Major changes to requirements regarding building envelope, lighting, mechanical and the energy cost budget are contained in the newly published energy standard from ASHRAE and IES.
ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1-2013, Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings, incorporates 110 addenda, reflecting changes made through the public review process. Appendix F gives brief descriptions and publication dates of the addenda to 90.1-2010 reflected in this new edition.
“While many things have changed since the first version of Standard 90 was published in 1975, the need to reduce building energy use and cost has not,” Steve Skalko, chair of the committee that wrote the 2013 standard, said. “This standard represents many advances over the 2010 standard, as we worked toward our goal of making the standard 40 to 50 percent more stringent than the 2004 standard.”
“Achieving the stringency goals established for the 2013 standard presented a challenge in reducing the requirements for lighting,” Rita Harrold, director of technology for the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America, said. “While interior lighting power densities (LPD) were re-evaluated and most lowered, there continues to be an ongoing concern about maintaining quality of lighting installations for occupant satisfaction and comfort while achieving energy savings. The focus in the 2013 standard, therefore, was not just on lowering LPDs but on finding ways to achieve savings by adding more controls and daylighting requirements as well as including lighting limits for exterior applications based on jurisdictional zoning.”
The most significant changes are:
- Building Envelope. Opaque elements and fenestration requirements have been revised to increase stringency while maintaining a reasonable level of cost-effectiveness. Opaque and fenestration assemblies in Tables 5.5-1 through 5.5-8 are revised in most climates. These changes include:
- Criteria requiring double glazed fenestration in many climates
- Minimum visible transmittance/solar heat gain coefficient (VT/SHGC) ratio to enable good daylighting with minimum solar gain, while not restricting triple- and quadruple-glazing.
- Simplification of the skylighting criteria.
- Lighting: These changes include improvements to daylighting and daylighting controls, space-by-space lighting power density limits, thresholds for toplighting and revised controls requirements and format.
- Mechanical: Equipment efficiencies are increased for heat pumps, packaged terminal air conditioners, single package vertical heat pumps and air conditioners evaporative condensers. Also, fan efficiency requirements are introduced for the first time. Additional provisions address commercial refrigeration equipment, improved controls on heat rejection and boiler equipment, requirements for expanded use of energy recovery, small motor efficiencies and fan power control and credits. Control revision requirements have been added to the standard such as direct digital controls in many applications. Finally, the 2013 edition completes the work that was begun on equipment efficiencies for chillers in the 2010 edition.
- Energy Cost Budget (ECB) & Modeling: Improvements were made to the ECB and Appendix G provisions to clarify the use of the prescriptive provisions when performing building energy use modeling. In addition, these sections were revised to enhance capturing daylighting when doing the modeling calculations.
Another important change for the 2013 standard is the first alternate compliance path in Chapter 6. Section 6.6 was added to the 2010 edition to provide a location for alternate methods of compliance with the standard. The first such alternate path has been developed for computer room systems and was formulated with the assistance of ASHRAE technical committee 9.9, Mission Critical Facilities, Data Centers, Technology Spaces and Electronic Equipment. This path uses the Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) metric established by the datacom industry. This alternate efficiency path format provides a framework that could be considered for other energy using facets of buildings not easily covered in the prescriptive provisions of the standard.
Also new to the standard are requirements for operating escalators and moving walkways at minimum speed per ASME A17.1 when not conveying passengers.
The cost of ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1-2013, Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings, is 135 ($115, ASHRAE members). To order, contact ASHRAE Customer Contact Center at 1-800-527-4723 (United States and Canada) or 404-636-8400 (worldwide), fax 678-539-2129, or visit www.ashrae.org/bookstore.
ASHRAE, founded in 1894, is a building technology society with more than 50,000 members worldwide. The Society and its members focus on building systems, energy efficiency, indoor air quality, refrigeration and sustainability. Through research, standards writing, publishing, certification and continuing education, ASHRAE shapes tomorrow’s built environment today.
Related Stories
| Aug 22, 2022
Less bad is no longer good enough
As we enter the next phase of our fight against climate change, I am cautiously optimistic about our sustainable future and the design industry’s ability to affect what the American Institute of Architects (AIA) calls the biggest challenge of our generation.
Giants 400 | Aug 21, 2022
Top 110 Architecture/Engineering Firms for 2022
Stantec, HDR, HOK, and Skidmore, Owings & Merrill top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture engineering (AE) firms for nonresidential and multifamily buildings work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 19, 2022
2022 Giants 400 Report: Tracking the nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms
Now 46 years running, Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report rankings the largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. This year a record 519 AEC firms participated in BD+C's Giants 400 report. The final report includes more than 130 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
| Aug 19, 2022
Cuningham appoints Jacqueline Dompe as new Chief Executive Officer
Cuningham, a national design firm, is thrilled to announce the appointment of Jacqueline Dompe as the firm’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO).
