A few months ago, the world’s first self-described “Marschitect” was working on developing architecture designed specifically to meet the challenges of living on Mars. Now, more and more architects and researchers are taking a shot at developing new and innovative ways for building habitable environments on the surface of the inhospitable planet.
Two of the most recent ideas for potential building materials come from NASA researchers and a team of scientists at Illinois’s Northwestern University.
As Occam’s razor states, the simplest solution is usually the right one, and NASA researchers have taken that idea to heart as they believe the building material that may help solve many of the problems associated with living and building on Mars is regular, everyday ice, csmonitor.com reports.
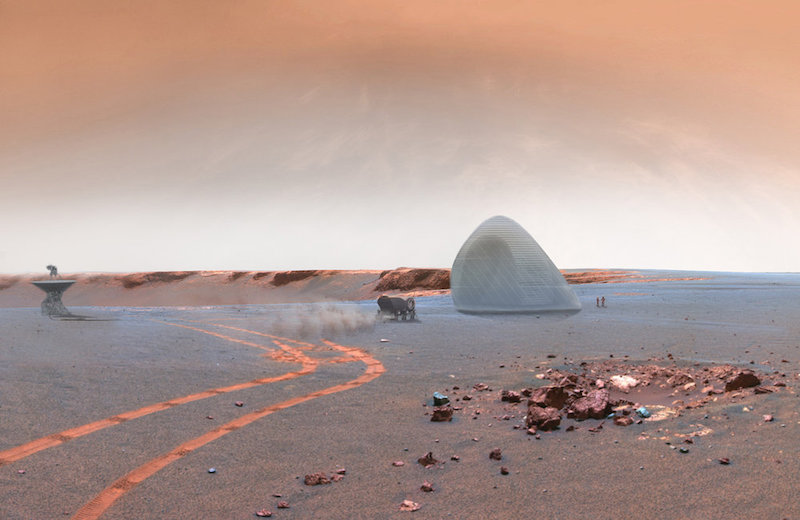
NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently revealed its design concept for the “Mars Ice Home,” which was developed with help from Space Exploration Architecture and the Clouds Architecture Office.
An inflatable inner-tube-like material would provide the actual living quarters for the astronauts while its exterior would be encased in a shell of 3D-printed ice. The ice would protect the structure, and those living within it, from cosmic rays, which are one of the biggest health concerns associated with humans living on Mars. While the ice structure would block the cosmic rays, it would still allow some light to pass through so it would more closely resemble living in a home than a cave or underground and allowing the astronauts to stay connected to natural diurnal cycles.
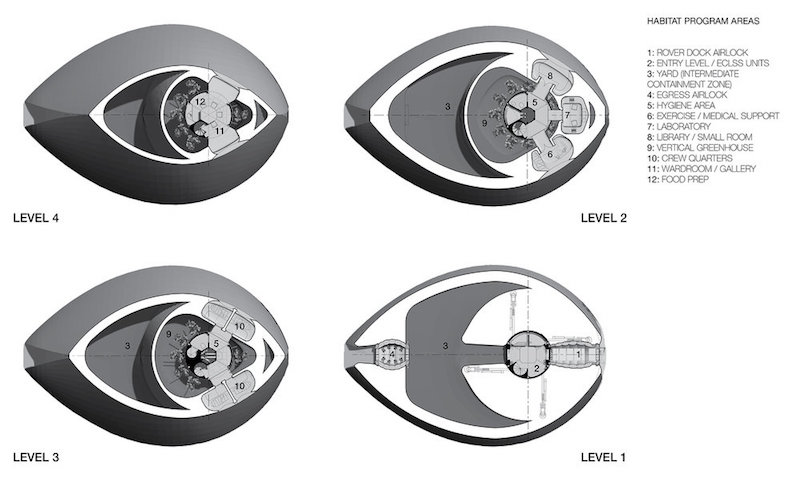
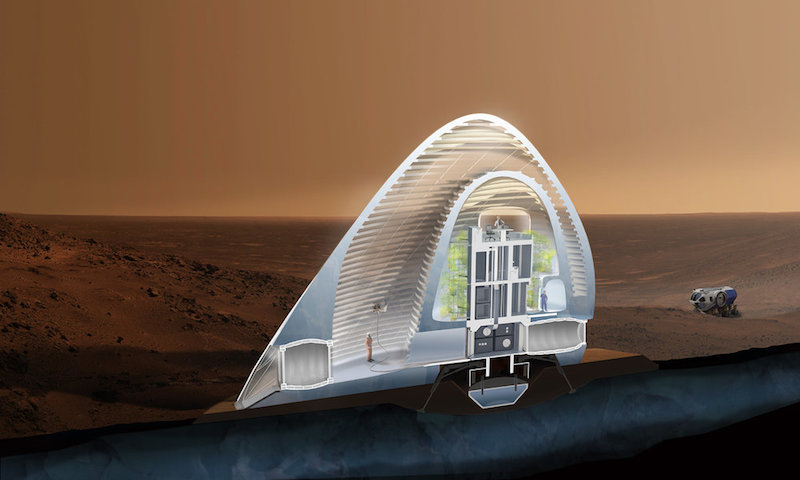 Cross section of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
Cross section of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
The ice shell would be five centimeters thick and is envisioned as a series of nested domes enclosed by a transparent ETFE (Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) membrane. The outer shell creates a “front yard” that astronauts can occupy without the use of an EVA suit. The inner shell will provide a vertical hydroponic greenhouse that surrounds the inhabitants.
