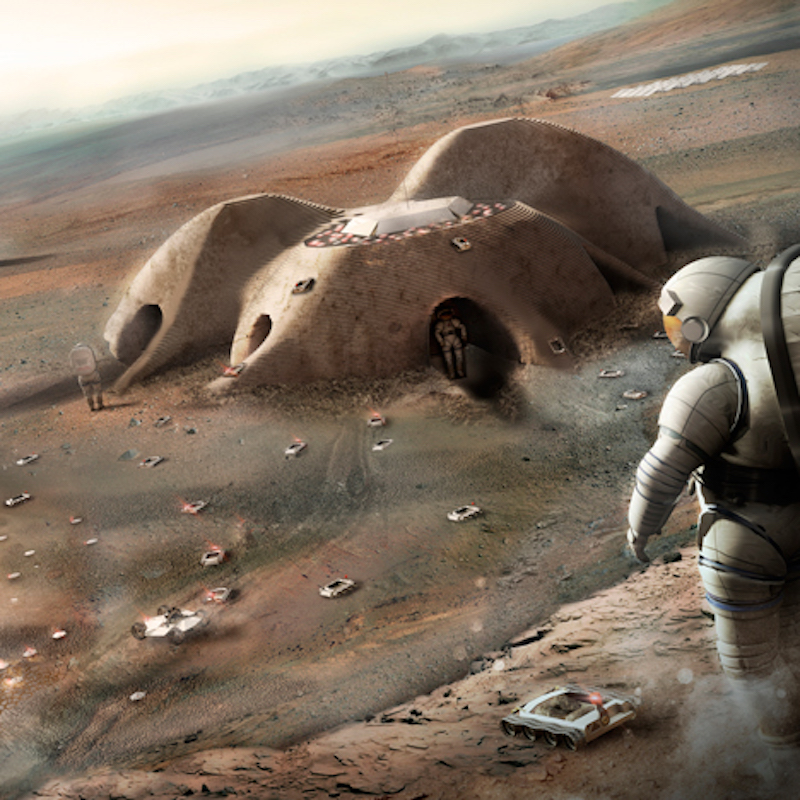 Foster + Partners' 3D-printed proposal. Courtesy of Foster + Partners.
Foster + Partners' 3D-printed proposal. Courtesy of Foster + Partners.
Related Stories
Building Materials | Jun 16, 2016
ABC: Construction material prices rise again in May
Nonresidential construction price gains were largely driven by iron and steel prices and steel mill product prices.
Green | Jun 2, 2016
USGBC offers new LEED pilot credit: Building Material Human Hazard and Exposure Assessment
For assessing human health-related exposure scenarios for construction products.
Building Materials | Jun 1, 2016
MIT study: Microscopic structure of natural materials can inspire better concrete
Bones and sea sponges are highly organized at the molecular level, while concrete consists of random composites.
Sponsored | Building Materials | May 25, 2016
Materials Manufactured to Move Protect Southwest Energy’s New Office
Codes and Standards | May 20, 2016
Industry leaders call for wider use of bamboo as a building material
Benefits include seismic resiliency and sustainability.
Building Materials | Apr 8, 2016
AIA: Architects release first white paper on materials transparency and risk
It provides the steps architects should be taking to ensure change, promote openness, and increase collaboration between themselves, their suppliers, and their clients.
Market Data | Feb 26, 2016
JLL upbeat about construction through 2016
Its latest report cautions about ongoing cost increases related to finding skilled laborers.
| Jan 28, 2016
AIA CES class: The rainscreen approach to a better building envelope
Building envelope expert Bradley Carmichael of Hoffmann Architects explains how rainscreen wall systems work and evaluates the effectiveness of various rain-control methods, including mass walls, perfect barriers, and masonry veneers. This AIA/CES class is worth 1.0 learning unit.
Building Materials | Jan 25, 2016
Johnson Controls to merge with Tyco International
The $20 billion deal is the latest corporate inversion maneuver.
















