The pressure to reduce cap-ex and op-ex costs in the data center sector, while meeting an ever-growing demand for IT capacity, is driving owners and operators to employ advanced tools and services for the precise tracking and monitoring of nearly every component within their installations—from energy performance and power reliability to IT systems capacity and space utilization.
With better information, and more of it, data center owners believe they will be able to extend the life and optimize the performance of their buildings and IT infrastructure, enabling them to defer, or even avoid, costly upgrades, renovations, expansions, and new construction projects.
The demand for sophisticated monitoring solutions has spurred a new market segment—data center infrastructure management (DCIM)—that is likely to impact the way data center projects are planned, designed, built, and operated.
“DCIM is a powerful tool, when properly designed and deployed, to help manage the capacity, delivery, consumption, and energy across a data center,” says Jay Chester, PE, Senior Project Manager with SSOE’s Advanced Technology group (www.ssoe.com). “The data captured for analysis models can be structured to help predict performance and allow for ‘what if’ testing of equipment placement and operational scheduling.”
While still in its infancy, the DCIM movement is expected to grow sixfold by 2020, according to a new report by Navigant Research (www.navigantresearch.com). The firm’s Research Director, Eric Woods, predicts annual spending on DCIM-related software and services will balloon to more than $4.5 billion over the next six years, from its current market size of $663 million. Moreover, research firm Gartner predicts that 60% of large data centers (at least 3,000 sf) in North America will adopt some type of DCIM solution by 2017.
“One of the underlying trends driving the greater adoption and visibility of DCIM solutions is new thinking about the relationship between the building infrastructure for data centers and the IT capacity,” says Woods. “Traditionally, you built the building, put in the basic infrastructure management systems, and largely forgot about it. That is, all the changes occurred at the IT level, in terms of the various evolutions of technology. The two functions—facilities and IT—operated in silos.”
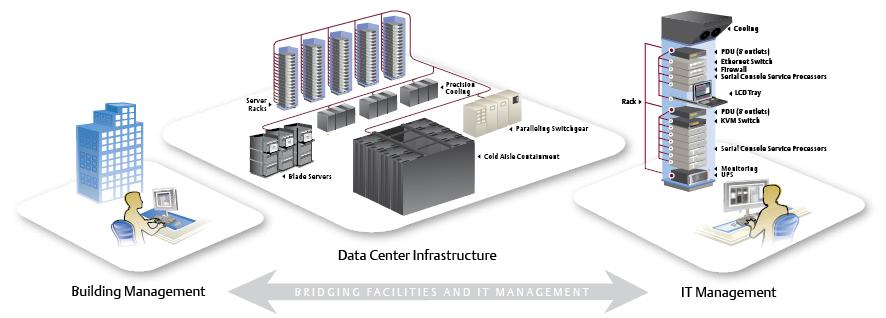
Emerson’s Trellis DCIM platform combines software and hardware into a solution that is managed with a single, Web-enabled, real-time view. It allows data center owners to monitor and measure, in real time, everything from energy and space efficiency to power allocation and server capacity.
Using advanced data collection and monitoring tools, data center providers believe they can bridge the gap between the facilities management function and IT function to offer a holistic, real-time view of their data centers, in an effort to optimize performance, utilization, and longevity.
“What we’re seeing among leading-edge players, as well as in academic research, is moving in the direction of thinking about data centers as a whole unit, sort of like a giant computer,” says Woods. “The data center is a big box that itself is part of the optimized capacity of the computing power in the space.”
DCIM's impact on the Building Team
This more holistic approach to data center planning and operations means that the design table is about to get a little more crowded, as IT managers begin to play a larger role in the planning, design, and preconstruction processes. It also means that Building Teams will be partly responsible for fostering collaboration between their clients’ facilities staff and IT team—two groups with very different priorities and agendas, says Addam Friedl, Senior Vice President, Mission Critical Facilities, with Environmental Systems Design (www.esdesign.com).
“Getting the two sides to sit down at the same table and agree on what the systems are supposed to do, what information needs to be gathered, and how it should be disseminated can be a real challenge, depending on the client,” says Friedl.
A thornier issue, he says, is the mind-boggling amount of data being collected and figuring out how to put it to use. Depending on the scale of the DCIM implementation, data center facilities could be looking at millions of data points that must be collected, organized, and analyzed.
“My challenge to the client is always: What are you going to do with all this data?” says Friedl. “A large data center with just a basic building management system and power monitoring system will have tens of thousands of data points; a DCIM setup could have millions. A lot of operators don’t use the data to the level they think they want to use it to.”
Furthermore, who’s going to be responsible for crunching the data? Facilities? IT? A third-party DCIM provider? An AEC firm? These are questions that need to be sorted out well before the data center is constructed and occupied. Friedl envisions many data center owners outsourcing the DCIM functions, either to an AEC firm involved in the project or a DCIM solutions provider.