The Mars Ice House would be constructed without the need of a crew being present. The module would descend to the planet’s surface and land. Then the construction process would begin: the foundation is sintered, the ETFE membrane is inflated, the airlocks are deployed, the ice for the outer and inner shells is printed, and the plant-growing process beings. Only after all of this occurs does the crew arrive.
Since one of the biggest hurdles to building on Mars revolves around transporting any possible building materials to the planet, the lightness of the inflatable structure and the availability of ice on Mars make the Mars Ice Home a very intriguing possibility.
 Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
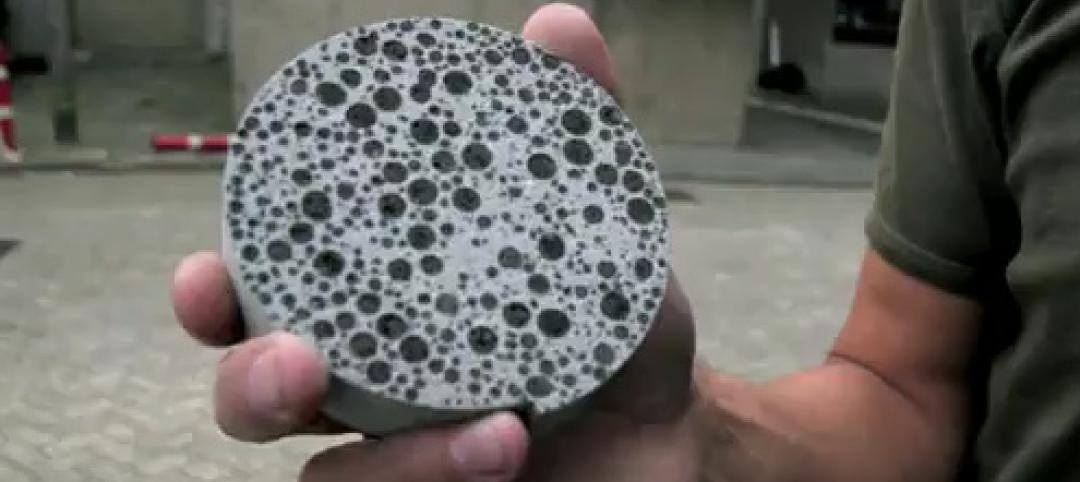
Another proposal for building on Mars uses the planets limited resources, as well, but instead of ice, a team of scientists from Northwestern University developed a form of “Martin concrete” that can be created using soil from the Red Planet, Dezeen reports.
The concrete is created by mixing the soil with molten sulfur and, according to the scientists, could be used to build entire villages on Mars. Most importantly, the concrete doesn’t require any water to make. The building material can endure low temperatures, is resistant to acid and salt, and can be melted down and recycled to build a different structure.
The idea of using the soil found on Mars to create a building material is not a new one. Foster + Partners created a concept for a 3D-printed habitat built by robots that uses regolith, loose soil, and rocks as the building materials, but according to Dezeen, this is the first time a report has detailed how this could actually be feasible.
After a series of trial and error experiments, the team, consisting of Lin Wan, Roman Wendner, and Gianluca Cusatis, determined an even mix of sulfur and aggregate would produce a material with a strength of 50 megapascals. When the difference of gravity on the surface of Mars is factored in, the material will be three times stronger, making it suitable for building on Mars.
The time it takes to travel to Mars makes the necessity of building a habitat for the astronauts on its surface unavoidable. While the development of Martian architecture may seem like nothing more than an exercise in creativity, it is actually an integral part of one day setting foot on Mars.
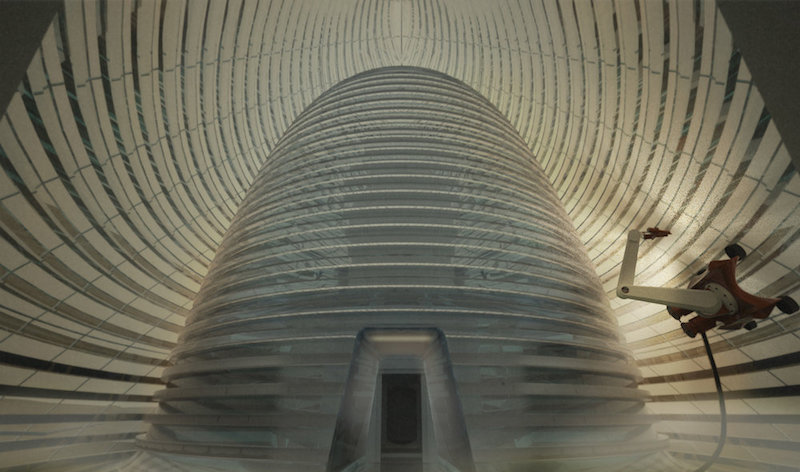 The "front yard" of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
The "front yard" of the Mars Ice House. Courtesy of Space Exploration Architecture.