| Aug 19, 2022
Future sea rise could expose 720,000 more people on East Coast to flooding
An analysis by NPR based on modeling from the National Hurricane Center for New York City, Washington, D.C., and Miami-Dade County found future sea rise could expose about 720,000 more people to damaging floods later this century.
| Aug 19, 2022
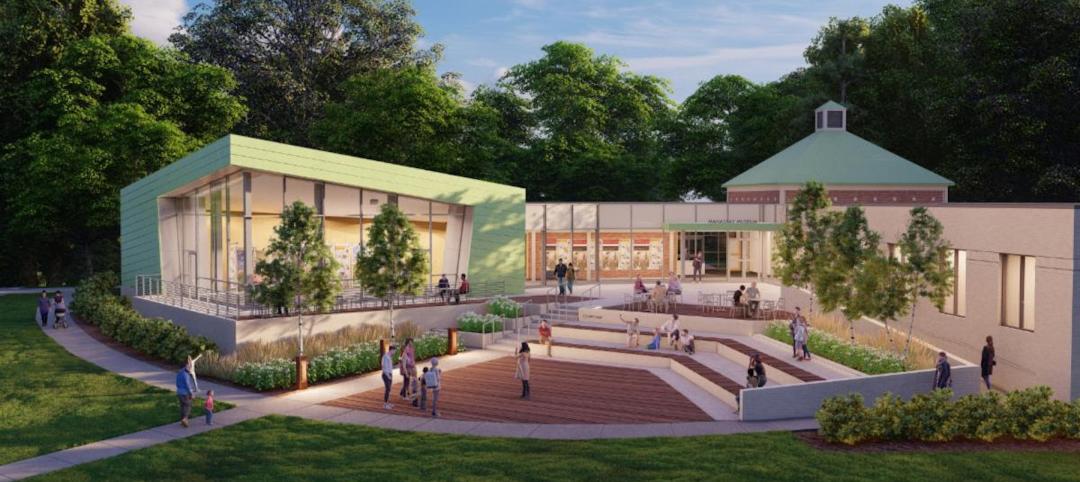
Manassas Museum renovated to reimagine a civic design & engage the community
Manassas, VA has recently added to its historic Manassas Museum.
| Aug 18, 2022
U.S. Treasury moves to boost affordable housing
The Department of the Treasury recently announced new guidance to “increase the ability of state, local, and tribal governments to use American Rescue Plan (ARP) funds to boost the supply of affordable housing in their communities,” according to a news release.
Daylighting | Aug 18, 2022
Lisa Heschong on 'Thermal and Visual Delight in Architecture'
Lisa Heschong, FIES, discusses her books, "Thermal Delight in Architecture" and "Visual Delight in Architecture," with BD+C's Rob Cassidy.
| Aug 18, 2022
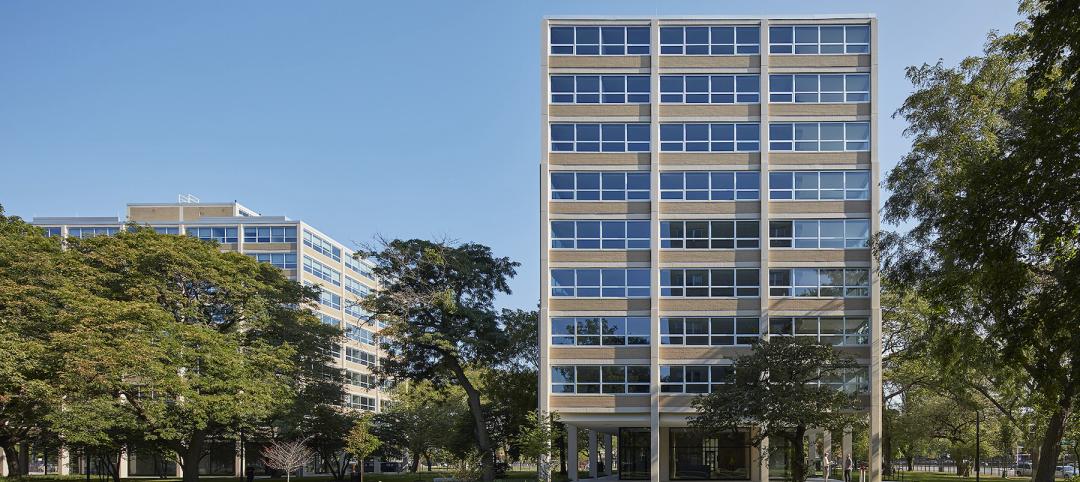
The Illinois Institute of Technology restores three Mies van der Rohe buildings
With Dirk Denison Architects and Gilbane Building Company, the Illinois Institute of Technology has recently completed a $70 million housing project that has restored three Ludwig Mies van der Rohe buildings.
Multifamily Housing | Aug 17, 2022
California strip mall goes multifamily residential
Tiny Tim Plaza started out as a gas station and a dozen or so stores. Now it’s a thriving mixed-use community, minus the gas station.