Boston will soon adopt a new stringent green state building code that aims to significantly reduce carbon emissions in new construction and major renovations.
Adoption of Massachusetts’s “stretch code” means that the city will not create an outright ban on fossil fuels for heating, cooling, and appliances. It will, though, drastically reduce fossil fuels in buildings by adding expensive, climate-friendly requirements for developers choosing to install fossil fuel connections. There will be varied energy efficiency requirements for different building types.
The legislation also requires developers building with gas or oil to pay for extra wiring so buildings can go all-electric in the future. Buildings in Boston account for close to three-quarters of the city’s carbon emissions, according to estimates.
At least two other Bay State communities have adopted the stretch code, but Boston is the largest and has a more diverse building stock including labs and life science buildings with highly specific electricity and infrastructure requirements.
In a related development, Mayor Michelle Wu recently pledged $10 million in city funds to help affordable multi-family buildings become more energy efficient.
Related Stories
Green | Apr 20, 2015
USGBC opens public comment period for LEED for existing multifamily buildings
The new LEED Operations and Maintenance: Multifamily program will offer solutions for existing multifamily projects with at least 20 units.
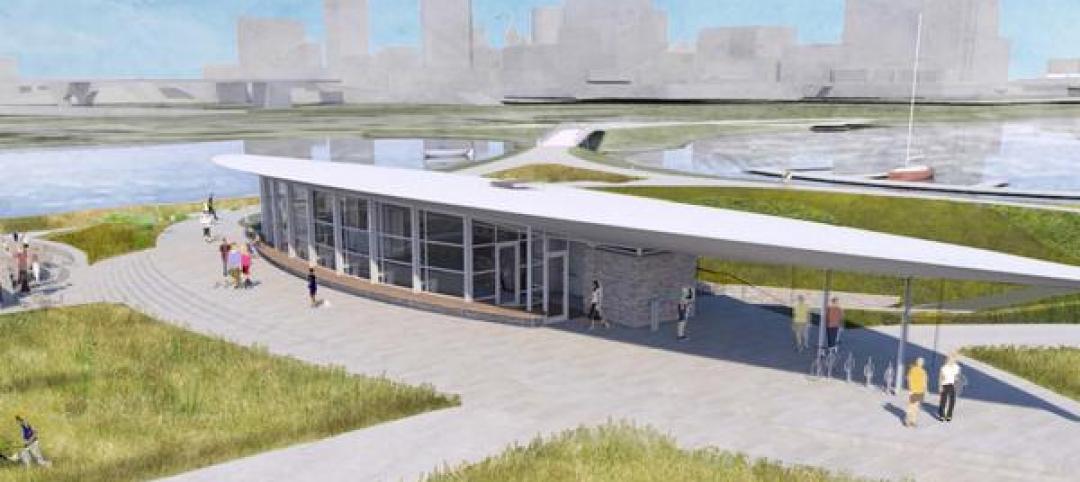
Cultural Facilities | Apr 16, 2015
Milwaukee’s Lakeshore State Park visitor center will be ‘off the grid’
The plans also include a built-in wastewater treatment system and rainwater collection.
Green | Apr 16, 2015
Passive House Institute introduces new categories for building certification
The new evaluation procedure considers the building in an environment where only renewable energy is used. Sun and wind provide the primary electricity.
Green | Apr 16, 2015
New version of Building Energy Data Exchange Specification launched
BEDES is a dictionary that facilitates consistent exchange of building characteristics and energy use data between tools and databases in the building energy efficiency sector.
Green | Apr 14, 2015
USGBC will recognize energy and water standards for the Living Building Challenge
This move means that projects achieving the energy and water requirements in Living Building Challenge will be considered as technically equivalent to LEED.
Green | Apr 7, 2015
USGBC survey shows Fortune 200 companies prioritize green building
The world’s top-performing companies are prioritizing sustainability as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts, and a majority of them are using LEED to achieve their goals, according to the new survey.
Codes and Standards | Apr 6, 2015
DOE releases Better Buildings Workforce Guidelines
The guidelines are aimed at strengthening and streamlining commercial building workforce training and certification programs for workers in energy auditing, building commissioning, building operations, and energy management.
Green | Apr 3, 2015
Georgia may ban use of LEED on state buildings
Georgia's state legislature is considering a measure to require all state buildings to only use green building standards that permit the use of Georgia's lumber.
Green | Apr 3, 2015
Energy benchmarking law helps make D.C. top ranked Energy Star city
First-in-the-nation law requires public reporting of annual energy performance
Green | Apr 1, 2015
Global wind power installations expected to slow through 2019
After a 20% falloff in 2013, the global wind power industry made a strong comeback in 2014, with a record 51.2 gigawatts installed. But a new report from Navigant Research forecasts a curtailment in growth.