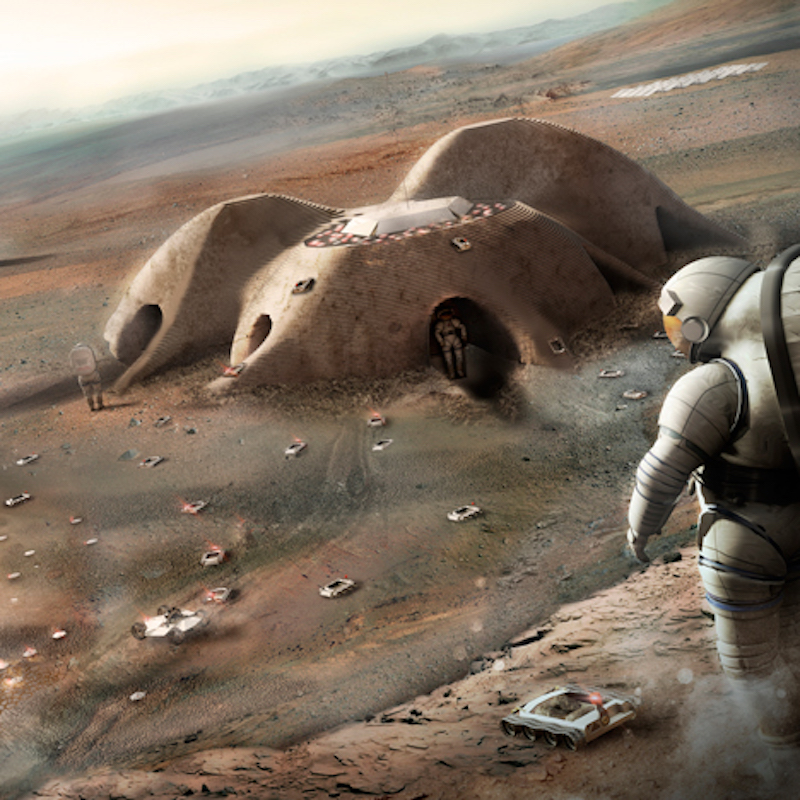 Foster + Partners' 3D-printed proposal. Courtesy of Foster + Partners.
Foster + Partners' 3D-printed proposal. Courtesy of Foster + Partners.
Related Stories
| Mar 29, 2013
Stanford researchers develop nanophotonic panel that reflects sun's heat out of the atmosphere
Researchers at Stanford University have developed a nanophotonic material that not only reflects sunlight, but actually beams the thermal energy out of the earth's atmosphere.
| Mar 21, 2013
Turner report: Construction costs up slightly in first quarter
Turner Construction Company announced that the First Quarter 2013 Turner Building Cost Index – which measures costs in the non-residential building construction market in the United States – has increased to a value of 849. This reflects a 1.19% increase from the Fourth Quarter 2012 and a 3.41% increase from the First Quarter 2012.
Building Enclosure Systems | Mar 13, 2013
5 novel architectural applications for metal mesh screen systems
From folding façades to colorful LED displays, these fantastical projects show off the architectural possibilities of wire mesh and perforated metal panel technology.
| Feb 26, 2013
Southern Pine Inspection Bureau publishes new design values effective June 1
New design values for all sizes and grades of visually graded Southern Pine dimension lumber were published in the Southern Pine Inspection Bureau’s (SPIB) Supplement No.13 to the 2002 Standard Grading Rules for Southern Pine Lumber on Feb. 11.
| Feb 26, 2013
ANSI standard for interior doors open for second public ballot
WDMA I.S.6A-11, Industry Standard for Interior Architectural Wood Stile and Rail Doors and WDMA I.S.1A-11, Industry Standard for Interior Architectural Wood Flush Doors, are now open for their second ballot for recognition as American National Standards.
| Feb 22, 2013
Dutch team's 'bioconcrete' can heal itself
Two researchers from Delft Technical University in Holland have developed a self-healing cement that can stop microcracks from forming in concrete.
| Feb 14, 2013
Firestone projects recognized for roofing excellence
Firestone Building Products has been awarded the 2012 RoofPoint Excellence in Design Award in two categories: Global Leadership and Advancing Sustainable Roofing.
| Feb 5, 2013
8 eye-popping wood building projects
From 100-foot roof spans to novel reclaimed wood installations, the winners of the 2013 National Wood Design Awards push the envelope in wood design.
| Jan 7, 2013
Jerry Yudelson's issues his "Top 10 Green Building Megatrends" for 2013
Yudelson, a Contributing Editor to Building Design+Construction, says, “It looks like a good year ahead for the green building industry. Based on our experience, it seems clear that green building will continue its rapid expansion globally in 2013 in spite of the ongoing economic slowdown in most countries of Europe and North America. More people are building green each year, with 50,000 LEED projects underway by the latest counts; there is nothing on the horizon that will stop this Mega-trend or its constituent elements.”