Other advice for Building Teams from our experts includes:
Be prepared to coach clients through the DCIM implementation process. Because the movement is so new, clients will likely lean on the Building Team for guidance on everything from choosing the DCIM components to identifying critical data points to figuring out how best to use the data for performance optimization.
Beef up the infrastructure. “As the DCIM system becomes more robust, you’ll need more cabling, a larger cable tray or raceway, and potentially more monitoring capabilities,” says SSOE’s Chester. A more sophisticated control room will also be required. In addition, he says Building Teams will need to design for I/O (input/output) points for gear and equipment that traditionally have not been monitored by a central system.
Flexibility will become more crucial. The ultimate goal of DCIM is to minimize future capital expenditures, so clients will be looking to Building Teams to create facilities that can be easily and inexpensively expanded or reconfigured to keep up with the fast pace of technology and demand for computing power.
Expect to lose business to DCIM solution providers. Some data center clients may choose to completely outsource the DCIM-related functions to a third-party provider, which would almost certainly impact billings on the project.
Related Stories
| Nov 16, 2010
Green building market grows 50% in two years; Green Outlook 2011 report
The U.S. green building market is up 50% from 2008 to 2010—from $42 billion to $55 billion-$71 billion, according to McGraw-Hill Construction's Green Outlook 2011: Green Trends Driving Growth report. Today, a third of all new nonresidential construction is green; in five years, nonresidential green building activity is expected to triple, representing $120 billion to $145 billion in new construction.
| Nov 16, 2010
Calculating office building performance? Yep, there’s an app for that
123 Zero build is a free tool for calculating the performance of a market-ready carbon-neutral office building design. The app estimates the discounted payback for constructing a zero emissions office building in any U.S. location, including the investment needed for photovoltaics to offset annual carbon emissions, payback calculations, estimated first costs for a highly energy efficient building, photovoltaic costs, discount rates, and user-specified fuel escalation rates.
| Nov 16, 2010
CityCenter’s new Harmon Hotel targeted for demolition
MGM Resorts officials want to demolish the unopened 27-story Harmon Hotel—one of the main components of its brand new $8.5 billion CityCenter development in Las Vegas. In 2008, inspectors found structural work on the Harmon didn’t match building plans submitted to the county, with construction issues focused on improperly placed steel reinforcing bar. In January 2009, MGM scrapped the building’s 200 condo units on the upper floors and stopped the tower at 27 stories, focusing on the Harmon having just 400 hotel rooms. With the Lord Norman Foster-designed building mired in litigation, construction has since been halted on the interior, and the blue-glass tower is essentially a 27-story empty shell.
| Nov 16, 2010
Where can your firm beat the recession? Try any of these 10 places
Wondering where condos and rental apartments will be needed? Where companies are looking to rent office space? Where people will need hotel rooms, retail stores, and restaurants? Newsweek compiled a list of the 10 American cities best situated for economic recovery. The cities fall into three basic groups: Texas, the New Silicon Valleys, and the Heartland Honeys. Welcome to the recovery.
| Nov 16, 2010
Landscape architecture challenges Andrés Duany’s Congress for New Urbanism
Andrés Duany, founder of the Congress for the New Urbanism, adopted the ideas, vision, and values of the early 20th Century landscape architects/planners John Nolen and Frederick Law Olmsted, Jr., to launch a movement that led to more than 300 new towns, regional plans, and community revitalization project commissions for his firm. However, now that there’s a societal buyer’s remorse about New Urbanism, Duany is coming up against a movement that sees landscape architecture—not architecture—as the design medium more capable of organizing the city and enhancing the urban experience.
| Nov 16, 2010
NFRC approves technical procedures for attachment product ratings
The NFRC Board of Directors has approved technical procedures for the development of U-factor, solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), and visible transmittance (VT) ratings for co-planar interior and exterior attachment products. The new procedures, approved by unanimous voice vote last week at NFRC’s Fall Membership Meeting in San Francisco, will add co-planar attachments such as blinds and shades to the group’s existing portfolio of windows, doors, skylights, curtain walls, and window film.
| Nov 15, 2010
Gilbane to acquire W.G. Mills, Inc.
Rhode Island-based Gilbane Building Company announced plans to acquire W.G. Mills, Inc., a construction management firm with operations based in Florida. The acquisition will dramatically strengthen Gilbane’s position in Florida’s growing market and complement its already established presence in the southeast.
| Nov 11, 2010
Saint-Gobain to make $80 million investment in SAGE Electrochromics
Saint-Gobain, one of the world’s largest glass and construction material manufacturers, is making a strategic equity investment in SAGE Electrochromics to make electronically tintable “dynamic glass” an affordable, mass-market product, ushering in a new era of energy-saving buildings.







